Intel® Integrated Performance Primitives Developer Guide and Reference
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-86AD202B-BE17-4D54-AB10-D05BE25DC541
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-86AD202B-BE17-4D54-AB10-D05BE25DC541
Integral
Transforms an image to the integral representation.
Syntax
IppStatus ippiIntegral_8u32s_C1R(const Ipp8u* pSrc, int srcStep, Ipp32s* pDst, int dstStep, IppiSize srcRoiSize, Ipp32s val);
IppStatus ippiIntegral_8u32f_C1R(const Ipp8u* pSrc, int srcStep, Ipp32f* pDst, int dstStep, IppiSize srcRoiSize, Ipp32f val);
IppStatus ippiIntegral_32f_C1R(const Ipp32f* pSrc, int srcStep, Ipp32f* pDst, int dstStep, IppiSize srcRoiSize);
Include Files
ippcv.h
Domain Dependencies
Headers: ippcore.h, ippvm.h, ipps.h, ippi.h
Libraries: ippcore.lib, ippvm.lib, ipps.lib, ippi.lib
Parameters
pSrc |
Pointer to the source image ROI. |
srcStep |
Distance in bytes between starts of consecutive lines in the source image. |
pDst |
Pointer to the ROI in the destination integral image. |
dstStep |
Distance in bytes between starts of consecutive lines in the destination image. |
srcRoiSize |
Size of source and destination image ROI in pixels. |
val |
The value to add to pDst image pixels. |
Description
This function operates with ROI (see Regions of Interest in Intel IPP). This function transforms a source image pSrc to the integral image pDst. Pixel values of the destination image pDst are computed using pixel values of the source image pSrc and the specified value val in accordance with the following formula:
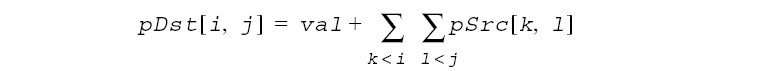
where i,j are coordinates of the destination image pixels (see Figure 11-1 ) varying in the range i = 1 ,..., srcRoiSize.height, j = 0,..., srcRoiSize.width. Pixel values of zero row and column of pDst (i=0) is set to val.
For the ippiIntegral_32f_C1 function flavor the value of val is considered to be equal to zero.
The size of the destination images is (srcRoiSize.width + 1) x (srcRoiSize.height + 1).
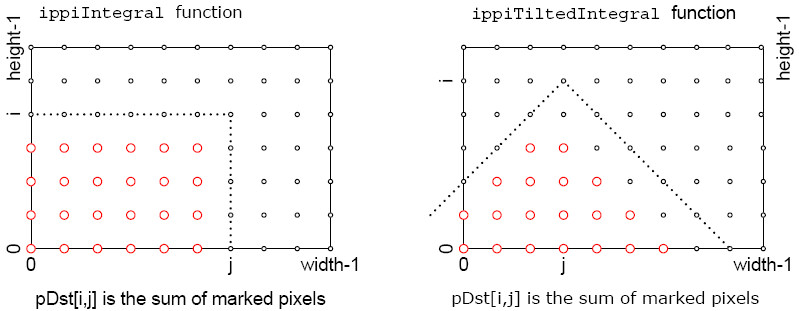
Figure “Operation of the Integral and TiltedIntegral functions” shows what pixels (red circles) of the source image are used in computation new pixel values in the i,j coordinates.
For large images the result of summation can exceed the upper bound of the output data type. Table “Maximum Image Size for Integral Functions” lists the maximum image size for different function flavors and values.
| Function Flavor | Value val | Maximum Image Size |
|---|---|---|
| ippiIntegral_8u32s_C1R | 0 | (231-1)/255 |
| -231 | 232/255 | |
| ippiIntegral_8u32f_C1R | 0 | 224/255 |
| -224 | (225+1)/255 |
Return Values
ippStsNoErr |
Indicates no error. |
ippStsNullPtrErr |
Indicates an error if pSrc or pDst is NULL. |
ippStsSizeErr |
Indicates an error condition if srcRoiSize has a field with zero or negative value. |
ippStsStepErr |
Indicates an error condition if srcStep is less than srcRoiSize.width * <pixelSize>, or dstStep is less than (srcRoiSize.width+1) * <pixelSize> . |
ippStsNotEvenStepErr |
Indicates an error condition if srcStep or dstStep is not divisible by <pixelSize>. |
Example
The code example below demonstrates how to use the ippiIntegral_8u32s_C1R function:
void func_integral_8u32s_C1R()
{
Ipp8u pSrc[5*4];
Ipp32s pDst[6*5];
IppiSize ROI = {5,4};
ippiSet_8u_C1R(1,pSrc,5,ROI);
Ipp32s val = 1;
ippiIntegral_8u32s_C1R(pSrc, 5, pDst, 6*sizeof(Ipp32s), ROI, val);
}
Result:
pSrc -> 1 1 1 1 1 pDst -> 1 1 1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 5 6
1 1 1 1 1 1 3 5 7 9 11
1 1 1 1 1 1 4 7 10 13 16
1 5 9 13 17 21
The code example below demonstrates how to use the ippiIntegral_32f_C1R function:
void func_integral_32f_C1R()
{
Ipp32f pSrc[5*4];
Ipp32f pDst[6*5];
IppiSize ROI = {5, 4};
ippiSet_32f_C1R(1, pSrc, 5*sizeof(Ipp32f), ROI);
ippiIntegral_32f_C1R(pSrc, 5*sizeof(Ipp32f), pDst, 6*sizeof(Ipp32f), ROI);
}
Result:
pSrc -> 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 pDst -> 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0
1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0
1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 3.0 6.0 9.0 12.0 15.0
0.0 4.0 8.0 12.0 16.0 20.0