Intel® Integrated Performance Primitives (Intel® IPP) Developer Guide and Reference
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
CrossCorrNorm
Calculates the cross-correlation of two vectors.
Syntax
IppStatus ippsCrossCorrNorm_32f (const Ipp32f* pSrc1, int src1Len, const Ipp32f* pSrc2, int src2Len, Ipp32f* pDst, int dstLen, int lowLag, IppEnum algType, Ipp8u* pBuffer);
IppStatus ippsCrossCorrNorm_64f (const Ipp64f* pSrc1, int src1Len, const Ipp64f* pSrc2, int src2Len, Ipp64f* pDst, int dstLen, int lowLag, IppEnum algType, Ipp8u* pBuffer);
IppStatus ippsCrossCorrNorm_32fc (const Ipp32fc* pSrc1, int src1Len, const Ipp32fc* pSrc2, int src2Len, Ipp32fc* pDst, int dstLen, int lowLag, IppEnum algType, Ipp8u* pBuffer);
IppStatus ippsCrossCorrNorm_64fc (const Ipp64fc* pSrc1, int src1Len, const Ipp64fc* pSrc2, int src2Len, Ipp64fc* pDst, int dstLen, int lowLag, IppEnum algType, Ipp8u* pBuffer);
Include Files
ipps.h
Parameters
pSrc1 |
Pointer to the first source vector. |
src1Len |
Number of elements in the first source vector. |
pSrc2 |
Pointer to the second source vector. |
src2Len |
Number of elements in the second source vector. |
pDst |
Pointer to the destination vector. This vector stores the calculated cross-correlation of the pSrc1 and pSrc2 vectors. |
dstLen |
Number of elements in the destination vector. This value determines the range of lags at which the cross-correlation is calculated. |
lowLag |
Cross-correlation lowest lag. |
algType |
Bit-field mask for the algorithm type definition. Possible values are the results of composition of the IppAlgType and IppsNormOp values. |
pBuffer |
Pointer to the buffer for internal calculations. |
Description
These functions calculate the cross-correlation of the pSrc1 vector and the pSrc2 vector, and store the results in the pDst vector. The result vector pDst is calculated by the following equations:
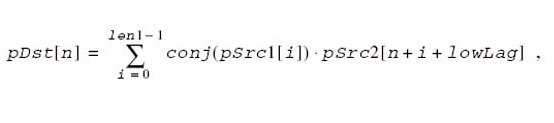
where


Before using this function, you need to compute the size of the work buffer using the ippsCrossCorrNormGetBufferSize function.
Return Values
ippStsNoErr |
Indicates no error. |
ippStsNullPtrErr |
Indicates an error when any of the specified pointers is NULL. |
ippStsSizeErr |
Indicates an error when the length of a vector is less than, or equal to zero. |
ippStsAlgTypeErr |
Indicates an error when:
|
Example
The code example below demonstrates how to use the ippsCrossCorrNormGetBufferSize and ippsCrossCorrNorm functions.
IppStatus CrossCorrNormExample (void) {
IppStatus status;
const int src1Len=5, src2Len=7, dstLen=16;
int lowLag = -5;
Ipp32f pSrc1[src1Len] = {1.f,1.f,1.f,1.f,1.f}, pSrc2[src2Len] = {1.f,1.f,1.f,1.f,1.f,1.f,1.f}, pDst[dstLen];
IppEnum funCfgNormNo = (IppEnum)(ippAlgAuto|ippsNormNone);
IppEnum funCfgNormA = (IppEnum)(ippAlgAuto|ippsNormA);
IppEnum funCfgNormB = (IppEnum)(ippAlgAuto|ippsNormB);
int bufSizeNo=0, bufSizeA=0, bufSizeB=0, bufSizeMax=0;
Ipp8u *pBuffer;
status = ippsCrossCorrNormGetBufferSize(src1Len, src2Len, dstLen, -5, ipp32f, funCfgNormNo, &bufSizeNo);
if ( status != ippStsNoErr ) return status;
status = ippsCrossCorrNormGetBufferSize(src1Len, src2Len, dstLen, -5, ipp32f, funCfgNormA, &bufSizeA);
if ( status != ippStsNoErr ) return status;
status = ippsCrossCorrNormGetBufferSize(src1Len, src2Len, dstLen, -5, ipp32f, funCfgNormB, &bufSizeB);
if ( status != ippStsNoErr ) return status;
bufSizeMax = IPP_MAX(bufSizeNo, IPP_MAX(bufSizeA, bufSizeB));// get max buffer size
pBuffer = ippsMalloc_8u( bufSizeMax );
status = ippsCrossCorrNorm_32f(pSrc1, src1Len, pSrc2, src2Len, pDst, dstLen, lowLag, funCfgNormNo, pBuffer);
printf_32f("pDst_NormNone", pDst, dstLen);
status = ippsCrossCorrNorm_32f(pSrc1, src1Len, pSrc2, src2Len, pDst, dstLen, lowLag, funCfgNormA, pBuffer);
printf_32f("pDst_NormA", pDst, dstLen);
status = ippsCrossCorrNorm_32f(pSrc1, src1Len, pSrc2, src2Len, pDst, dstLen, lowLag, funCfgNormB, pBuffer);
printf_32f("pDst_NormB", pDst, dstLen);
ippsFree( pBuffer );
return status;
}
The result is as follows:
pDst_NormNone -> 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 pDst_NormA -> 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 pDst_NormB -> 0.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0