Developer Reference for Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library for C
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
vslLeapfrogStream
Initializes a stream using the leapfrog method.
status = vslLeapfrogStream( stream, k, nstreams );
- mkl.h
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
stream |
VSLStreamStatePtr |
Pointer to the stream state structure to which leapfrog method is applied |
k |
const MKL_INT |
Index of the computational node, or stream number |
nstreams |
const MKL_INT |
Largest number of computational nodes, or stride |
The vslLeapfrogStream function generates random numbers in a random stream with non-unit stride. This feature is particularly useful in distributing random numbers from the original stream across the nstreams buffers without generating the original random sequence with subsequent manual distribution.
One of the important applications of the leapfrog method is splitting the original sequence into non-overlapping subsequences across nstreams computational nodes. The function initializes the original random stream (see Figure "Leapfrog Method") to generate random numbers for the computational node k, 0 ≤k < nstreams, where nstreams is the largest number of computational nodes used.
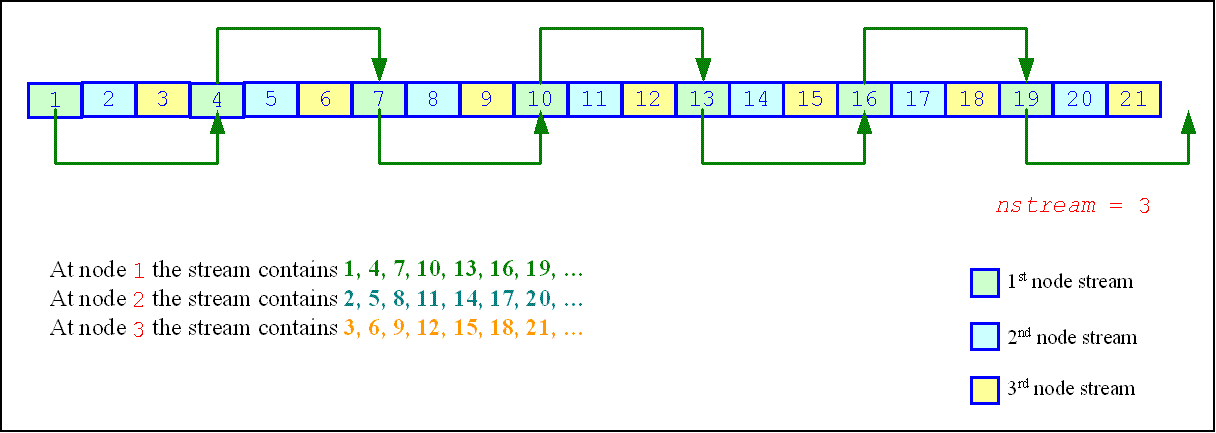

The leapfrog method is supported only for those basic generators that allow splitting elements by the leapfrog method, which is more efficient than simply generating them by a generator with subsequent manual distribution across computational nodes. See VS Notes for details.
For quasi-random basic generators, the leapfrog method allows generating individual components of quasi-random vectors instead of whole quasi-random vectors. In this case nstreams parameter should be equal to the dimension of the quasi-random vector while k parameter should be the index of a component to be generated (0 ≤k < nstreams). Other parameters values are not allowed.
The following code illustrates the initialization of three independent streams using the leapfrog method:
Code for Leapfrog Method
... VSLStreamStatePtr stream1; VSLStreamStatePtr stream2; VSLStreamStatePtr stream3; /* Creating 3 identical streams */ status = vslNewStream(&stream1, VSL_BRNG_MCG31, 174); status = vslCopyStream(&stream2, stream1); status = vslCopyStream(&stream3, stream1); /* Leapfrogging the streams */ status = vslLeapfrogStream(stream1, 0, 3); status = vslLeapfrogStream(stream2, 1, 3); status = vslLeapfrogStream(stream3, 2, 3); /* Generating random numbers */ ... /* Deleting the streams */ status = vslDeleteStream(&stream1); status = vslDeleteStream(&stream2); status = vslDeleteStream(&stream3); ...
- VSL_ERROR_OK, VSL_STATUS_OK
-
Indicates no error, execution is successful.
- VSL_ERROR_NULL_PTR
-
stream is a NULL pointer.
- VSL_RNG_ERROR_BAD_STREAM
-
stream is not a valid random stream.
- VSL_RNG_ERROR_LEAPFROG_UNSUPPORTED
-
BRNG does not support Leapfrog method.