Visible to Intel only — GUID: efy1652306149731
Ixiasoft
1. Overview
2. Getting Started
3. F-Tile Ethernet Intel® FPGA Hard IP Parameters
4. Functional Description
5. Clocks
6. Resets
7. Interface Overview
8. Configuration Registers
9. Supported Modules and IPs
10. Supported Tools
11. F-Tile Ethernet Intel® FPGA Hard IP User Guide Archives
12. Document Revision History for F-Tile Ethernet Intel® FPGA Hard IP User Guide
4.4.1. Features
4.4.2. PTP Timestamp Accuracy
4.4.3. PTP Client Flow
4.4.4. RX Virtual Lane Offset Calculation for No FEC Variants
4.4.5. Virtual Lane Order and Offset Values
4.4.6. UI Adjustment
4.4.7. Reference Time Interval
4.4.8. Minimum and Maximum Reference Time (TAM) Interval for UI Measurement (Hardware)
4.4.9. UI Value and PMA Delay
4.4.10. Routing Delay Adjustment for Advanced Timestamp Accuracy Mode
4.4.11. Routing Delay Adjustment for Basic Timestamp Accuracy Mode
5.1. Clock Connections in Single Instance Operation
5.2. Clock Connections in Multiple Instance Operation
5.3. Clock Connections in MAC Asynchronous FIFO Operation
5.4. Clock Connections in PTP-Based Synchronous and Asynchronous Operation
5.5. Clock Connections in Synchronous Ethernet Operation
5.6. Custom Cadence
7.1. Status Interface
7.2. TX MAC Avalon ST Client Interface
7.3. RX MAC Avalon ST Aligned Client Interface
7.4. TX MAC Segmented Client Interface
7.5. RX MAC Segmented Client Interface
7.6. MAC Flow Control Interface
7.7. PCS Mode TX Interface
7.8. PCS Mode RX Interface
7.9. FlexE and OTN Mode TX Interface
7.10. FlexE and OTN Mode RX Interface
7.11. Custom Rate Interface
7.12. Deterministic Latency Interface
7.13. 32-bit Soft CWBIN Counters
7.14. Reconfiguration Interfaces
7.15. Precision Time Protocol Interface
7.2.1. TX MAC Avalon ST Client Interface with Disabled Preamble Passthrough
7.2.2. TX MAC Avalon ST Client Interface with Enabled Preamble Passthrough
7.2.3. Using MAC Avalon ST skip_crc Signal to Control Source Address, PAD, and CRC Insertion
7.2.4. Using MAC Avalon ST i_tx_error Signal to Mark Packets Invalid
7.4.1. TX MAC Segmented Client Interface with Disabled Preamble Passthrough
7.4.2. TX MAC Segmented Client Interface with Enabled Preamble Passthrough
7.4.3. Using MAC Segmented skip_crc Signal to Control Source Address, PAD, and CRC Insertion
7.4.4. Using MAC Segmented i_tx_mac_error to Mark Packets Invalid
Visible to Intel only — GUID: efy1652306149731
Ixiasoft
7.12. Deterministic Latency Interface
The Deterministic Latency Interface ports are available when you turn on Include Deterministic Latency Interface in FlexE mode using the IP Parameter Editor.
Use the deterministic latency interface if you want to precisely measure the latency along the TX/RX datapaths. It compares the arrival time of a known digital bit (typically the start of an alignment marker) with the arrival time of an analog pulse generated at the same point.
Figure 53. Enable Deterministic Latency Interface IP Parameter Editor
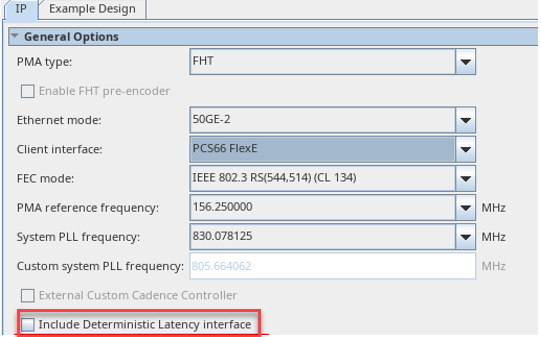

Note: You cannot enable the Deterministic Latency Interface and PTP interface at the same time.
The table below depicts the deterministic latency interface ports that are exposed to the user when the FlexE mode is turned on.
Note: When the Deterministic Latency Interface is enabled, you need to drive sync pulses to the i_tx_pcs66_am port and expect pulses from the o_rx_pcs66_am_valid port.
| Signal Name |
Width | Description |
|---|---|---|
| o_tx_dl_async_pulse[n-1:0] | <n> | Asynchronous output latency pulse from TX datapath. |
| o_rx_dl_async_pulse[n-1:0] | <n> | Asynchronous output latency pulse from RX datapath. |
| i_latency_sclk[n-1:0] | <n> | Asynchronous latency calibration pulse input. |
| i_tx_dl_measure_sel[n-1:0] | <n> |
Mux select signal for the TX path.
|
| i_rx_dl_measure_sel[n-1:0] | <n> |
Mux select signal for the RX path.
|