Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-582557F0-6B08-4DC0-9026-C9010065E8CD
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-582557F0-6B08-4DC0-9026-C9010065E8CD
DFTI_FORWARD_DOMAIN
The general form of a discrete Fourier transform is
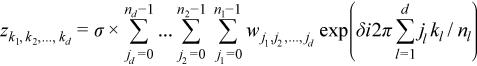
for kl = 0, ... nl-1 (l = 1, ..., d), where σ is a scale factor, δ = -1 for the forward transform, and δ = +1 for the backward transform.
The Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library (oneMKL) implementation of the FFT algorithm, used for fast computation of discrete Fourier transforms, supports forward transforms on input sequences of two domains, as specified by the DFTI_FORWARD_DOMAIN configuration parameter: general complex-valued sequences (DFTI_COMPLEX domain) and general real-valued sequences (DFTI_REAL domain). The forward transform maps the forward domain to the corresponding backward domain, as shown in Table "Correspondence of Forward and Backward Domain".
The conjugate-even domain covers complex-valued sequences with the symmetry property:
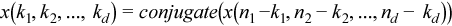
where the index arithmetic is performed modulo respective size, that is,
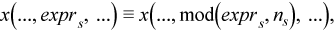
and therefore

Due to this property of conjugate-even sequences, only a part of such sequence is stored in the computer memory, as described in DFTI_CONJUGATE_EVEN_STORAGE.
Forward Domain |
Implied Backward Domain |
|---|---|
Complex (DFTI_COMPLEX) |
Complex (DFTI_COMPLEX) |
Real (DFTI_REAL) |
Conjugate-even |
DFTI_FORWARD_DOMAIN does not have a default value. Set it explicitly by calling the DftiCreateDescriptor function.
To better understand usage of the DFTI_FORWARD_DOMAIN configuration parameter, you can refer to these examples in your Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library (oneMKL) directory:
./examples/dftf/source/basic_sp_complex_dft_1d.f90
./examples/dftf/source/basic_sp_real_dft_1d.f90