Visible to Intel only — GUID: hvb1706644506339
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: hvb1706644506339
Ixiasoft
6.3. Example 3: Known Cooling Capacity
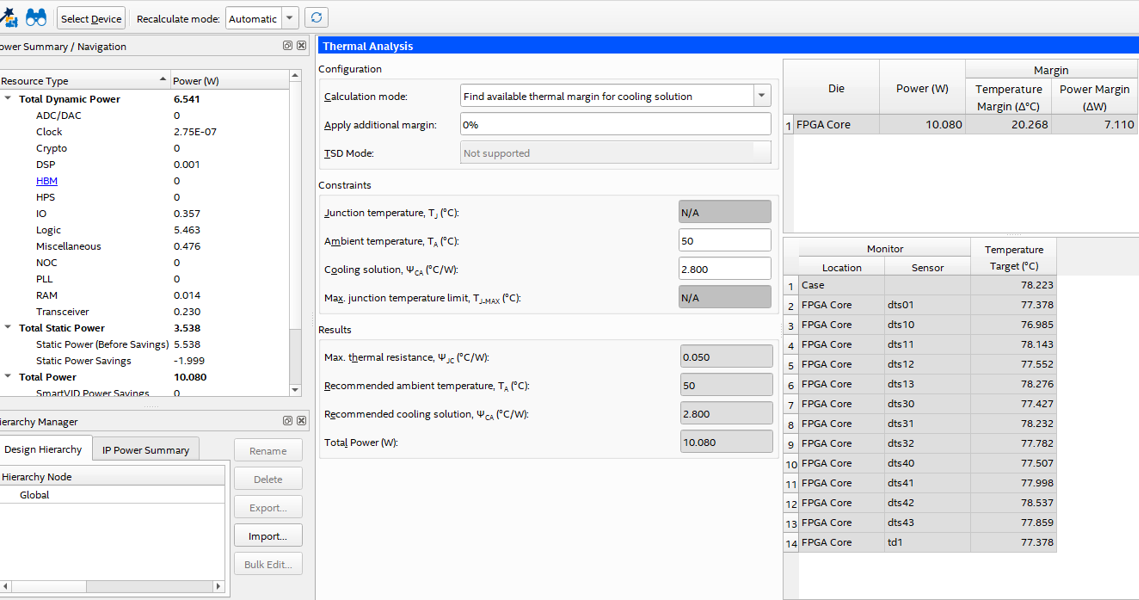
This example assumes the same FPGA as in the previous examples. It is to be used in a design where the ΨCA is 2.8⁰ C/W.
By entering the ambient temperature and the known ΨCA value into the PTC, we can calculate the die thermal and power margins relative to the TJ-MAX of 100⁰ C. The figure below shows the results on the PTC Thermal tab. We can conclude that the power consumption of this FPGA can be increased by an additional 7 watts, while remaining within the limits of this cooling solution.
You can also use the following equation to calculate TJ once the thermal parameters are known:
TJ = TA + TDP * (ѰJC + ѰCA)
TJ = 50 + 10 * (0.5 + 2.8) = 78.5