Visible to Intel only — GUID: bgd1682556174052
Ixiasoft
1. About the External Memory Interfaces Agilex™ 5 FPGA IP
2. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP – Introduction
3. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP – Product Architecture
4. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP – End-User Signals
5. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP – Simulating Memory IP
6. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP - DDR4 Support
7. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP - DDR5 Support
8. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP - LPDDR4 Support
9. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP - LPDDR5 Support
10. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP – Timing Closure
11. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP – Controller Optimization
12. Agilex™ 5 FPGA EMIF IP – Debugging
13. Document Revision History for External Memory Interfaces (EMIF) IP User Guide
3.2.1. Agilex™ 5 EMIF Architecture: I/O Subsystem
3.2.2. Agilex™ 5 EMIF Architecture: I/O SSM
3.2.3. Agilex™ 5 EMIF Architecture: HSIO Bank
3.2.4. Agilex™ 5 EMIF Architecture: I/O Lane
3.2.5. Agilex™ 5 EMIF Architecture: Input DQS Clock Tree
3.2.6. Agilex™ 5 EMIF Architecture: PHY Clock Tree
3.2.7. Agilex™ 5 EMIF Architecture: PLL Reference Clock Networks
3.2.8. Agilex™ 5 EMIF Architecture: Clock Phase Alignment
3.2.9. User Clock in Different Core Access Modes
6.2.3.1. Address and Command Pin Placement for DDR4
6.2.3.2. DDR4 Data Width Mapping
6.2.3.3. General Guidelines
6.2.3.4. x4 DIMM Implementation
6.2.3.5. Specific Pin Connection Requirements
6.2.3.6. Command and Address Signals
6.2.3.7. Clock Signals
6.2.3.8. Data, Data Strobes, DM/DBI, and Optional ECC Signals
6.4.3.1. 1 Rank x 8 Discrete (Memory Down) Topology
6.4.3.2. 1 Rank x 16 Discrete (Memory Down) Topology
6.4.3.3. VREF_CA/RESET Signal Routing Guidelines for 1 Rank x 8 and 1 Rank x 16 Discrete (Memory Down) Topology
6.4.3.4. Skew Matching Guidelines for DDR4 (Memory Down) Discrete Configurations
6.4.3.5. Power Delivery Recommendation for DDR4 Discrete Configurations
6.4.3.6. DDR4 Simulation Strategy
12.1. Interface Configuration Performance Issues
12.2. Functional Issue Evaluation
12.3. Timing Issue Characteristics
12.4. Verifying Memory IP Using the Signal Tap Logic Analyzer
12.5. Debugging with the External Memory Interface Debug Toolkit
12.6. Generating Traffic with the Test Engine IP
12.7. Guidelines for Developing HDL for Traffic Generator
12.8. Guidelines for Traffic Generator Status Check
12.9. Hardware Debugging Guidelines
12.10. Create a Simplified Design that Demonstrates the Same Issue
12.11. Measure Power Distribution Network
12.12. Measure Signal Integrity and Setup and Hold Margin
12.13. Vary Voltage
12.14. Operate at a Lower Speed
12.15. Determine Whether the Issue Exists in Previous Versions of Software
12.16. Determine Whether the Issue Exists in the Current Version of Software
12.17. Try A Different PCB
12.18. Try Other Configurations
12.19. Debugging Checklist
12.20. Categorizing Hardware Issues
12.21. Signal Integrity Issues
12.22. Characteristics of Signal Integrity Issues
12.23. Evaluating Signal Integrity Issues
12.24. Skew
12.25. Crosstalk
12.26. Power System
12.27. Clock Signals
12.28. Address and Command Signals
12.29. Read Data Valid Window and Eye Diagram
12.30. Write Data Valid Window and Eye Diagram
12.31. Hardware and Calibration Issues
12.32. Memory Timing Parameter Evaluation
12.33. Verify that the Board Has the Correct Memory Component or DIMM Installed
Visible to Intel only — GUID: bgd1682556174052
Ixiasoft
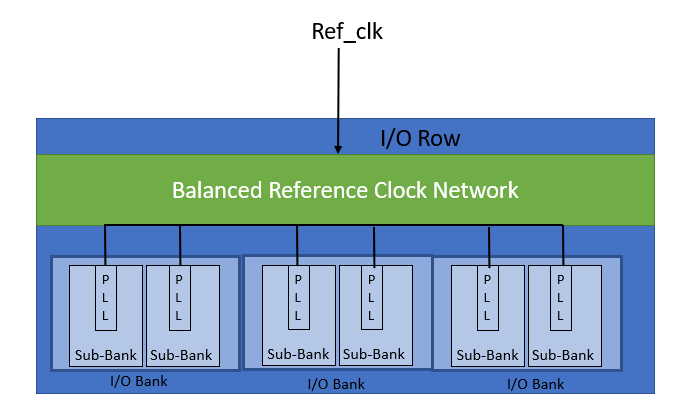
3.2.7. Agilex™ 5 EMIF Architecture: PLL Reference Clock Networks
Each HSIO sub-bank includes an I/O bank I/O PLL that can drive the PHY clock trees of that bank, through dedicated connections. In addition to supporting EMIF-specific functions, the I/O bank I/O PLLs can also serve as general-purpose PLLs for user logic.
The PLL reference clock must be constrained to the address and command sub-bank only.
Agilex™ 5 external memory interfaces that span multiple HSIO banks use the PLL in each bank. The Agilex™ 5 architecture allows for relatively short PHY clock networks, reducing jitter and duty-cycle distortion.
The following mechanisms ensure that the clock outputs of individual HSIO bank I/O PLLs in a multi-bank interface remain in phase:
- A single PLL reference clock source feeds all HSIO bank I/O PLLs. The reference clock signal reaches the PLLs by a balanced PLL reference clock tree. The Quartus® Prime software automatically configures the PLL reference clock tree so that it spans the correct number of banks. This clock must be free-running and stable prior to FPGA configuration.
- The EMIF IP sets the PLL configuration (counter settings, bandwidth settings, compensation and feedback mode setting) values appropriately to maintain synchronization among the clock dividers across the PLLs. This requirement restricts the legal PLL reference clock frequencies for a given memory interface frequency and clock rate. If you plan to use an on-board oscillator, you must ensure that its frequency matches the PLL reference clock frequency that you select from the displayed list.
Figure 8. PLL Balanced Reference Clock Tree