Intel® Integrated Performance Primitives (Intel® IPP) Developer Guide and Reference
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
IIRIIR Filter Functions
The functions described in this section initialize an infinite impulse response (IIR) filter and perform a zero-phase digital filtering of input data in both forward and backward directions. The formulas below explain why the filtered signal has zero-phase distortion. Consider the following case in the frequency domain: if x(n) is the input sequence and h(n) is the IIR filter's impulse response, then the result of the forward filter pass is:

where
- X(eiφ) is the Fourier transform of x(n)
- H(eiφ) is the Fourier transform of h(n)
- Y1(eiφ) is the Fourier transform of the forward filter pass
Backward filtering corresponds to filtering of time-reversed signal. Time reversal corresponds to replacing φ with -φ in the frequency domain, so the result of time reversal is:

When the filter is applied for the second time, the above formula is multiplied by the Fourier transform of the filter's impulse response function H(eiφ):

The final time reversal in the frequency domain results in:
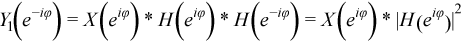
You can see from the resulting equation that:
- The filtered signal has zero-phase distortion (as the filtering was done with |H(eiφ)|2, which is purely real-valued)
- The filter transfer function has the squared magnitude of the original filter transfer function
- The filter order is double the order of the initialized IIR filter
To initialize and use an IIRIIR filter, follow this general scheme:
- Call ippsIIRIIRInit to initialize the IIRIIR filter in the external buffer. To compute the size of the buffer, use the ippsIIRIIRGetStateSize function.
- Call ippsIIRIIR to filter a vector.
- Call ippsIIRIIRGetDlyLine and ippsIIRIIRSetDlyLine to get and set the delay line values in the IIRIIR state structure.
- IIRIIRGetStateSize
Computes the length of the external buffer for the IIRIIR filter state structure. - IIRIIRInit
Initializes the IIRIIR filter state structure. - IIRIIRGetDlyLine
Retrieves the delay line contents from the IIIRIR filter state structure. - IIRIIRSetDlyLine
Sets the delay line contents in the IIRIIR filter state structure. - IIRIIR
Filters a source vector through an IIRIIR filter.