A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Window: Bottom-up
Use the Bottom-up window to analyze performance of each program from the bottom level when a child function is placed directly above its parent (bottom-up analysis).
To access this window: Click the Bottom-up tab. Depending on the analysis type, the Bottom-up window may include the following panes:
Bottom-up Pane
Data provided in the Bottom-up pane depends on the analysis, data collection type, and viewpoint you apply.
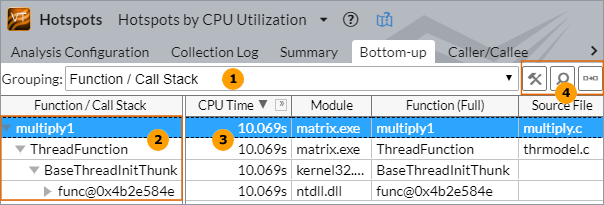
|
Grouping menu. Each row in the grid corresponds to a grouping level (granularity) of program units (module, function, synchronization object, and others). For example, the data in the Hotspots viewpoint is grouped by Function/Call Stack. |
|
Call stack. Analyze a tree hierarchy of the call stacks that lead to the selected program unit. Click the triangle sign to expand a row and view call trees for each program unit. Each tree is a call stack that called the selected unit. Each tree lists all the program units that had only one caller in the same row, with an arrow The time value for a row is equal to the sum of all the nested items from that row.
NOTE:
|
|
Performance metrics. Each data column in the grid corresponds to a performance metric. By default, all program units are sorted in the descending order by metric values in the fist column providing the most performance-critical program units first. You may click a column header to sort the table by the required metric. The list of performance metrics varies depending on the analysis type. Mouse over a column header (metric) to read the metric description, or right-click and select the What's This Column? option from the context menu. If a metric has a threshold value set up by the VTune Profiler architect and this value is exceeded, the VTune Profiler highlights such a value in pink. You may mouse over a pink cell to read the description of the detected issue and tuning advice for this issue. For some analysis types, you may see grayed out metric values in the grid, which indicates that the data collected for such a metric is unreliable. This may happen, for example, if the number of samples collected for PMU events is too low. In this case, when you hover over such an unreliable metric value, the VTune Profiler displays a message: The amount of collected PMU samples is too low to reliably calculate the metric. Depending on the analysis type and viewpoint, the Bottom-up view may represent the CPU Time by utilization levels. Focus your tuning efforts on the program units with the largest Poor value. This means that during the execution of these program units your application underutilized the CPU time. The overall goal of optimization is to achieve Ideal (green |
|
Toolbar. Select the following options to manage the Bottom-up view:
|





 Customize Grouping button to open the
Customize Grouping button to open the  Find button to open a search bar and search for a string in the grid.
Find button to open a search bar and search for a string in the grid.  Change Stack Layout button to switch between call stack layouts.
Change Stack Layout button to switch between call stack layouts. 
 are more natural for the top-down view:
are more natural for the top-down view: 