Visible to Intel only — GUID: ame1670545308787
Ixiasoft
1. Answers to Top FAQs
2. Overview of the Intel® FPGA Power and Thermal Calculator
3. Estimating Power Consumption with the Intel® FPGA Power and Thermal Calculator
4. Intel® FPGA Power and Thermal Calculator Graphical User Interface
5. Intel® FPGA Power and Thermal Calculator Pages
6. Factors Affecting the Accuracy of the Intel® FPGA PTC
7. Intel® FPGA Power and Thermal Calculator User Guide Archive
8. Document Revision History for the Intel® FPGA Power and Thermal Calculator User Guide
A. Measuring Static Power
5.1. Intel® FPGA PTC - Power Summary
5.2. Intel® FPGA PTC - Common Page Elements
5.3. Intel® FPGA PTC - Main Page
5.4. Intel® FPGA PTC - Logic Page
5.5. Intel® FPGA PTC - RAM Page
5.6. Intel® FPGA PTC - DSP Page
5.7. Intel® FPGA PTC - Clock Page
5.8. Intel® FPGA PTC - PLL Page
5.9. Intel® FPGA PTC - I/O Page
5.10. Intel® FPGA PTC - Transceiver Page
5.11. Intel® FPGA PTC - HPS Page
5.12. Intel® FPGA PTC - Crypto Page
5.13. Intel® FPGA PTC - HBM Page
5.14. Intel® FPGA PTC - Thermal Page
5.15. Intel® FPGA PTC - Report Page
Visible to Intel only — GUID: ame1670545308787
Ixiasoft
4.4. Intel® FPGA PTC - IP Wizard
The IP Wizard page of the Intel® FPGA Power and Thermal Calculator (PTC) allows you to select, configure, and instantiate IP blocks which are then appended to your current design.
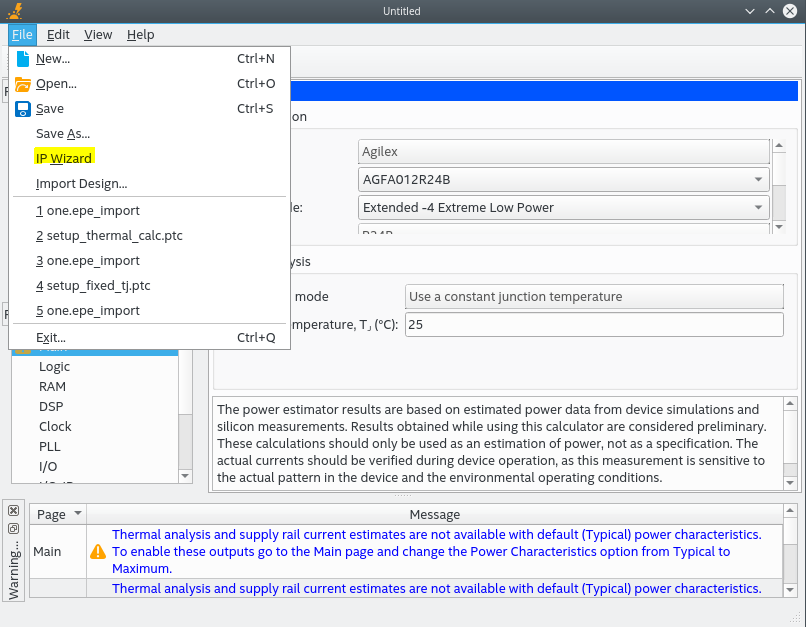
- You can launch the IP Wizard from the PTC File menu, by clicking File > IP Wizard
Figure 20. Launching the IP Wizard
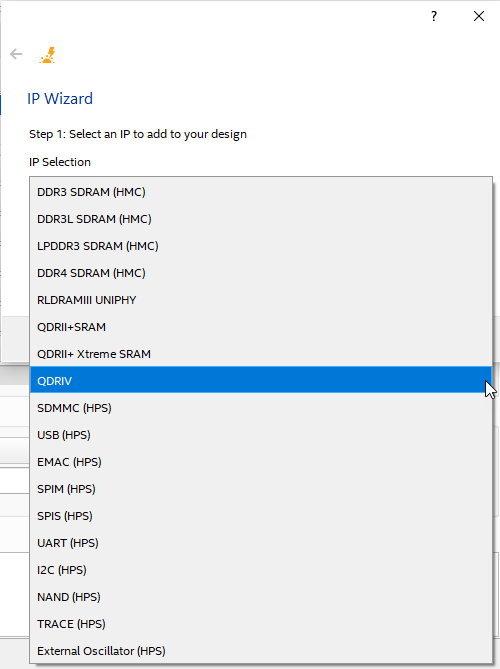
- The opening dialog box of the IP Wizard prompts you to select an IP from a pulldown list. Select the IP that you want to add to your design, and click Next..
Figure 21. IP Selection Page
- The IP Wizard then displays a dialog box for configuring your selected IP. Enter the appropriate information, and click Next.
Figure 22. IP Configuration Page
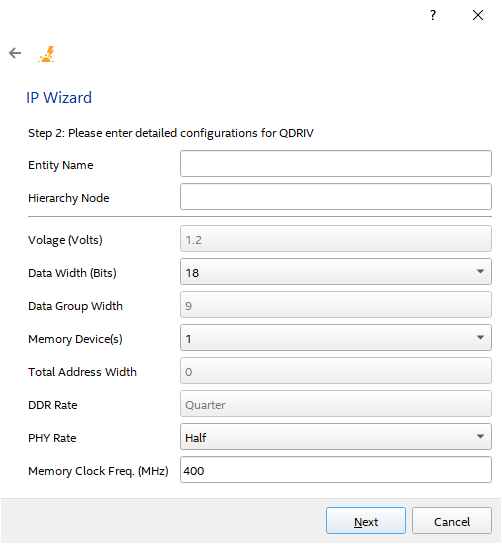
Table 8. IP Configuration Fields Column Heading Description Entity Name Specify a name for the entity. Hierarchy Node Specifies the name of the IP instance. Voltage Specifies the I/O voltage of the signaling between periphery device and interface. Data Width (Bits) Specifies the interface data width of the specific IP (in bits). Data Group Width Specifies the data group width. Memory Device(s) Specifies the number of memory devices connected to the interface. Total Address Width Specifies the total address width. This value is used to derive the total number of address pins required. DDR Rate Specifies the clock rate of user logic. Determines the clock frequency of user logic in relation to the memory clock frequency. For example, if the memory clock sent from the FPGA to the memory device is toggling at 800MHz, a "Quarter rate" interface means that the user logic in the FPGA runs at 200MHz. PHY Rate Specifies the clock rate of PHY logic. Determines the clock frequency of PHY logic in relation to the memory clock frequency. For example, if the memory clock sent from the FPGA to the memory device is toggling at 800MHz, a "Quarter rate" interface means that the PHY logic in the FPGA runs at 200MHz. Memory Clock Frequency (MHz) Specifies the frequency of memory clock (in MHz). - The IP Wizard then displays the configuration details for your review. If you want to change any of the configuration, you can go back by clicking the arrow at the top-left corner of the Wizard. Otherwise, if you are satisfied with the configuration, click Finish.
Figure 23. IP Configuration Review Page
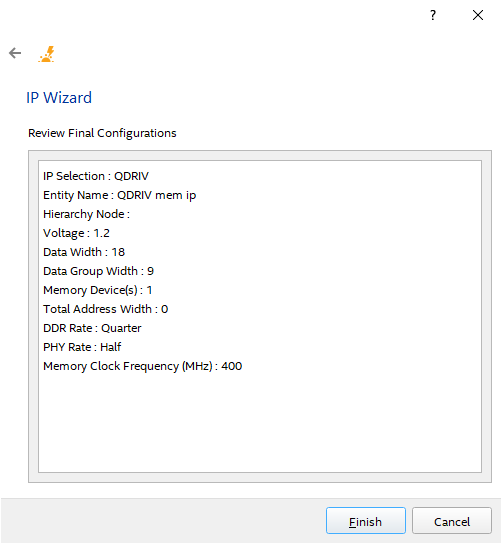
After you exit the IP Wizard, the system appends new rows to the PTC pages (Logic, PLL, I/O, etc.), in accordance with the IP that you have added.