Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-8358E91F-8D60-4D7B-AC05-98F1C1CB31BC
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-8358E91F-8D60-4D7B-AC05-98F1C1CB31BC
Morphological Operations
This chapter describes the Intel® IPP image processing functions that perform morphological operations on images.
Generally, the erosion and dilation smooth the boundaries of objects without significantly changing their area. Opening and closing smooth thin projections or gaps. Morphological operations use a structuring element (SE) that is a a user-defined rectangular mask, or for some functions - symmetric 3x3 mask.
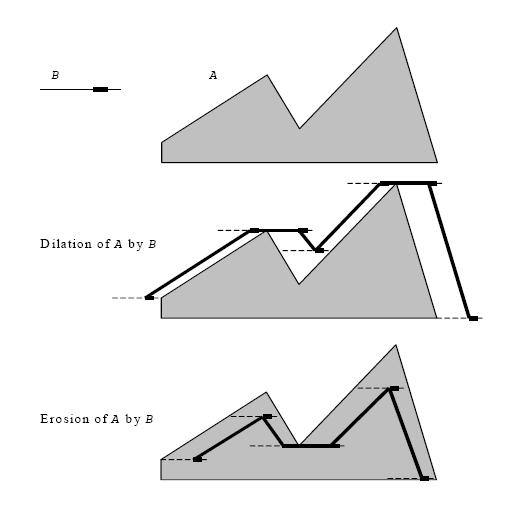
In a more general sense, morphological operations involve an image A called the object of interest and a kernel element B called the structuring element. The image and structuring element could be in any number of dimensions, but the most common use is with a 2D binary image, or with a 3D gray scale image. The element B is most often a square or a circle, but it could be of any shape. Just like in convolution, B is a kernel or template with an anchor point. Figure "Dilation and Erosion of A by B" shows dilation and erosion of object A by B. In the figure, B is rectangular with an anchor point at upper left shown as a dark square.
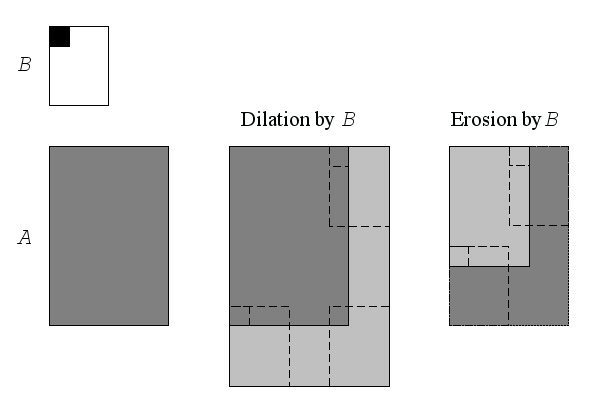
Let Bt is the SE with pixel t in the anchor position, B is transpose of the SE.
Dilation of binary image A {A(t) = 1, t∈A; 0 - otherwise} by binary SE B is
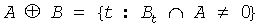
It means that every pixel is in the set, if the intersection is not null. That is, a pixel under the anchor point of B is marked “on”, if at least one pixel of B is inside of A.
Erosion of the binary image A by the binary SE B is
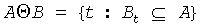
That is, a pixel under the anchor of B is marked “on”, if B is entirely within A.
Generalization of dilation and erosion for the gray-scale image A and the binary SE B is
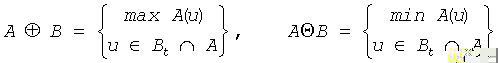
Generalization of dilation and erosion for the gray-scale image A and the gray-scale SE B is
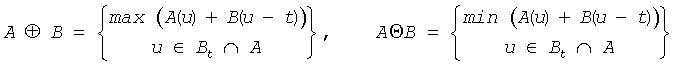
Opening operation of A by B is A∘B = (AΘB) ⊕B.
Closing operation of A by B is A•B = ( A⊕B) ΘB.
Top-hat operation of A by B is A - AºB.
Black-hat operation of A by B is A•B - A.
Black-hat operation of A by B is A⊕B - AΘB.
Morphological reconstruction [Vincent93]ρA(C) of an image A from the image C, A(t) ≥C(t) ∀t by dilation with the mask B is an image
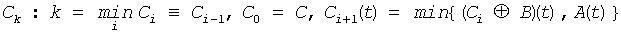
Morphological reconstruction ρA(C) of an image A from the image C, A(t) ≤C(t) ∀t by erosion with the mask B is an image
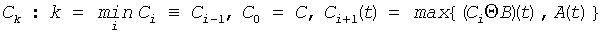
Figure "Morphological Operations Performed by Intel IPP" presents the results of different morphological operations applied to the initial image. In these operations, the SE is a matrix of 3x3 size with the following values:
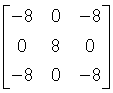
for common and advanced morphology, and

for gray morphology.
The anchor cell is in the center cell (1,1) of the matrix.

Flat Structuring Elements for Grayscale Image
Erosion and dilation can be done in 3D space, that is, with gray levels. 3D structuring elements can be used, but the simplest and the best way is to use a flat structuring element B. Figure "1D Cross Section of Dilation and Erosion of A by B" is a 1D cross section of dilation and erosion of a grayscale image A by a flat structuring element B. In the figure, B has an anchor slightly to the right of the center as shown by the dark mark on B.
In Figure "1D Cross Section of Dilation and Erosion of A by B" above, dilation is mathematically
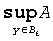
and erosion is
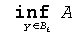
.
- Dilate3x3
Performs dilation of an image using a 3x3 mask. - Dilate
Performs dilation of an image using a specified mask. - DilateBorder
Performs dilation of an image. - DilateGetBufferSize
Computes the size of the working buffer for the Dilate function. - DilateGetSpecSize
Computes the size of the internal state or specification structure for the Dilate function. - DilateInit
Initializes the internal state or specification structure for the Dilate function. - Erode3x3
Performs erosion of an image using a 3x3 mask. - Erode
Performs erosion of an image using a specified mask. - ErodeBorder
Performs erosion of an image. - ErodeGetBufferSize
Computes the size of the working buffer for the Erode function. - ErodeGetSpecSize
Computes the size of the internal state or specification structure for the Erode function. - ErodeInit
Initializes the internal state or specification structure for the Erode function. - GrayDilateBorder
Performs gray-kernel dilation of an image. - GrayErodeBorder
Performs gray-kernel erosion of an image. - MorphAdvInit
Initializes the specification structure for advanced morphological operations. - MorphAdvGetSize
Computes the size of the specification structure for advanced morphological operations. - MorphGetBufferSize
Computes the size of the working buffer for advanced morphological operations. - MorphGetSpecSize
Computes the size of the internal state or specification structure for advanced morphological operations. - MorphInit
Initializes the internal state or specification structure for advanced morphological operations. - MorphologyBorderGetSize
Computes the size of the morphology specification structure. - MorphologyBorderInit
Initializes the morphology specification structure for erosion or dilation operations. - MorphBlackhat
Performs top-hat operation on an image. - MorphBlackhatBorder
Performs black-hat operation on an image. - MorphClose
Closes an image. - MorphCloseBorder
Closes an image. - MorphGradient
Calculates morphological gradient of an image. - MorphGradientBorder
Calculates morphological gradient of an image. - MorphOpen
Opens an image. - MorphOpenBorder
Opens an image. - MorphTophat
Performs top-hat operation on an image. - MorphTophatBorder
Performs top-hat operation on an image. - MorphGrayInit
Initializes morphology state structure for gray-kernel morphology operations. - MorphGrayGetSize
Computes the size of the gray-kernel morphology state structure. - MorphReconstructGetBufferSize
Computes the size of the buffer for morphological reconstruction operation. - MorphReconstructDilate
Reconstructs an image by dilation. - MorphReconstructErode
Reconstructs an image by erosion. - MorphSetMode
Sets the mask processing mode for advanced morphological operations.