Notes for Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library Vector Statistics
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-F144B02A-5C11-4602-BCB7-3B1B6650E4E0
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-F144B02A-5C11-4602-BCB7-3B1B6650E4E0
Gaussian (VSL_RNG_METHOD_GAUSSIAN_BOXMULLER2)
Random number generator of normal (Gaussian) distribution with parameters a and s. You can produce a successive pair of the random numbers x1, x2 of the standard normal distribution according to the formula

where u1, u2 are a pair of successive random numbers uniformly distributed over the interval (0, 1). For details, see [Box58].
The normal distribution with the parameters a and s is transformed to the random number y by scaling and the shift y = sx+a.
You can safely call this VS method even when the random numbers are generated in blocks with the size aliquant to 2.
For example, you use the VSL_METHOD_DGAUSSIAN_BOXMULLER2 method to generate a pair of random numbers of the standard normal distribution.
Option 1
Single call of method VSL_METHOD_DGAUSSIAN_BOXMULLER2 with the vector length equal to 2:
... double x[2]; ... vdRngGaussian(VSL_RNG_METHOD_GAUSSIAN_BOXMULLER2, stream, 2, x, 0.0, 1.0); ...
In this case, you generate the random numbers x[0], x[1] by the formula:
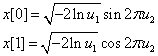
Option 2
Double call of the method VSL_METHOD_DGAUSSIAN_BOXMULLER2 with the vector length equal to 1:
... double x[2]; ... vdRngGaussian(VSL_RNG_METHOD_GAUSSIAN_BOXMULLER2, stream, 1, &x[0], 0.0, 1.0); vdRngGaussian(VSL_RNG_METHOD_GAUSSIAN_BOXMULLER2, stream, 1, &x[1], 0.0, 1.0); ...
At the first call of vdRngGaussian you produce the random number x[0] by the formula:
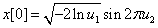
At the second call of vdRngGaussian the vector length, over which you initially called the function to generate the random stream, is recognized as odd (equal to 1 in this case). Then the random number x[1] is generated by the formula:

and not by the formula:

See Intel® oneAPI Math Kernel Library Vector Statistics Random Number Generator Performance Data for test results summary.