Intel® FPGA SDK for OpenCL™ Pro Edition: Best Practices Guide
ID
683521
Date
3/28/2022
Public
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
1. Introduction to Intel® FPGA SDK for OpenCL™ Pro Edition Best Practices Guide
2. Reviewing Your Kernel's report.html File
3. OpenCL Kernel Design Concepts
4. OpenCL Kernel Design Best Practices
5. Profiling Your Kernel to Identify Performance Bottlenecks
6. Strategies for Improving Single Work-Item Kernel Performance
7. Strategies for Improving NDRange Kernel Data Processing Efficiency
8. Strategies for Improving Memory Access Efficiency
9. Strategies for Optimizing FPGA Area Usage
10. Strategies for Optimizing Intel® Stratix® 10 OpenCL Designs
11. Strategies for Improving Performance in Your Host Application
12. Intel® FPGA SDK for OpenCL™ Pro Edition Best Practices Guide Archives
A. Document Revision History for the Intel® FPGA SDK for OpenCL™ Pro Edition Best Practices Guide
2.1. High-Level Design Report Layout
2.2. Reviewing the Summary Report
2.3. Viewing Throughput Bottlenecks in the Design
2.4. Using Views
2.5. Analyzing Throughput
2.6. Reviewing Area Information
2.7. Optimizing an OpenCL Design Example Based on Information in the HTML Report
2.8. Accessing HLD FPGA Reports in JSON Format
4.1. Transferring Data Via Intel® FPGA SDK for OpenCL™ Channels or OpenCL Pipes
4.2. Unrolling Loops
4.3. Optimizing Floating-Point Operations
4.4. Allocating Aligned Memory
4.5. Aligning a Struct with or without Padding
4.6. Maintaining Similar Structures for Vector Type Elements
4.7. Avoiding Pointer Aliasing
4.8. Avoid Expensive Functions
4.9. Avoiding Work-Item ID-Dependent Backward Branching
5.1. Best Practices for Profiling Your Kernel
5.2. Instrumenting the Kernel Pipeline with Performance Counters (-profile)
5.3. Obtaining Profiling Data During Runtime
5.4. Reducing Area Resource Use While Profiling
5.5. Temporal Performance Collection
5.6. Performance Data Types
5.7. Interpreting the Profiling Information
5.8. Profiler Analyses of Example OpenCL Design Scenarios
5.9. Intel® FPGA Dynamic Profiler for OpenCL™ Limitations
8.1. General Guidelines on Optimizing Memory Accesses
8.2. Optimize Global Memory Accesses
8.3. Performing Kernel Computations Using Constant, Local or Private Memory
8.4. Improving Kernel Performance by Banking the Local Memory
8.5. Optimizing Accesses to Local Memory by Controlling the Memory Replication Factor
8.6. Minimizing the Memory Dependencies for Loop Pipelining
8.7. Static Memory Coalescing
2.6. Reviewing Area Information
The <your_kernel_filename>/reports/report.html file contains information about area usage of your OpenCL system. You can view the area usage information of the system.
The area report serves the following purposes:
- Provides detailed area breakdown of the whole OpenCL system. The breakdown is related to the source code.
- Provides architectural details to give insight into the generated hardware and offers actionable suggestions to resolve potential inefficiencies.
As observed in the following figure, the area report is divided into three levels of hierarchy:
- System area: It is used by all kernels, channels, interconnects, and board logic.
- Kernel area: It is used by a specific kernel, including overheads, for example, dispatch logic.
- Block area: It is used by a specific basic block within a kernel. A basic block area represents a branch-free section of your source code, for example, a loop body.
Figure 24. Area Report Hierarchy
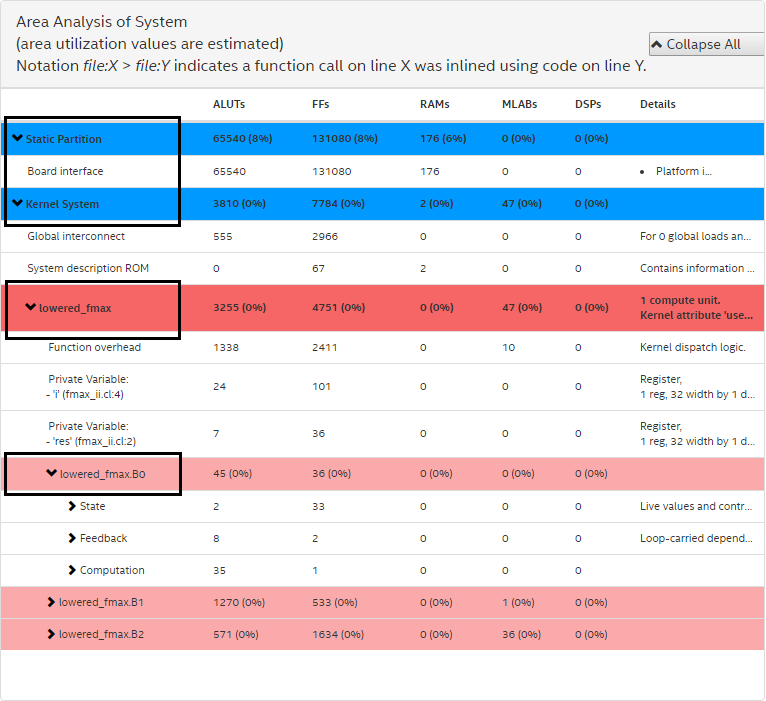

Note: The area usage data are estimates that the Intel® FPGA SDK for OpenCL™ Offline Compiler generates. These estimates might differ from the final area utilization results.
In the Reports pane's Area Analysis drop-down menu, select Area Analysis of System.
In the system view, the kernel is divided into logic blocks. To view the area usage information for the code lines associated with a block, simply expand the report entry for that block.
Note: The analyze-area Intel® FPGA SDK for OpenCL™ utility option has been deprecated. For reference information on the deprecated area report, refer to the Review Your Kernel's Area Report to Identify Inefficiencies in Resource Usage section in version 16.0 of the Altera SDK for OpenCL Best Practices Guide.