Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-A9773676-7D2D-40AE-9B57-E6F6DF980A50
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-A9773676-7D2D-40AE-9B57-E6F6DF980A50
?lartgs
Generates a plane rotation designed to introduce a bulge in implicit QR iteration for the bidiagonal SVD problem.
Syntax
call slartgs( x, y, sigma, cs, sn )
call dlartgs( x, y, sigma, cs, sn )
call lartgs( x,y,sigma,cs,sn )
Include Files
- mkl.fi
Description
The routine generates a plane rotation designed to introduce a bulge in Golub-Reinsch-style implicit QR iteration for the bidiagonal SVD problem. x and y are the top-row entries, and sigma is the shift. The computed cs and sn define a plane rotation that satisfies the following:
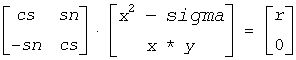
with r nonnegative.
If x2 - sigma and x * y are 0, the rotation is by π/2
Input Parameters
The data types are given for the Fortran interface.
- x, y
-
REAL for slartgs
DOUBLE PRECISION for dlartgs
The (1,1) and (1,2) entries of an upper bidiagonal matrix, respectively.
- sigma
-
REAL for slartgs
DOUBLE PRECISION for dlartgs
Shift
Output Parameters
- cs
-
REAL for slartgs
DOUBLE PRECISION for dlartgs
The cosine of the rotation.
- sn
-
REAL for slartgs
DOUBLE PRECISION for dlartgs
The sine of the rotation.
LAPACK 95 Interface Notes
Routines in Fortran 95 interface have fewer arguments in the calling sequence than their FORTRAN 77 counterparts. For general conventions applied to skip redundant or reconstructible arguments, see LAPACK 95 Interface Conventions.
Specific details for the routine ?lartgs interface are as follows:
- x
-
Holds the (1,1) entry of an upper diagonal matrix.
- y
-
Holds the (1,2) entry of an upper diagonal matrix.
- sigma
-
Holds the shift.
- cs
-
Holds the cosine of the rotation.
- sn
-
Holds the sine of the rotation.