Visible to Intel only — GUID: zba1711585811012
Ixiasoft
1. Introduction
2. Features
3. Getting Started with GTS AXI Streaming IP
4. IP Architecture and Functional Description
5. IP Parameters
6. Interfaces and Signals
7. Registers
8. Document Revision History for the GTS AXI Streaming Intel® FPGA IP for PCI Express* User Guide
A. Troubleshooting/Debugging
B. PIPE Mode Simulation
C. Implementation of Address Translation Services (ATS) in Endpoint Mode
3.1. Downloading and Installing Quartus® Prime Software
3.2. Configuring and Generating the GTS AXI Streaming IP
3.3. Configuring and Generating GTS System PLL Clocks Intel® FPGA IP
3.4. Configuring and Generating GTS Reset Sequencer Intel® FPGA IP
3.5. Instantiating and Connecting GTS AXI Streaming IP Interfaces (and Other IPs)
3.6. Simulating the GTS AXI Streaming IP Variant
3.7. Compiling the GTS AXI Streaming IP Variant
4.1. Clocking
4.2. Resets
4.3. PCIe* Hard IP
4.4. Hard IP Interface (IF) Adaptor
4.5. Interrupts
4.6. Transaction Ordering
4.7. TX Non-Posted Metering Requirement on Application
4.8. AXI4-Stream Interface
4.9. Tag Allocation
4.10. Power Management
4.11. Config Retry Status Enable
4.12. Hot-Plug
4.13. Configuration Space Extension
4.14. Page Request Service (EP only)
4.15. Precision Time Measurement (PTM)
4.16. Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV)
4.17. Transaction Layer Packet (TLP) Bypass Mode
4.18. Scalable IOV
5.2.2.3.1. PCIe0/PCIe1 Device
5.2.2.3.2. PCIe0/PCIe1 Link
5.2.2.3.3. PCIe0/PCIe1 Slot
5.2.2.3.4. PCIe0/PCIe1 Legacy Interrupt Pin Register
5.2.2.3.5. PCIe0/PCIe1 PTM
5.2.2.3.6. PCIe0/PCIe1 LTR
5.2.2.3.7. PCIe0/PCIe1 MSI
5.2.2.3.8. PCIe0/PCIe1 MSI-X
5.2.2.3.9. PCIe0/PCIe1 PASID
5.2.2.3.10. PCIe0/PCIe1 DEV SER
5.2.2.3.11. PCIe0/PCIe1 PRS
5.2.2.3.12. PCIe0/PCIe1 Power Management
5.2.2.3.13. PCIe0/PCIe1 VSEC
5.2.2.3.14. PCIe0/PCIe1 ATS
5.2.2.3.15. PCIe0/PCIe1 TPH
5.2.2.3.16. PCIe0/PCIe1 ACS
5.2.2.3.17. PCIe0/PCIe1 Hot-Plug
5.2.2.3.18. PCIe0/PCIe1 VIRTIO
6.1. Overview
6.2. Clocks and Resets
6.3. AXI4-Stream Interfaces
6.4. Configuration Intercept Interface
6.5. Configuration Extension Bus (CEB) Interface
6.6. Control Shadow Interface
6.7. Transmit Flow Control Credit Interface
6.8. Completion Timeout Interface
6.9. Control and Status Register Responder Interface
6.10. Function Level Reset Interface
6.11. TLP Bypass Error Reporting Interface
6.12. Error Interface
6.13. VF Error Flag Interface
6.14. VIRTIO PCI* Configuration Access Interface
6.15. Precision Time Measurement (PTM) Interface
6.16. Serial Data Signals
6.17. Miscellaneous Signals
7.6.1. VF PCI-Compatible Configuration Space Header Type0
7.6.2. VF PCI Express* Capability Structure
7.6.3. VF Message Signal Interrupt Extended (MSI-X) Capability Structure
7.6.4. VF Alternative Routing ID (ARI) Capability Structure
7.6.5. VF TLP Processing Hints (TPH) Capability Structure
7.6.6. VF Address Translation Services (ATS) Capability Structure
7.6.7. VF Access Control Services (ACS) Capability Structure
7.6.2.1. PCI Express* Capability List Register
7.6.2.2. PCI Express* Device Capabilities Register
7.6.2.3. PCI Express* Device Control and Status Register
7.6.2.4. Link Capabilities Register
7.6.2.5. Link Control and Status Register
7.6.2.6. PCI Express* Device Capabilities 2 Register
7.6.2.7. PCI Express* Device Control and Status 2 Register
7.6.2.8. Link Capabilities 2 Register
7.6.2.9. Link Control and Status 2 Register
Visible to Intel only — GUID: zba1711585811012
Ixiasoft
A.2.4.2.2. Event Counter
This tab allows you to read the error events like the number of receiver errors, framing errors, and others, for each port. You can use the Clear P0 counter to reset the error counter.
Figure 74. Example of Agilex™ 5 Event Counter Tab
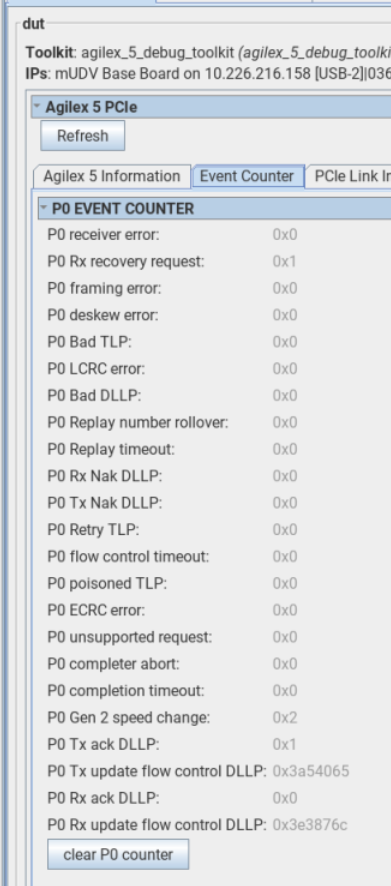

Note: P0 PCIe* 2.0 speed change, P0 TX ack DLLP, P0 RX ack DLLP, P0 TX update flow control DLLP, and P0 RX update flow control DLLP value would be corrupted when there is a reset such as SBR/Link Disable.