Visible to Intel only — GUID: qhz1681753471837
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: qhz1681753471837
Ixiasoft
3.2.3.1. Memory Subsystem Multi-Bin Lookup (MBL) Functional Description
The following figure illustrates the functional blocks of the MBL.
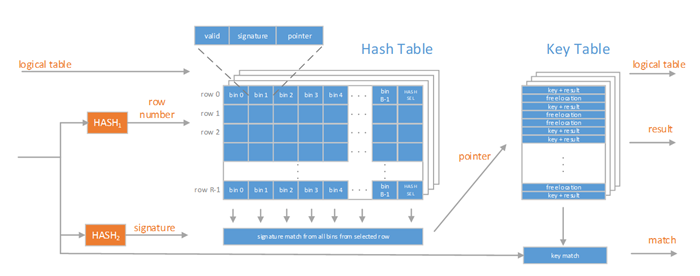
Key Table
The key table stores full keys and the associated results. It is also used in free pointers management, described later in this document.
Hash Table
The hash table is addressed by HASH1 and comprises R rows, each row containing B bins. Each bin stores a key signature, generated using HASH2 and a pointer to the key table.
HASH1
HASH1 is a hash generator that is used to address a row in the hash table. The width of the hash function equals log2(R), where R denotes the number of rows in the hash table.
HASH2
HASH2 is a hash generator that is used to generate a key signature – a compressed representation of a key. The key signature is stored in a bin belonging to a row selected by HASH1 and must be unique within the selected row.