AN 669: Drive-On-Chip Design Example for Cyclone V Devices
ID
683466
Date
5/15/2022
Public
1. About the Drive-On-Chip Design Example for Cyclone V Devices
2. Motor Control Boards
3. Drive-On-Chip Design Example for Cyclone V Devices Features
4. Getting Started
5. Building the Design
6. Debugging and Monitoring the Drive-On-Chip Design Example with System Console
7. About the Scaling of Feedback Signals
8. Motor Control Software
9. Functional Description of the Drive-On-Chip Design Example
10. Achieving Timing Closure on a Motor Control Design
11. Design Security Recommendations
12. Reference Documents for the Drive-on-Chip Design Example
13. Document Revision History for AN 669: Drive-on-Chip Reference Design
4.1. Software Requirements for the Drive-On-Chip Design Example for Cyclone V Devices
4.2. Downloading and Installing the Drive-On-Chip Design Example for Cyclone V Devices
4.3. Setting Up the Motor Control Board with your Development Board
4.4. Programming the Hardware onto the Device
4.5. Setting Up Terminal Emulator
4.6. Downloading the HPS Software to the Device
6.1. System Console GUI Upper Pane for the Drive-On-Chip Design Example
6.2. System Console GUI Lower Pane for the Drive-On-Chip Design Example
6.3. Vibration Suppression Tab
6.4. Controlling the DC-DC Converter
6.5. Tuning the PI Controller Gains
6.6. Controlling the Speed and Position Demonstrations
6.7. Monitoring Performance
9.1. Processor Subsystem
9.2. Six-channel PWM Interface
9.3. DC Link Monitor
9.4. Drive System Monitor
9.5. Quadrature Encoder Interface
9.6. Sigma-Delta ADC Interface for Drive Axes
9.7. DC-DC Converter
9.8. Motor Control Modes
9.9. FOC Subsystem
9.10. FFTs
9.11. DEKF Technique for Battery Management
9.12. Signals
9.13. Registers
9.9.1. DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs Model for the Drive-On-Chip Designs
9.9.2. Avalon Memory-Mapped Interface
9.9.3. About DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs
9.9.4. DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs Folding
9.9.5. DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs Model Resource Usage
9.9.6. DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs Design Guidelines
9.9.7. Generating VHDL for the DSP Builder Models for the Drive-On-Chip Reference Designs
9.7.1. DC-DC Control Simulink Models
The Drive-On-Chip Design Example includes three MATLAB Simulink models, which lead step by step from offline simulation to HDL code generation while maintaining the numerical simulation results.
The models are:
- lvdcdc_simpower.slx where the power electronics simulate in SimScape and the PI control loops in Simulink standard blocks
- lvdcdc_2phase_hwsim.slx is similar to lvdcdc_simpower.slx but the power electronics simulate in standard Simulink blocks, not SimScape
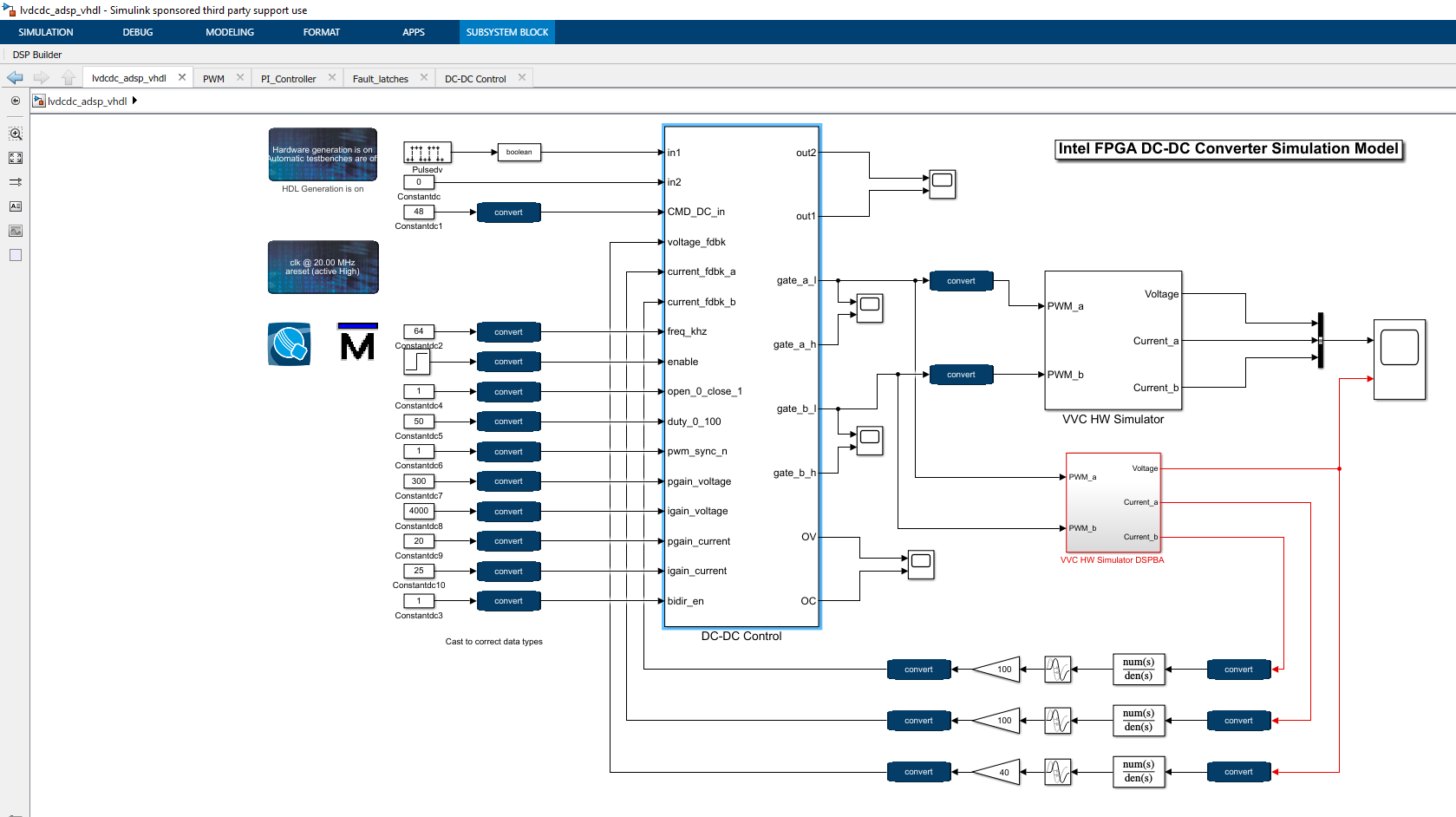
- lvdcdc_adsp_vhdl.slx is like lvdcdc_2phase_hwsim.slx but the algorithm is implemented using DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs so that you can generate HDL code.
Figure 35. DC-DC Converter Linear MATLAB ModelThe figure shows the linear MATLAB model (lvdcdc_simpower.slx). The linear model cannot generate VHDL, but you create it to provide a rapid simulation to develop control dynamics and determine controller gains.
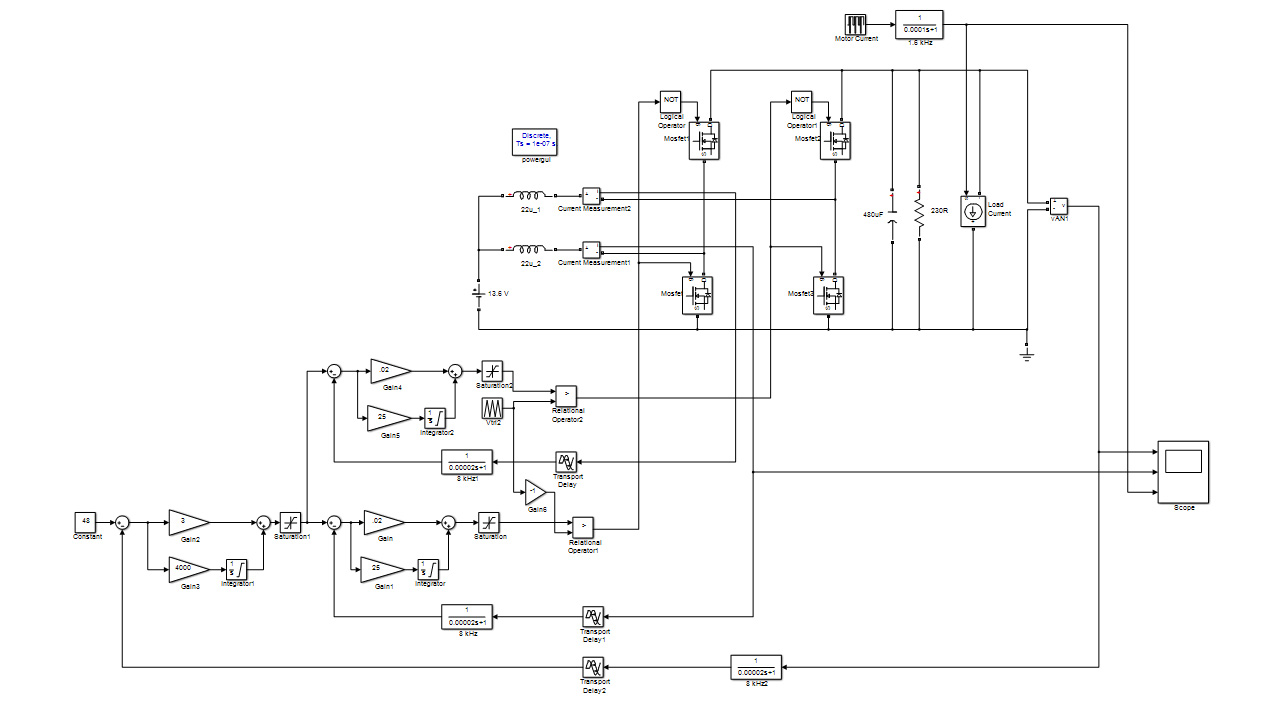

Figure 36. DC-DC Converter: DC bus Voltage, Inductor Currents, Motor Load Current (stimulus)The figure shows the linear MATLAB model (lvdcdc_simpower.slx) and simulation.
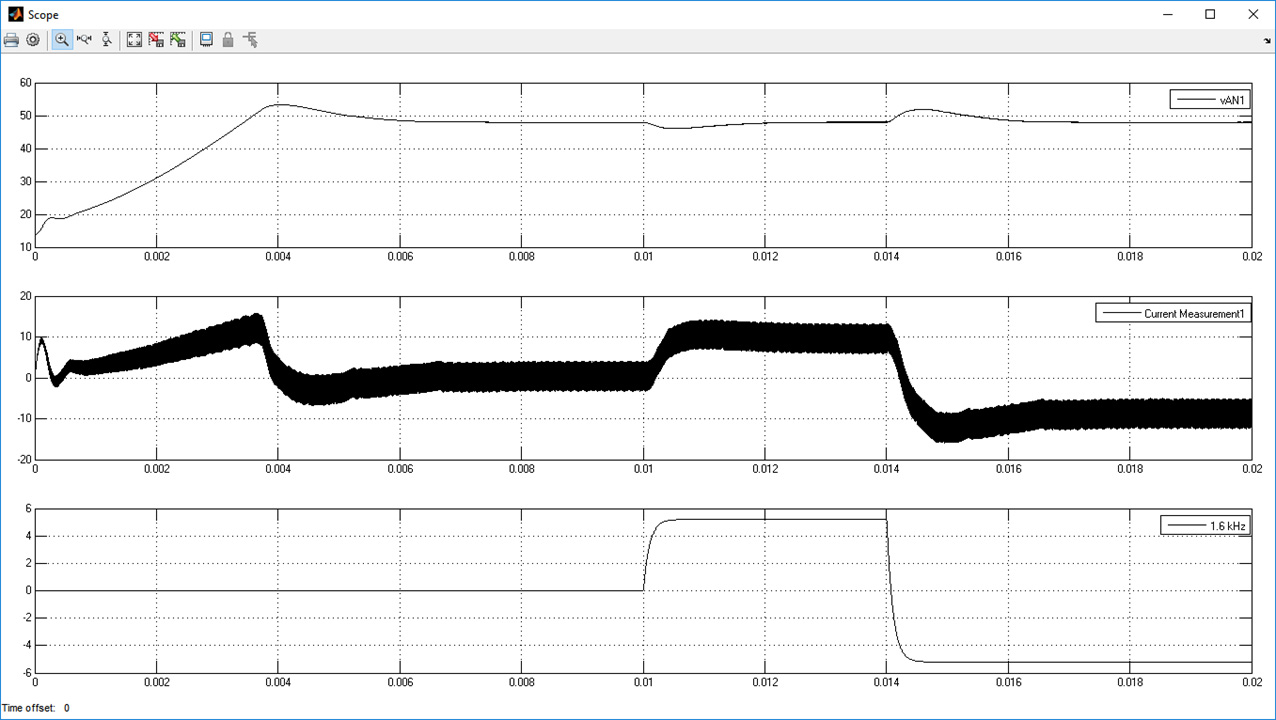

Figure 37. DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs Top-level ModelThe DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs model (lvdcdc_adsp_vhdl.slx) performs the same simulation as above, but includes DSP Builder for Intel FPGAs blocks that allow simulation of VHDL and auto-generation of VHDL code.