Developer Reference for Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library for C
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
?gglse
Solves the linear equality-constrained least squares problem using a generalized RQ factorization.
lapack_int LAPACKE_sgglse (int matrix_layout, lapack_int m, lapack_int n, lapack_int p, float* a, lapack_int lda, float* b, lapack_int ldb, float* c, float* d, float* x);
lapack_int LAPACKE_dgglse (int matrix_layout, lapack_int m, lapack_int n, lapack_int p, double* a, lapack_int lda, double* b, lapack_int ldb, double* c, double* d, double* x);
lapack_int LAPACKE_cgglse (int matrix_layout, lapack_int m, lapack_int n, lapack_int p, lapack_complex_float* a, lapack_int lda, lapack_complex_float* b, lapack_int ldb, lapack_complex_float* c, lapack_complex_float* d, lapack_complex_float* x);
lapack_int LAPACKE_zgglse (int matrix_layout, lapack_int m, lapack_int n, lapack_int p, lapack_complex_double* a, lapack_int lda, lapack_complex_double* b, lapack_int ldb, lapack_complex_double* c, lapack_complex_double* d, lapack_complex_double* x);
- mkl.h
The routine solves the linear equality-constrained least squares (LSE) problem:
minimize ||c - A*x||2 subject to B*x = d
where A is an m-by-n matrix, B is a p-by-n matrix, c is a given m-vector, andd is a given p-vector. It is assumed that p≤n≤m+p, and
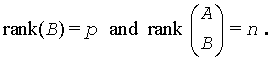
These conditions ensure that the LSE problem has a unique solution, which is obtained using a generalized RQ factorization of the matrices (B, A) given by
B=(0 R)*Q, A=Z*T*Q
- matrix_layout
-
Specifies whether matrix storage layout is row major (LAPACK_ROW_MAJOR) or column major (LAPACK_COL_MAJOR).
- m
-
The number of rows of the matrix A (m≥ 0).
- n
-
The number of columns of the matrices A and B (n≥ 0).
- p
-
The number of rows of the matrix B
(0 ≤p≤n≤m+p).
- a, b, c, d
-
Arrays:
a(size max(1, lda*n) for column major layout and max(1, lda*m) for row major layout) contains the m-by-n matrix A.
b(size max(1, ldb*n) for column major layout and max(1, ldb*p) for row major layout) contains the p-by-nmatrix B.
c size at least max(1, m), contains the right hand side vector for the least squares part of the LSE problem.
d, size at least max(1, p), contains the right hand side vector for the constrained equation.
- lda
-
The leading dimension of a; at least max(1, m)for column major layout and max(1, n) for row major layout.
- ldb
-
The leading dimension of b; at least max(1, p)for column major layout and max(1, n) for row major layout.
- a
-
The elements on and above the diagonal contain the min(m, n)-by-n upper trapezoidal matrix T as returned by ?ggrqf.
- x
-
The solution of the LSE problem.
- b
-
On exit, the upper right triangle contains the p-by-p upper triangular matrix R as returned by ?ggrqf.
- d
-
On exit, d is destroyed.
- c
-
On exit, the residual sum-of-squares for the solution is given by the sum of squares of elements n-p+1 to m of vector c.
This function returns a value info.
If info=0, the execution is successful.
If info = -i, the i-th parameter had an illegal value.
If info = 1, the upper triangular factor R associated with B in the generalized RQ factorization of the pair (B, A) is singular, so that rank(B) < p; the least squares solution could not be computed.
If info = 2, the (n-p)-by-(n-p) part of the upper trapezoidal factor T associated with A in the generalized RQ factorization of the pair (B, A) is singular, so that

; the least squares solution could not be computed.