Visible to Intel only — GUID: gsg1693483304106
Ixiasoft
1. About the Intel Agilex® 7 F-Series and I-Series FPGA Memory Subsystem IP
2. Introduction to Memory Subsystem IP
3. Memory Subsystem IP Architecture and Feature Description
4. Memory Subsystem Features
5. Memory Subsystem Interfaces and Signals
6. Memory Subsystem User Operations
7. Memory Subsystem Register Descriptions
8. Parameterizing the Memory Subsystem IP
9. Simulating a Design Example
10. Document Revision History for Intel Agilex® 7 F-Series and I-Series FPGA Memory Subsystem IP User Guide
5.3.1. TCAM AXI-ST Request Interface
5.3.2. TCAM AXI-ST Response Interface
5.3.3. TCAM AXI-Lite Interface
5.3.4. BCAM AXI-ST Request Interface
5.3.5. BCAM AXI-ST Response Interface
5.3.6. BCAM AXI-Lite Interface
5.3.7. MBL AXI-ST Request Interface
5.3.8. MBL AXI-ST Response Interface
5.3.9. MBL AXI-Lite Interface
6.4.1. MBL Flush Operation
6.4.2. MBL Insert Key Operation
6.4.3. MBL Delete Key Operation
6.4.4. MBL Lookup Operation Using Key
6.4.5. MBL Modify Operation
6.4.6. MBL Modify Result Using Handle Operation
6.4.7. MBL Delete Key Using Handle Operation
6.4.8. MBL Lookup Using Handle Operation
6.4.9. MBL Insert Key if Not Present or Modify Result if Present Operation
6.4.10. MBL Get Handle Operation
7.2.1. Offset 0x0000 Version
7.2.2. Offset 0x0004 Feature List
7.2.3. Offset 0x0010 Memory Interfaces 0-7
7.2.4. Offset 0x0014 Memory Interfaces 8-15
7.2.5. Offset 0x0018 Memory Interfaces 16-23
7.2.6. Offset 0x001C Memory Interfaces 24-31
7.2.7. Offset 0x0020 Scratch Pad
7.2.8. Offset 0x0030 Control Policy (Lower DWORD)
7.2.9. Offset 0x0034 Control Policy (Upper DWORD)
7.2.10. Offset 0x0038 Read Access Control Policy (Lower DWORD)
7.2.11. Offset 0x003C Read Access Control Policy (Upper DWORD)
7.2.12. Offset 0x0040 Write Access Control Policy (Lower DWORD)
7.2.13. Offset 0x0044 Write Access Control Policy (Upper DWORD)
7.2.14. Offset 0x0050 Memory Status Bitmask 0
7.2.15. Offset 0x0054 Memory Status Bitmask 1
7.2.16. Offset 0x0058 Memory Ready Status 0
7.2.17. Offset 0x005C Memory Ready Status 1
7.2.18. Offset 0x0060 Memory Error Status 0
7.2.19. Offset 0x0064 Memory Error Status 1
7.3.2.1. Version
7.3.2.2. Feature List
7.3.2.3. Interface Attribute Parameters
7.3.2.4. Interface Attribute Parameters 1
7.3.2.5. Scratch Pad
7.3.2.6. General Control (GEN_CTRL)
7.3.2.7. Management Control (MGMT_CTRL)
7.3.2.8. Hash function_0 seed
7.3.2.9. Hash function_1 seed
7.3.2.10. Hash function_2 seed
7.3.2.11. Warning 0 (WARNING_0)
7.3.2.12. Fatal Error (FATAL_ERROR_0)
7.3.2.13. Monitor 0 (MON_)
7.3.2.14. Total Entries (TOTAL_ENTRIES)
7.3.2.15. Max. Rehouse Iterations (Max_Rehouse_Iterations)
7.3.2.16. Statistics Control (STATS_CTRL)
7.3.2.17. Active Table Entries (TABLE_ENTRIES)
7.3.2.18. Key_N
7.3.2.19. Result_N
7.5.1. General MBL Registers
7.5.2. Version
7.5.3. Mbl_scratch
7.5.4. Mbl_gen_ctrl
7.5.5. Mbl_mgmt_ctrl
7.5.6. Mbl_key_handle
7.5.7. Mbl_nxt_handle_req
7.5.8. Mbl_nxt_handle
7.5.9. Mbl_warning_0
7.5.10. Mbl_fatal_0
7.5.11. Mbl_mon_0
7.5.12. Mbl_total_entries
7.5.13. Mbl_total_rehashes
7.5.14. Mbl_max_used_bins
7.5.15. Mbl_stats_ctrl
7.5.16. Mbl_stats_result
7.5.17. Mbl_max_lkup_latency
7.5.18. Mbl_max_rehash_index
7.5.19. Mbl_key
7.5.20. Mbl_res
8.2.5.1. Parameterizing the External Memory Interface (EMIF) IP
8.2.5.2. Parameterizing the Memory-Specific Adapter
8.2.5.3. Parameterizing the Content-Addressable Memory (CAM) IP
8.2.5.4. Parameterizing the External Memory Interfaces Intel Calibration IP
8.2.5.5. Saving the IPs Within the Memory Subsystem
8.2.5.6. Propagation of Changes Across IPs within the Memory Subsystem IP
Visible to Intel only — GUID: gsg1693483304106
Ixiasoft
8.2.2. Selecting the Required Application Interfaces
The memory subsystem IP includes three different applications.
The three applications are:
- Storage – This is accessed by user logic and can only be mapped to EMIF IPs. The memory subsystem IP adds an MSA block that allows you to improve performance.
- Associative storage – This category includes all three types of content-addressable memory: BCAM, TCAM, and MBL. Because MBL relies on external memory, the memory subsystem IP adds an MSA block to the associated EMIF.
- Storage for HPS – Devices that have an HPS use a specific I/O bank to interface with External Memory. The Memory Subsystem IP creates an instance of the external memory interface for HPS and exports all the required ports to connect it with an HPS instance.
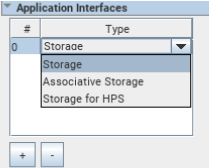
Continuing with the example shown in the Defining the Number of Memory Interfaces, Type, and Location topic, you select three applications: one storage and two associative storage. The following figure shows the Application Interfaces section of this example.
Figure 48. Selecting Application Interfaces

The process of defining the high-level connection between the application and a memory interface is discussed in the next topic.