Developer Reference for Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library for C
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
v?Erf
Computes the error function value of vector elements.
Syntax
vsErf( n, a, y );
vsErfI(n, a, inca, y, incy);
vmsErf( n, a, y, mode );
vmsErfI(n, a, inca, y, incy, mode);
vdErf( n, a, y );
vdErfI(n, a, inca, y, incy);
vmdErf( n, a, y, mode );
vmdErfI(n, a, inca, y, incy, mode);
Include Files
- mkl.h
Input Parameters
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
n |
const MKL_INT |
Specifies the number of elements to be calculated. |
a |
const float* for vsErf, vmsErf const double* for vdErf, vmdErf |
Pointer to an array that contains the input vector a. |
inca, incy |
const MKL_INT |
Specifies increments for the elements of a and y. |
mode |
const MKL_INT64 |
Overrides global VM mode setting for this function call. See vmlSetMode for possible values and their description. |
Output Parameters
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
y |
float* for vsErf, vmsErf double* for vdErf, vmdErf |
Pointer to an array that contains the output vector y. |
Description
The Erf function computes the error function values for elements of the input vector a and writes them to the output vector y.
The error function is defined as given by:
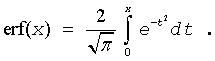
Useful relations:

where erfc is the complementary error function.

where
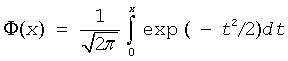
is the cumulative normal distribution function.

where Φ-1(x) and erf-1(x) are the inverses to Φ(x) and erf(x) respectively.
The following figure illustrates the relationships among Erf family functions (Erf, Erfc, CdfNorm).

Useful relations for these functions:
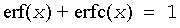
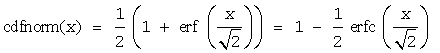
| Argument | Result | Exception |
|---|---|---|
| +∞ | +1 | |
| -∞ | -1 | |
| QNAN | QNAN | |
| SNAN | QNAN | INVALID |