Visible to Intel only — GUID: edy1520633302735
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: edy1520633302735
Ixiasoft
3.2.1.4.1. PCIe Address to Avalon-MM Address Mapping
The Bursting Master module transforms PCIe memory read (MRd) and memory write (MWr) request packets received from the PCIe system into Avalon® -MM read and write transactions.
The Bursting Master module compares the address of each incoming read or write TLP with the BARs defined in the PCIe Hard IP. For TLPs that match with a BAR, the offset from the BAR is put out on the address bus and the number of the matching BAR comes out on the bam_bar_o bus.
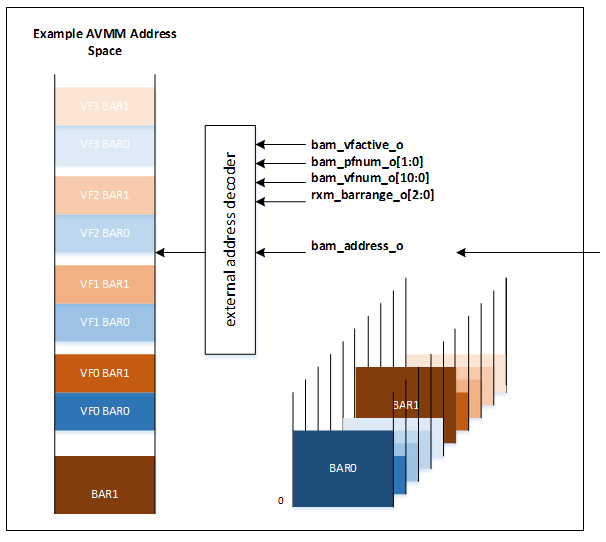
Although these signals are in conduits separate from the Avalon® -MM master interface, they are synchronous to it and can be treated as extensions of the address bus. The user logic can decode the Avalon® -MM address and physical/virtual function numbers to translate them into the Avalon® -MM address space.
Because the additional signals are in a separate conduit, they must be routed along with the signals from the Avalon® -MM master interface to a single module with an Avalon® -MM slave interface and matching conduits for the BAR and function numbers. This module decodes the BAR information contained in the bam_bar_o signals in the conduit, and routes the data to one or more standard Avalon® -MM slaves. This decoder (referred to as the BAR Interpreter in the available design example) is necessary because Platform Designer cannot route the conduit to multiple points.
The following figure shows an example of translating the PCIe address into an Avalon® -MM address. This example shows that PCIe address regions grouped with BAR number are translated into Avalon® -MM address regions grouped with virtual function number.