Visible to Intel only — GUID: ihl1654714897169
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: ihl1654714897169
Ixiasoft
3.2.1.1. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Controller
An external reference voltage (VDC), the capacitor voltage, or an output voltage (up to 800 V) provides the output reference voltage. The output voltages are initially subtracted from the reference voltage, and the current reference controls it. Direct Quadrature (DQ) synchronous reference frame voltages are achieved at the control output. Normalize these two voltage values by a factor of 1 (shift-left logical) and 1/800 to get a waveform that you can use in the Space Vector PWM (SVPWM) block. After normalization, the values are converted from the DQ frame to the alpha-beta frame (orthogonal stationary) and used in the SVPWM block to control the switching of the power transistors in the six-switch converter module.
To find the values of the PI constants, refer to the Analysis and Control of Three-Phase PWM Rectifier for Power Factor Improvement of IM Drive 1 paper for the following formulas:
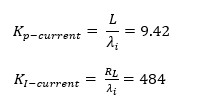
-
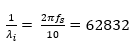
- L is the input inductance.
- RL is the associated resistance.
Similarly, you can calculate voltage loop constants as follows:
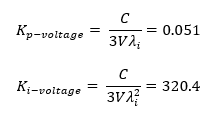
- C is the DC link capacitance.
- V is the input RMS voltage.
Even though the values calculated using the equations provide a good control response, manual tuning is necessary to achieve the desired overshoot and settling time. After manual tuning, you can find values for the constants in the Simulink model blocks as follows:
- Kp-voltage = 0.075
- Ki-voltage = 22 Ts
- Kp-current1 = 11
- Ki-current1 = 500 Ts
- Kp-current2 = 12.5
- Ki-current2 = 500 Ts