AN 672: Transceiver Link Design Guidelines for High-Gbps Data Rate Transmission
Visible to Intel only — GUID: nik1412632463051
Ixiasoft
1.2. Stackup Design
The assignment of critical high-speed routing layers within the PCB stack-up is a critical part of the design decision. The assignment of high-speed signal layers within the stackup directly affects the signal performance. Signals routed on external layers of the PCB board are referred to as microstrip, while those routed on internal layers are called stripline.
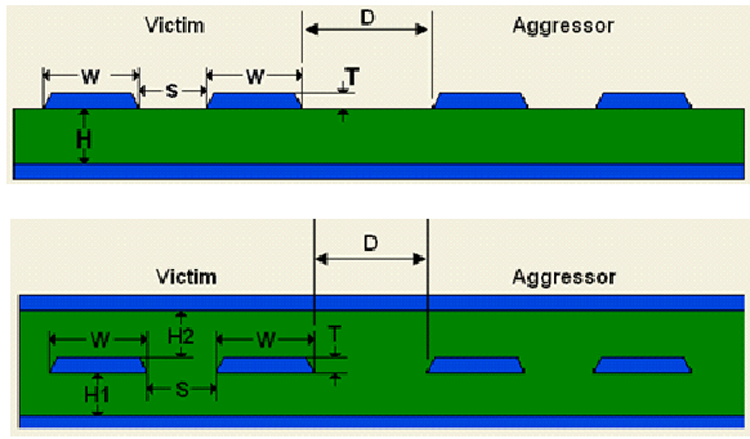
By manipulating the various parameters such as trace width (W), separation (S), and height from the reference plane (H for microstrip and H1, H2 for stripline), the trace impedance can be adjusted appropriately. Additionally, edge-coupled crosstalk from neighboring traces can be well-controlled by adjusting the pair separation (D). For more information on crosstalk, refer to Crosstalk Control.
| Topology | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Microstrip |
|
|
| Stripline |
|
|
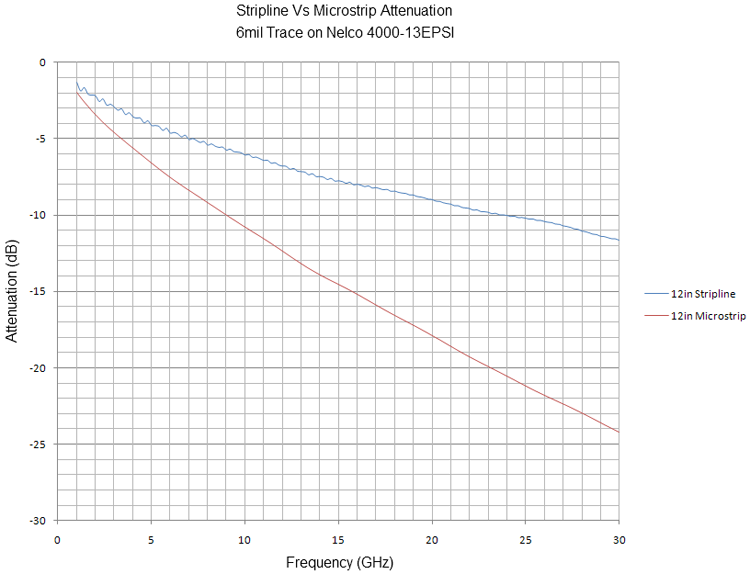
The decision to use one topology over the other examines the first-order factors that affect signal bandwidth. While impedance and crosstalk can be well-controlled in both routing topologies, stripline provides lower signal attenuation vs. microstrip for the same trace width and copper thickness.