Visible to Intel only — GUID: xez1693102211275
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: xez1693102211275
Ixiasoft
7.6.1. PCB Stack-up and Design Considerations
You can implement DDR5 interfaces with Type-III or Type-IV PCB stack-ups. A Type-III PCB with zero-built up layers and PTH vias which is used to implement a DDR4 design can also be used for DDR5 designs. Backdrill can be considered to reach higher supported DDR5 data rate. You can run simulation to determine whether backdrill is necessary.
A high-quality type-IV PCB with higher cost, uses not only plated-through-hole (PTH) vias to connect from the top to bottom layer, but also stacked vias, micro vias, and buried vias to connect between layers. The following figure shows a cross-sectional comparison of a PTH and stacked via.
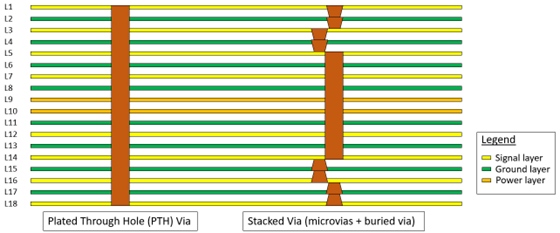
To support maximum data rate operation, DDR5 board design requires a high-quality PCB stackup using backdrill, micro vias, buried vias, or stacked vias to reduce crosstalk for high performance. Reducing the length of signal via is essential to minimizing the crosstalk between signals. You can perform simulation to determine whether to add backdrill or not based on your own stack-up.