Intel® Integrated Performance Primitives Developer Guide and Reference
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-8CAEE8EF-D242-4998-861F-D6571BCC750A
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-8CAEE8EF-D242-4998-861F-D6571BCC750A
Image Downsampling
Conventionally, digital color images are represented by setting specific values of the color space coordinates for each pixel. Color spaces with decoupled luminance and chrominance coordinates (YUV type) allow the number of bits required for acceptable color description of an image to be reduced. This reduction is based on greater sensitivity of the human eye to changes in luminance than to changes in chrominance. The idea behind this approach is to set individual value of luminance component to each pixel, while assigning the same color (chrominance components) to certain groups of pixels (sometimes called macropixels) in accordance with some specific rules. This process is called downsampling and there are different sampling formats depending on the underlying scheme.
The following sampling formats are supported by the Intel IPP image processing functions (excluding the JPEG functions):
4:4:4 YUV (YCbCr) - conventional format, no downsampling, Y, U(Cb), V(Cr) components are sampled at every pixel. If each component takes 8 bits, than every pixel requires 24 bits. This format is often denoted as YUV (YCbCr) with the 4:4:4 descriptor omitted.
4:2:2 YUV (YCbCr) - uses the 2:1 horizontal downsampling. It means that the Y component is sampled at each pixel, while U(Cb) and V(Cr) components are sampled every 2 pixels in horizontal direction. If each component takes 8 bits, the pair of pixels requires 32 bits.
4:1:1 YCbCr - uses the 4:1 horizontal downsampling. It means that the Y component is sampled at each pixel, while Cb and Cr components are sampled every 4 pixels horizontally. If each component takes 8 bits, each four horizontal pixels require 48 bits.
4:2:0 YUV (YCbCr) - uses the 2:1 horizontal downsampling and the 2:1 vertical downsampling. Y is sampled at each pixel, U(Cb) and V(Cr) are sampled at every block of 2x2 pixels. If each component takes 8 bits, each four-pixel block requires 48 bits.
In JPEG compression, downsampling has specific distinctive features and is denoted in a slightly different way. In JPEG domain, sampling formats determine the structure of minimal coded units, or MCUs. Therefore, the Intel IPP functions specific for a JPEG codec, support the following sampling formats:
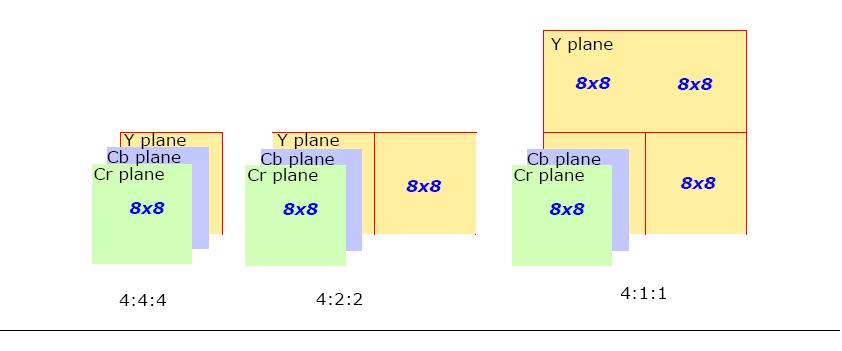
4:4:4 YCbCr - for every 8x8 block of Y samples, there is one 8x8 block of each Cb and Cr samples.
4:2:2 YCbCr - for every two horizontal 8x8 blocks of Y samples, there is one 8x8 block of each Cb and Cr samples.
4:1:1 YCbCr - for every four (two in horizontal and two in vertical direction) 8x8 blocks of Y samples, there is one 8x8 block of each Cb and Cr samples.
Structure of the corresponding MCU for each of these sampling formats is shown in Figure MCU Structure for Different JPEG Sampling Formats.