Visible to Intel only — GUID: iga1457472193447
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: iga1457472193447
Ixiasoft
38.6.1.2.3. VIC Connections
When you have added the VIC to your system, it appears in Platform Designer as shown below.
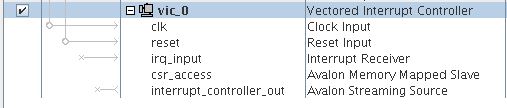
After adding a VIC to the Platform Designer system, you must parameterize the VIC and the EIC interface at the system level. Immediately after you add the VIC, several error messages appear. Resolve these error messages by executing the following actions in any order:
- Connect the VIC’s interrupt_controller_out Avalon® -ST source to the interrupt_controller_in Avalon® -ST sink on either the Nios II processor or the next VIC in a daisy-chained configuration.
- Connect the Nios® II processor's data_master Avalon® -MM ports to the csr_access Avalon® -MM agent port.
- Assign an interrupt number for each interrupt-based component in the system, as shown below. This step connects each component to an interrupt port on the VIC.
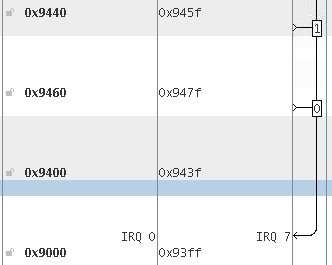
When you use the HAL VIC driver, the driver makes a default assignment from register sets to interrupts. The default assignment makes some assumptions about interrupt priorities, based on how devices are connected to the VIC.