Developer Reference for Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library for C
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
vslSkipAheadStream
Initializes a stream using the block-splitting method.
Syntax
status = vslSkipAheadStream( stream, nskip);
Include Files
- mkl.h
Input Parameters
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|
stream |
VSLStreamStatePtr |
Pointer to the stream state structure to which block-splitting method is applied |
nskip |
const long long int |
Number of skipped elements |
Description
The vslSkipAheadStream function skips a given number of elements in a random stream. This feature is particularly useful in distributing random numbers from original random stream across different computational nodes. If the largest number of random numbers used by a computational node is nskip, then the original random sequence may be split by vslSkipAheadStream into non-overlapping blocks of nskip size so that each block corresponds to the respective computational node. The number of computational nodes is unlimited. This method is known as the block-splitting method or as the skip-ahead method. (see Figure "Block-Splitting Method").
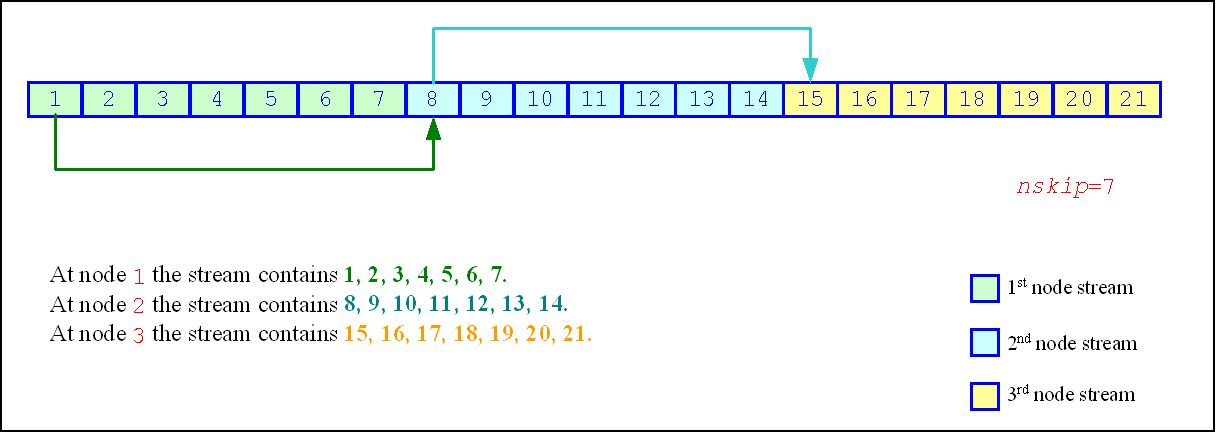

The skip-ahead method is supported only for those basic generators that allow skipping elements by the skip-ahead method, which is more efficient than simply generating them by generator with subsequent manual skipping. See VS Notes for details.
Please note that for quasi-random basic generators the skip-ahead method works with components of quasi-random vectors rather than with whole quasi-random vectors. Therefore, to skip NS quasi-random vectors, set the nskip parameter equal to the NS*DIMEN, where DIMEN is the dimension of the quasi-random vector. If this operation results in exceeding the period of the quasi-random number generator, which is 232-1, the library returns the VSL_RNG_ERROR_QRNG_PERIOD_ELAPSED error code.
The following code illustrates how to initialize three independent streams using the vslSkipAheadStream function:
Code for Block-Splitting Method
VSLStreamStatePtr stream1; VSLStreamStatePtr stream2; VSLStreamStatePtr stream3; /* Creating the 1st stream */ status = vslNewStream(&stream1, VSL_BRNG_MCG31, 174); /* Skipping ahead by 7 elements the 2nd stream */ status = vslCopyStream(&stream2, stream1); status = vslSkipAheadStream(stream2, 7); /* Skipping ahead by 7 elements the 3rd stream */ status = vslCopyStream(&stream3, stream2); status = vslSkipAheadStream(stream3, 7); /* Generating random numbers */ ... /* Deleting the streams */ status = vslDeleteStream(&stream1); status = vslDeleteStream(&stream2); status = vslDeleteStream(&stream3); ...
Return Values
- VSL_ERROR_OK, VSL_STATUS_OK
-
Indicates no error, execution is successful.
- VSL_ERROR_NULL_PTR
-
stream is a NULL pointer.
- VSL_RNG_ERROR_BAD_STREAM
-
stream is not a valid random stream.
- VSL_RNG_ERROR_SKIPAHEAD_UNSUPPORTED
-
BRNG does not support the Skip-Ahead method.
- VSL_RNG_ERROR_QRNG_PERIOD_ELAPSED
-
Period of the quasi-random number generator is exceeded.