Visible to Intel only — GUID: joc1463348716654
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: joc1463348716654
Ixiasoft
CFP4 Connector Routing Topologies Design Example
In the figure below, notice that the CFP4 connector has not been included in simulations. The standard 24-layer stack-up at 117 mil thickness is used for this design example. The stack-up material is Megron6 and has eight signal layers and four PDR layers.
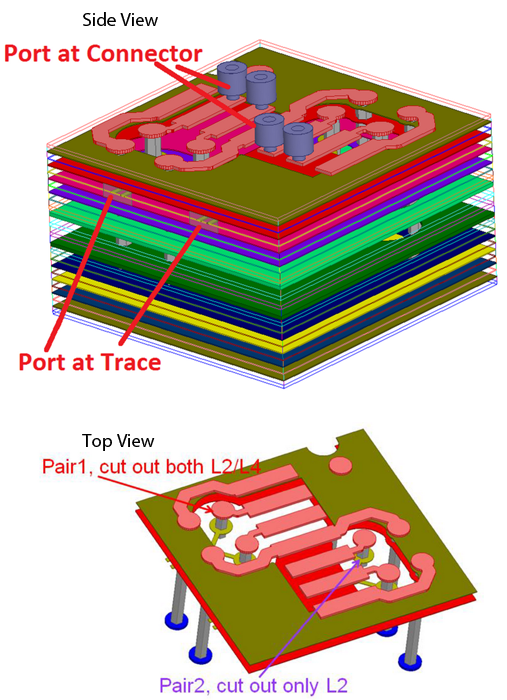
The channel trace routing is on layer 5 for both of the pairs above. Pair1 has two GND cutouts (on layers 2 and 4) under the connector pads, while pair1 has only one GND cutout on layer 2.
The reason for not having a GND cutout on layer 4 for pair 2 is because trace routing needs a reference GND plane while routed and passed under the connector pads. This aids in obtaining a minimum channel path as opposed to breaking out of the opposite direction and looping back, which creates a longer channel path.
The following figures compare the performances of pair 1 and pair 2.

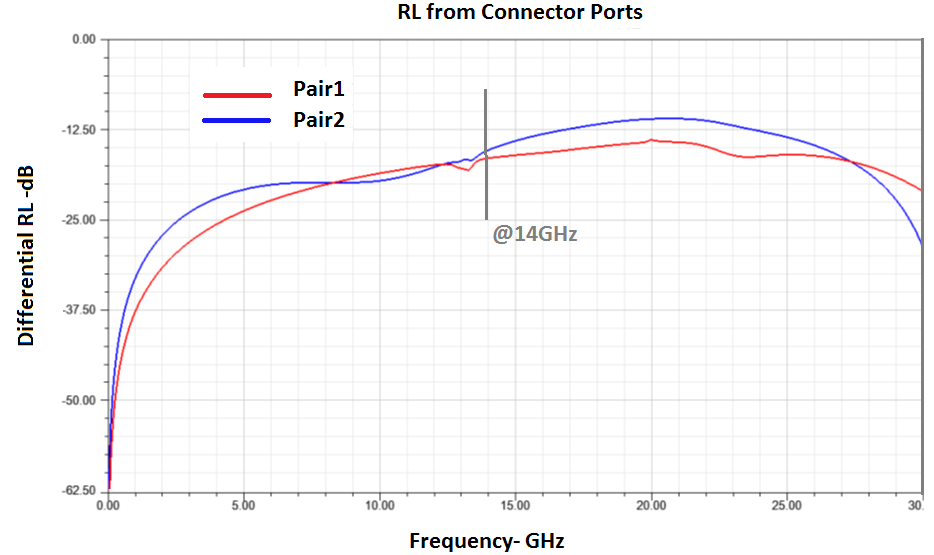

A quick comparison shows that pair 2 has up to 0.2 dB more insertion loss within a 15 GHz bandwidth. This is due to the lack of a GND cutout on layer 4 under the connector pads in addition to the extra routing length under the connector pads. Pair 2 also has up to 2.5 dB return loss with a 15 GHz bandwidth.
The TDR differential impedance also shows less impedance mismatch for pair 1.
In the following figure, the layout configuration has been changed from pair 2 (in the previous example) to pair 3.
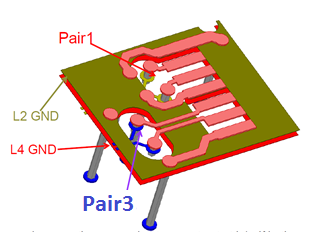
In the example above, pair 3 signal vias have been moved to the left side. This allows an additional GND cutout on layer 4 for pair 2 below the CFP4 connector pads. In this configuration, pair 3 can be routed on signal layer 3. The total routing length for both pair 1 and pair 3 are now equal.
The following figures compare the performances of pair 2 and pair 3.

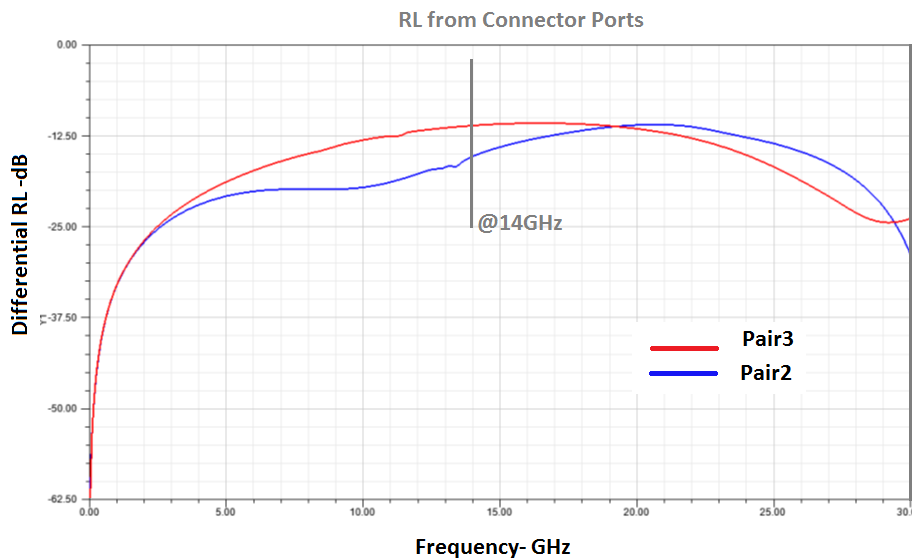
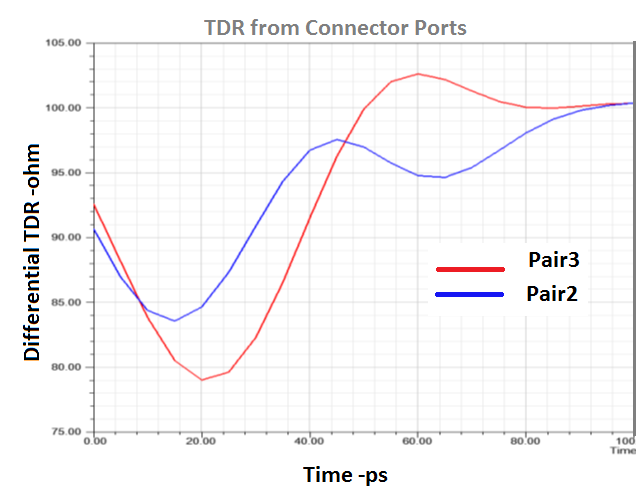
The insertion and return loss results above show better performance for pair 2 within a 15 GHz bandwidth. This is due to a larger GND cutout below the CFP4 connector pads (combined rectangular cut out and signal via anti-pads). This is also observed from TDR differential impedance results. However, above 15 GHz, pair 2 in Figure 60 exhibits greater performance degradation than pair3 in Figure 64.