Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-42986DEF-8710-453A-9DAC-2086EE55F1F5
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-42986DEF-8710-453A-9DAC-2086EE55F1F5
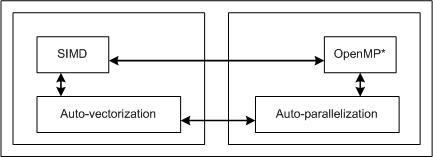
User-Mandated or SIMD Vectorization
User-mandated or SIMD vectorization supplements automatic vectorization just like OpenMP parallelization supplements automatic parallelization. The following figure illustrates this relationship. User-mandated vectorization is implemented as a single-instruction-multiple-data (SIMD) feature and is referred to as SIMD vectorization.
The SIMD vectorization feature is available for both Intel® microprocessors and non-Intel microprocessors. Vectorization may call library routines that can result in additional performance gain on Intel® microprocessors than on non-Intel microprocessors. The vectorization can also be affected by certain options, such as /arch (Windows), -m (Linux), or [Q]x.
SIMD vectorization uses the !$OMP SIMD directive to effect loop vectorization. You must add this directive to a loop and recompile to vectorize the loop using the option -qopenmp-simd (Linux) or Qopenmp-simd (Windows).
For example, if the following code appears in example1.f90, the compiler does not automatically vectorize the loop because of the unknown data dependence distance between I and 2*I .
subroutine add(A, N, X) integer N, X real A(N) DO I=X, N A(I) = A(I) + A(2*I) END DO End
The example is compiled with the following command:
ifx example1.f90 -c -nologo -qopt-report -qopt-report-file=stderr
The example gives output like the following, reporting that vectorization did not occur:
Global optimization report for: add_
LOOP BEGIN at exmaple1.f90 (4, 1)
remark #15344: Loop was not vectorized: vector dependence prevents vectorization
remark #15346: vector dependence: assumed FLOW dependence between a (5:3) and a (5:3)
remark #25439: Loop unrolled with remainder by 4
LOOP END
LOOP BEGIN at example1.f90 (4, 1)
<Remainder loop>
LOOP END
=================================================================
Using the previous example, if you know that X is large enough that data A(I) and A(2*I) do not overlap within a reasonable number of iterations you can enforce vectorization of the loop using !$OMP SIMD. If you know that they do not overlap in at least 8 iterations you may additionally specify !$OMP SIMD SIMDLEN(8) to avoid vectorization that is too wide, which might lead to overlap.
You can update your code from the previous example to use !$OMP SIMD:
subroutine add(A, N, X) integer N, X real A(N) ! X may be 8 or more, so on overlap with 8 iterations at least !$OMP SIMD SIMDLEN(8) DO I=X, N A(I) = A(I) + A(2*I) END DO End
The example is compiled with the following command:
ifx example1.f90 -c -nologo -qopt-report -qopt-report-file=stderr –qopenp-simd
The example gives output like the following, reporting that vectorization did occur:
Global optimization report for: add_
LOOP BEGIN at example1.f90 (5, 1)
remark #15301: SIMD LOOP WAS VECTORIZED
remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 8
LOOP END
LOOP BEGIN at example1.f90 (5, 1)
<Remainder loop for vectorization>
LOOP END
=================================================================
The difference between using !$OMP SIMD and auto-vectorization hints is that with !$OMP SIMD, the compiler generates a warning when it is unable to vectorize the loop. With auto-vectorization hints, actual vectorization is still under the discretion of the compiler, even when you use the hint !DIR$ VECTOR ALWAYS.
!$OMP SIMD has optional clauses to guide the compiler on how vectorization must proceed. Use these clauses appropriately so that the compiler obtains enough information to generate correct vector code. For more information on the clauses, see the !$OMP SIMD description.
Additional Semantics
Note the following points when using the !$OMP SIMD directive.
A variable may belong to zero or one of the following clauses: private, linear, or reduction.
Within the vector loop, an expression is evaluated as a vector value if it is private, linear, reduction, or it has a sub-expression that is evaluated to a vector value. Otherwise, it is evaluated as a scalar value (that is, broadcast the same value to all iterations). Scalar value does not necessarily mean loop invariant, although that is the most frequently seen usage pattern of scalar value.
A vector value may not be assigned to a scalar L-value. It is an error.
A scalar L-value may not be assigned under a vector condition. It is an error.
Using a vector Declaration
The following Intel® Fortran example code shows how a program can compare serial and vector computations using a user-defined function, foo().
This example shows you code where the user-defined function is not vectorized:
!! file simdmain.f90 program simdtest use IFPORT ! Test vector function in external file. implicit none interface integer function foo(a, b) integer a, b end function foo end interface integer, parameter :: M = 48, N = 64 integer i, j integer, dimension(M,N) :: a1 integer, dimension(M,N) :: a2 integer, dimension(M,N) :: s_a3 integer, dimension(M,N) :: v_a3 logical :: err_flag = .false. ! compute random numbers for arrays do j = 1, N do i = 1, M a1(i,j) = rand() * M a2(i,j) = rand() * M end do end do ! compute serial results do j = 1, N !dir$ novector do i = 1, M s_a3(i,j) = foo(a1(i,j), a2(i,j)) end do end do ! compute vector results do j = 1, N do i = 1, M v_a3(i,j) = foo(a1(i,j), a2(i,j)) end do end do ! compare serial and vector results do j = 1, N do i = 1, M if (s_a3(i,j) .ne. v_a3(i,j)) then err_flag = .true. print *, s_a3(i, j), v_a3(i,j) end if end do end do if (err_flag .eq. .true.) then write(*,*) "FAILED" else write(*,*) "PASSED" end if end program !! file: vecfoo.f90 integer function foo(a, b) implicit none integer, intent(in) :: a, b foo = a - b end function
This example gives output like the following, reporting that vectorization did not occur:
[49 C:/temp] ifx -nologo -qopt-report -qopt-report-file=stderr simdmain.f90 vecfoo.f90
Global optimization report for : MAIN__
LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (22, 1)
LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (23, 3)
LOOP END
LOOP END
LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (30, 1)
LOOP BEGIN at foo.f90 (32, 3)
LOOP END
LOOP END
LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (38, 3)
LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (39, 4)
LOOP END
LOOP END
LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (46, 3)
remark #25567: 2 loops have been collapsed
remark #15527: Loop was not vectorized: function call to foo cannot be vectorized
LOOP END
=================================================================
When you compile the above code, the loop containing the foo() function is not auto-vectorized because the auto-vectorizer does not know what foo() does unless it is inlined to this call site.
In such cases where the function call is not inlined, you can use the !DIR$ ATTRIBUTES VECTOR::function-name-list declaration to vectorize the loop and the function foo(). All you need to do is add the vector declaration to the function declaration and recompile the code. The loop and function are vectorized.
For example, a loop with a user-defined function where the vector declaration is auto-vectorized:
!! file simdmain.f90 program simdtest ! Test vector function in external file. use IFPORT implicit none interface integer function foo(a, b) !$omp declare simd integer a, b end function foo end interface integer, parameter :: M = 48, N = 64 integer i, j integer, dimension(M,N) :: a1 integer, dimension(M,N) :: a2 integer, dimension(M,N) :: s_a3 integer, dimension(M,N) :: v_a3 logical :: err_flag = .false. ! compute random numbers for arrays do j = 1, N do i = 1, M a1(i,j) = rand() * M a2(i,j) = rand() * M end do end do ! compute serial results do j = 1, N !dir$ novector do i = 1, M s_a3(i,j) = foo(a1(i,j), a2(i,j)) end do end do ! compute vector results do j = 1, N do i = 1, M v_a3(i,j) = foo(a1(i,j), a2(i,j)) end do end do ! compare serial and vector results do j = 1, N do i = 1, M if (s_a3(i,j) .ne. v_a3(i,j)) then err_flag = .true. print *, s_a3(i, j), v_a3(i,j) end if end do end do if (err_flag .eq. .true.) then write(*,*) "FAILED" else write(*,*) "PASSED" end if end program !! file: vecfoo.f90 integer function foo(a, b) !$omp declare simd implicit none integer, intent(in) :: a, b foo = a - b end function
This example gives output like the following, reporting that vectorization did occur:
[49 C:/temp] ifx -nologo -qopt-report -qopt-report-file=stderr simdmain.f90 vecfoo.f90 –qopenmp Global optimization report for: MAIN__ LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (23, 1) LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (24, 3) LOOP END LOOP END LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (31, 1) remark #15553: loop was not vectorized: outer loop is not an auto-vectorization candidate. LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (33, 3) remark #15319: Loop was not vectorized: novector directive used remark #25436: Loop completely unrolled by 48 LOOP END LOOP END LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (39, 3) remark #15553: loop was not vectorized: outer loop is not an auto-vectorization candidate. LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (40, 4) remark #15300: LOOP WAS VECTORIZED remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 4 LOOP END LOOP END LOOP BEGIN at simdmain.f90 (47, 3) remark #25567: 2 loops have been collapsed remark #15527: Loop was not vectorized: function call to cannot be vectorized LOOP END ================================================================= Global optimization report for: foo_ ================================================================= Global optimization report for: _ZGVeN16vv_foo_ LOOP BEGIN at foo.f90 (6, 3) remark #15301: SIMD LOOP WAS VECTORIZED remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 16 remark #25436: Loop completely unrolled by 1 LOOP END ================================================================= Global optimization report for: _ZGVcM4vv_foo_ LOOP BEGIN at foo.f90 (6, 3) remark #15301: SIMD LOOP WAS VECTORIZED remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 4 remark #25436: Loop completely unrolled by 1 LOOP END ================================================================= Global optimization report for: _ZGVdN8vv_foo_ LOOP BEGIN at foo.f90 (6, 3) remark #15301: SIMD LOOP WAS VECTORIZED remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 8 remark #25436: Loop completely unrolled by 1 LOOP END ================================================================= Global optimization report for: _ZGVdM8vv_foo_ LOOP BEGIN at foo.f90 (6, 3) remark #15301: SIMD LOOP WAS VECTORIZED remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 8 remark #25436: Loop completely unrolled by 1 LOOP END ================================================================= Global optimization report for: _ZGVcN4vv_foo_ LOOP BEGIN at foo.f90 (6, 3) remark #15301: SIMD LOOP WAS VECTORIZED remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 4 remark #25436: Loop completely unrolled by 1 LOOP END ================================================================= Global optimization report for: _ZGVeM16vv_foo_ LOOP BEGIN at foo.f90 (6, 3) remark #15301: SIMD LOOP WAS VECTORIZED remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 16 remark #25436: Loop completely unrolled by 1 LOOP END ================================================================= Global optimization report for: _ZGVbM4vv_foo_ LOOP BEGIN at foo.f90 (6, 3) remark #15301: SIMD LOOP WAS VECTORIZED remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 4 remark #25436: Loop completely unrolled by 1 LOOP END ================================================================= Global optimization report for: _ZGVbN4vv_foo_ LOOP BEGIN at foo.f90 (6, 3) remark #15301: SIMD LOOP WAS VECTORIZED remark #15305: vectorization support: vector length 4 remark #25436: Loop completely unrolled by 1 LOOP END =================================================================
Restrictions on Using an !$OMP DECLARE SIMD Declaration
Vectorization depends on two major factors: hardware and the style of source code. When using the vector declaration, the following features are not allowed:
Locks, barriers, atomic construct, critical sections
Computed and assigned GOTO and SELECT CASE, SELECT TYPE, and SELECT RANK constructs (in some cases these may be supported and converted to IF statements)
The GOTO statement, into or out of a function
An ENTRY statement
Non-vector function calls are generally allowed within vector functions but calls to such functions are serialized lane-by-lane and so might perform poorly. Also, for SIMD-enabled functions it is not allowed to have side effects except writes by their arguments. This rule can be violated by non-vector function calls, so be careful executing such calls in SIMD-enabled functions and subroutines.
Formal parameters must be of the following data types:
- (un)signed 8, 16, 32, or 64-bit integer
- 32- or 64-bit floating point
- 64- or 128-bit complex