Developer Guide
FPGA Optimization Guide for Intel® oneAPI Toolkits
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-CA023031-4C80-400E-8EA4-299430732C75
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-CA023031-4C80-400E-8EA4-299430732C75
Task Parallelism
While the compiler achieves concurrency by scheduling independent individual operations to execute simultaneously, it does not achieve concurrency at coarser granularities (for example, across loops).
For larger code structures to execute in parallel, you must write them as separate kernels that launch simultaneously. These kernels then run asynchronously with each other, and you can achieve synchronization and communication using pipes, as illustrated in the following figure:
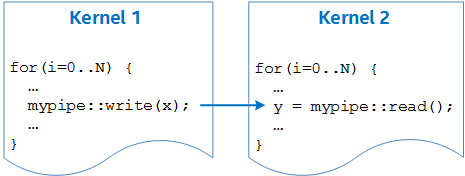
This is similar to how a CPU program can leverage threads running on separate cores to achieve simultaneous asynchronous behavior.