PCB Design Guidelines (HSSI, EMIF, MIPI, True Differential, PDN) User Guide: Agilex™ 5 FPGAs and SoCs
Visible to Intel only — GUID: hqg1724037576927
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: hqg1724037576927
Ixiasoft
5.3. LPDDR4 Interface Design Guidelines
LPDDR4 Memory Down Topology (up to 32 bits interface)
LPDDR4 memory down supports single rank and dual-rank configurations up to 32 bits. There are four DRAM interface signal groupings, namely: data group, command-address group, control group, and clock group. The connection between the FPGA and DRAM device uses point-to-point topology as depicted in the following two figures.
The following figure illustrates the stripline routing for inner pins.
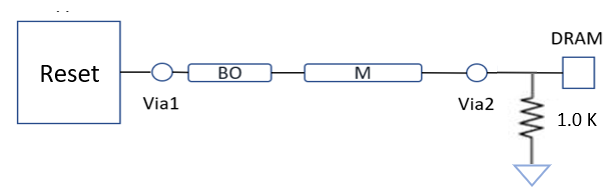
The following figure illustrates the Reset signal routing topology, recommend using 1.0K Ohm pull-down resistor for Reset signal termination.
The following figure illustrates the microstrip routing for the edge pins of BGA per byte.
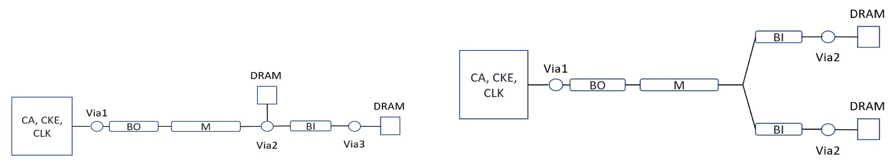
The following figure shows the daisy-chain and T-Line connections topology for CA, CLK, CTRL signals for LPDDR4.
The following tables provide comprehensive routing guidelines for each of the LPDDR4 signals based on memory down topology, such as the trace impedance, the total trace length, and the maximum main segment trace length that can be derived by subtracting the break-out segment and break-in segment trace length from the total trace length.
|
|
|
|
Reset signal routing design also follows the CMD/ADD/CTRL routing design. Keep the space at least 3xh between the Reset signal to other signals on the same layer (measured edge to edge).
Skew matching for LPDDR4 interfaces consists of both package routing skew and PCB physical routing skew. Use 3 time of dielectric height (h) for serpentine routing spacing. Skew matching of CA and CTRL with respect to the clock signals to ensure signals at the receiver are correctly sampled. In addition, there are skew matching requirement for DQ and DQS within a byte group, DQS and CLK. The following table provides a detailed skew matching guideline.
|
|
LPDDR4 eye margin is sensitive to crosstalk, especially when the signals are routed on deep layers. Note the deep-layer vertical transition induces more vertical coupling and crosstalk between signals. You can run simulation to determine the routing layer and whether to use backdrilling or not.