Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-DFA68E6B-2507-4AEA-A0E7-32972A8B6704
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-DFA68E6B-2507-4AEA-A0E7-32972A8B6704
DSS Distributed Symmetric Matrix Storage
The distributed assembled matrix input format can be used by the Parallel Direct Sparse Solver for Clusters Interface.
In this format, the symmetric input matrix A is divided into sequential row subsets, or domains. Each domain belongs to an MPI process. Neighboring domains can overlap. For such intersection between two domains, the element values of the full matrix can be obtained by summing the respective elements of both domains.
As in the centralized format, the distributed format uses three arrays to describe the input data, but the values, columns, and rowIndex arrays on each processor only describe the domain belonging to that particular processor and not the entire matrix.
For example, consider a symmetric matrix A:
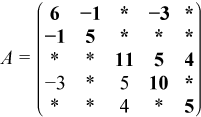
This array could be distributed between two domains corresponding to two MPI processes, with the first containing rows 1 through 3, and the second containing rows 3 through 5.
For the symmetric input matrix, it is not necessary to store the values from the lower triangle.

| one-based indexing | |||||||
| values | = | (6 | -1 | -3 | 5 | 3 | 2) |
| columns | = | (1 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 5) |
| rowIndex | = | (1 | 4 | 5 | 7) | ||
| zero-based indexing | |||||||
| values | = | (6 | -1 | -3 | 5 | 3 | 2) |
| columns | = | (0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4) |
| rowIndex | = | (0 | 3 | 4 | 6) |

| one-based indexing | ||||||
| values | = | (8 | 5 | 2 | 10 | 5) |
| columns | = | (3 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5) |
| rowIndex | = | (1 | 4 | 5 | 6) | |
| zero-based indexing | ||||||
| values | = | (8 | 5 | 2 | 10 | 5) |
| columns | = | (2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4) |
| rowIndex | = | (0 | 3 | 4 | 5) |
The third row of matrix A is common between domain 1 and domain 2. The values of row 3 of matrix A are the sums of the respective elements of row 3 of matrix ADomain1 and row 1 of matrix ADomain2.
Storage Format Restrictions
The storage format for the sparse solver must conform to two important restrictions:
the non-zero values in a given row must be placed into the values array in the order in which they occur in the row (from left to right);
no diagonal element can be omitted from the values array for any symmetric or structurally symmetric matrix.
The second restriction implies that if symmetric or structurally symmetric matrices have zero diagonal elements, then they must be explicitly represented in the values array.
Product and Performance Information |
|---|
Performance varies by use, configuration and other factors. Learn more at www.Intel.com/PerformanceIndex. Notice revision #20201201 |