Visible to Intel only — GUID: ife1517938316340
Ixiasoft
1. Introduction to Standard Edition Best Practices Guide
2. Reviewing Your Kernel's report.html File
3. OpenCL Kernel Design Best Practices
4. Profiling Your Kernel to Identify Performance Bottlenecks
5. Strategies for Improving Single Work-Item Kernel Performance
6. Strategies for Improving NDRange Kernel Data Processing Efficiency
7. Strategies for Improving Memory Access Efficiency
8. Strategies for Optimizing FPGA Area Usage
A. Additional Information
2.1. High Level Design Report Layout
2.2. Reviewing the Report Summary
2.3. Reviewing Loop Information
2.4. Reviewing Area Information
2.5. Verifying Information on Memory Replication and Stalls
2.6. Optimizing an OpenCL Design Example Based on Information in the HTML Report
2.7. HTML Report: Area Report Messages
2.8. HTML Report: Kernel Design Concepts
3.1. Transferring Data Via Channels or OpenCL Pipes
3.2. Unrolling Loops
3.3. Optimizing Floating-Point Operations
3.4. Allocating Aligned Memory
3.5. Aligning a Struct with or without Padding
3.6. Maintaining Similar Structures for Vector Type Elements
3.7. Avoiding Pointer Aliasing
3.8. Avoid Expensive Functions
3.9. Avoiding Work-Item ID-Dependent Backward Branching
4.3.4.1. High Stall Percentage
4.3.4.2. Low Occupancy Percentage
4.3.4.3. Low Bandwidth Efficiency
4.3.4.4. High Stall and High Occupancy Percentages
4.3.4.5. No Stalls, Low Occupancy Percentage, and Low Bandwidth Efficiency
4.3.4.6. No Stalls, High Occupancy Percentage, and Low Bandwidth Efficiency
4.3.4.7. Stalling Channels
4.3.4.8. High Stall and Low Occupancy Percentages
7.1. General Guidelines on Optimizing Memory Accesses
7.2. Optimize Global Memory Accesses
7.3. Performing Kernel Computations Using Constant, Local or Private Memory
7.4. Improving Kernel Performance by Banking the Local Memory
7.5. Optimizing Accesses to Local Memory by Controlling the Memory Replication Factor
7.6. Minimizing the Memory Dependencies for Loop Pipelining
Visible to Intel only — GUID: ife1517938316340
Ixiasoft
2.4. Reviewing Area Information
The <your_kernel_filename>/reports/report.html file contains information about area usage of your OpenCL system. You may view the area usage information either by source (that is, code line) or by system.
The area report serves the following purposes:
- Provides detailed area breakdown of the whole OpenCL system. The breakdown is related to the source code.
- Provides architectural details to give insight into the generated hardware and offers actionable suggestions to resolve potential inefficiencies.
As observed in the following figure, the area report is divided into three levels of hierarchy:
- System area: It is used by all kernels, channels, interconnects, and board logic.
- Kernel area: It is used by a specific kernel, including overheads, for example, dispatch logic.
- Basic block area: It is used by a specific basic block within a kernel. A basic block area represents a branch-free section of your source code, for example, a loop body.
Figure 23. Area Report Hierarchy
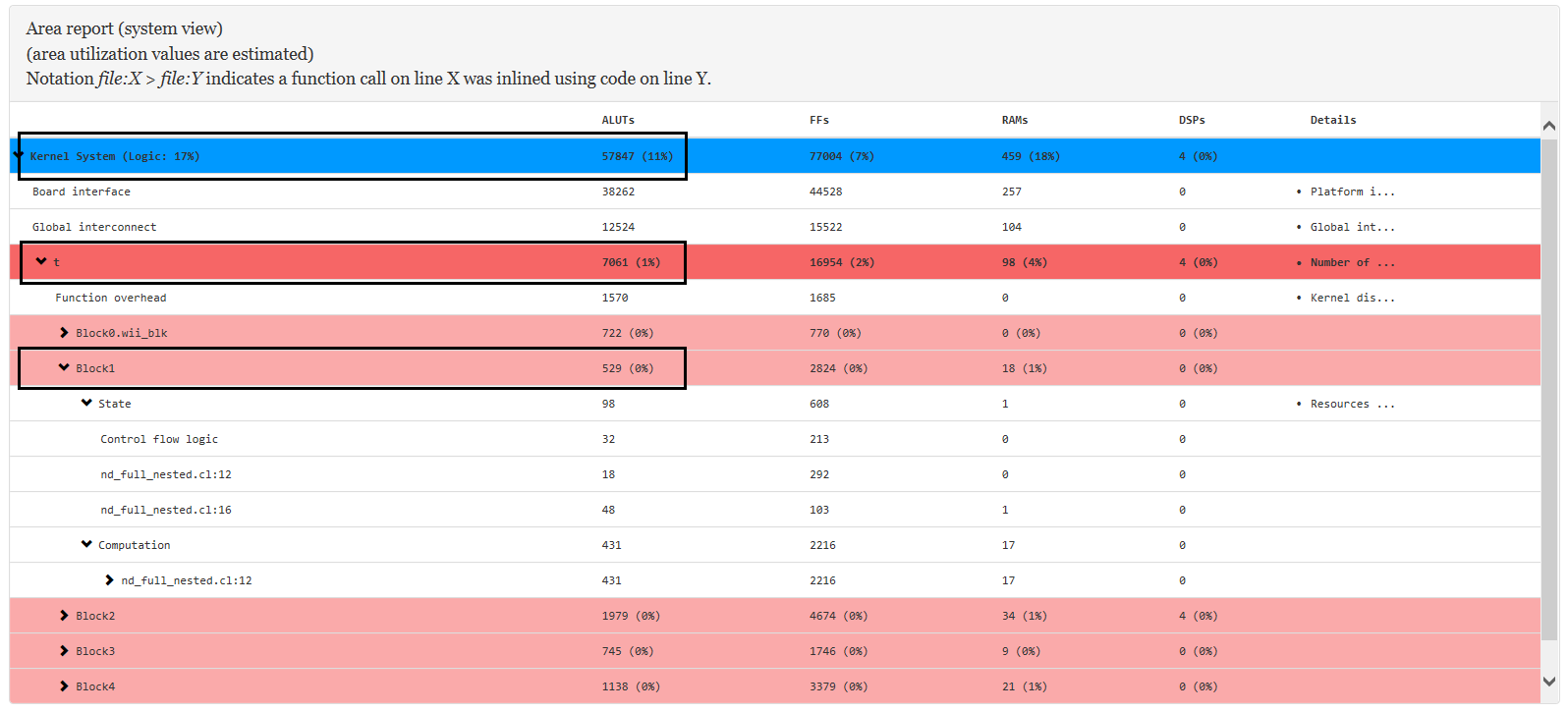

Note: The area usage data are estimates that the generates. These estimates might differ from the final area utilization results.
In the report menu's View reports... pull-down menu, select Area analysis by source or Area analysis of system.