Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-FC02F323-B883-4D14-A230-F52B10C41CF7
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-FC02F323-B883-4D14-A230-F52B10C41CF7
Sparse BLAS Coordinate Matrix Storage Format
The coordinate format is the most flexible and simplest format for the sparse matrix representation. Only non-zero elements are stored, and the coordinates of each non-zero element are given explicitly. Many commercial libraries support the matrix-vector multiplication for the sparse matrices in the coordinate format.
The Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library (oneMKL) coordinate format is specified by three arrays:values, rows, and column, and a parameter nnz which is number of non-zero elements in A. All three arrays have dimension nnz. The following table describes the arrays in terms of the values, row, and column positions of the non-zero elements in a sparse matrix A.
- values
-
A real or complex array that contains the non-zero elements of A in any order.
- rows
-
Element i of the integer array rows is the number of the row in A that contains the i-th value in the values array.
- columns
-
Element i of the integer array columns is the number of the column in A that contains the i-th value in the values array.
Note that the Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library (oneMKL) Sparse BLAS routines support the coordinate format both with one-based indexing and zero-based indexing.
For example, the sparse matrix C
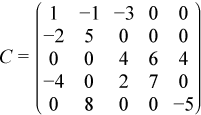
can be represented in the coordinate format as follows:
| one-based indexing | ||||||||||||||
| values | = | (1 | -1 | -3 | -2 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 4 | -4 | 2 | 7 | 8 | -5) |
| rows | = | (1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5) |
| columns | = | (1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 5) |
| zero-based indexing | ||||||||||||||
| values | = | (1 | -1 | -3 | -2 | 5 | 4 | 6 | 4 | -4 | 2 | 7 | 8 | -5) |
| rows | = | (0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4) |
| columns | = | (0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4) |