Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGA and SoC FPGA
Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGA and SoC FPGA deliver innovative advantages in performance, power efficiency, density, and system integration. Featuring the revolutionary Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture and built combining Intel's patented Embedded Multi-Die Interconnect Bridge (EMIB) technology, the Advanced Interface Bus (AIB), and a growing portfolio of chiplets, Intel® Stratix® 10 devices deliver up to 2X performance gains over previous-generation, high-performance FPGA.1
See also: FPGA Design Software, Design Store, Downloads, Community, and Support
Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGA and SoC FPGA
Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture
To address the challenges presented by next-generation systems, Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGAs and SoCs feature the new Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture, which delivers 2X the clock frequency performance and up to 70% lower power compared to previous-generation, high-end FPGAs.2
Benefits
Higher Throughput
Leverage 2X core clock frequency performance to obtain throughput breakthroughs.
Greater Design Functionality
Use faster clock frequencies to reduce bus widths and reduce intellectual property (IP) size, freeing up additional FPGA resources to add greater functionality.
Improved Power Efficiency
Use reduced IP size—enabled by the Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture—to consolidate designs spanning multiple devices into a single device, thereby reducing power by up to 70% versus previous-generation devices.
Increased Designer Productivity
Boost performance with less routing congestion and fewer design iterations using Hyper-Aware design tools.
The Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture introduces additional by passable registers everywhere throughout the FPGA fabric. These additional registers, called Hyper-Registers, are available on every interconnect routing segment and at the inputs of all functional blocks. Hyper-Registers enable three key design techniques to achieve the 2X core performance increase:
- Fine grained Hyper-Retiming to eliminate critical paths.
- Zero latency Hyper-Pipelining to eliminate routing delays.
- Flexible Hyper-Optimization to achieve the best performance.
When you use these techniques in your design, the Hyper-Aware design tools automatically use the Hyper-Registers to achieve maximum core clock frequency.
Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture in Intel® Stratix® 10 Devices
Learn how the Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture innovations help designers achieve their performance goals.
Learn how the Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture design software innovations reduce design iterations and increase designer productivity for fast time to market.
Optimize Designs with the Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture
The Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture enables three key design techniques to achieve 2X performance: Hyper-Retiming, Hyper-Pipelining, and Hyper-Optimization. Read the Intel® Stratix® 10 device High-Performance Design Handbook to learn how to combine these performance optimization techniques to achieve the highest clock frequencies in Intel® Stratix® 10 devices.
Download the Intel® Stratix® 10 High-Performance Design Handbook ›
Start Designing with the Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture Today
The Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture leverages the Hyper-Aware design flow. This flow incorporates the innovative Fast Forward Compile feature that allows designers to perform rapid design performance exploration and attain breakthrough levels of performance.
The Fast Forward Compile feature is available today, so you can start designing with the Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture for Intel® Stratix® 10 devices. Contact your sales representative to obtain a license.
Contact your local sales representative about evaluating the Fast Forward Compile feature.
Watch the Fast Forward Compile Feature Demo Video
Watch this demo video about the Fast Forward Compile feature for Intel® Stratix® 10 device designs. This video shows you how the Fast Forward Compile feature provides innovative performance exploration capabilities and implement the three key design optimizations for the Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture, including.
- How to overcome retiming restrictions to enable Hyper-Retiming.
- How to optimize designs to implement Hyper-Pipelining.
- How to identify and overcome performance bottlenecks for Hyper-Optimization.
Find Training on the Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture
Intel offers instructor-led training and online training courses covering design optimization techniques to extract the maximum performance from your design using the Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture.
Heterogeneous 3D System-In-Package Integration
Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGAs and SoCs leverage heterogeneous 3D system-in-package (SiP) technology to integrate a monolithic FPGA core fabric with 3D SiP transceiver tiles and other advanced components in a single package.
Scalable and Flexible Solutions
Heterogeneous 3D SiP integration enables a scalable and flexible path to deliver multiple product variants that mix functionality and/or process nodes effectively within a single package.
Mixing Functionality and Process Nodes
Heterogeneous 3D SiP integration enables a number of major system-level benefits including:
High Performance
Heterogeneous integration provides a path to integrate higher bandwidth interface capabilities to meet the needs of 400-Gigabit to 1-Terabit systems.
Lower Power
Compared to discrete components on a PCB, heterogeneous integration reduces the amount of power spent on driving long interconnect to deliver an overall lower power solution.
Smaller Form Factor
By integrating discrete components in a single package, overall solution size can be decreased significantly including less board area used for routing.
Learn More About Heterogeneous 3D SiP Integration
Download this white paper to learn more about how Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGAs and SoC FPGAs leverage heterogeneous 3D SiP integration to deliver performance, power, and form factor breakthroughs while providing greater scalability and flexibility. In addition, learn how Intel EMIB technology delivers a superior solution for multi-die integration.
Intel EMIB Packaging Technology for Intel® Stratix® 10 Devices
Intel’s patented Embedded Multi-Die Interconnect Bridge (EMIB) technology enables effective in-package integration of system-critical components, such as analog, memory, ASICs, CPU, and so on. EMIB technology offers a simpler manufacturing flow, compared to other in-package integration technologies. Additionally, EMIB eliminates the need to use through silicon vias (TSV) and specialized interposer silicon enabling a solution that offers higher performance, less complexity, and superior signal and power integrity. EMIB uses a small silicon chip embedded in the substrate to provide ultra-high density interconnect between die. Standard Flip Chip assembly connects power and user signals from the chip to package balls. This approach minimizes interference from core switching noise and crosstalk to deliver superior signal and power integrity.
For details on the specific implementation of this technology on the upcoming Intel® Stratix® 10 device family, see the Transceivers section.
Transceivers
Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGAs and SoC FPGAs deliver a new era of transceiver technology with the introduction of innovative heterogeneous 3D system-in-package (SiP) transceivers. Transceiver tiles are combined with a monolithic programmable core fabric using system-in-package integration to address ever-increasing system bandwidth demands across virtually all market segments. Transceiver tiles enable the highest transceiver channel count FPGA without sacrificing ease-of-use.

Features |
Transceiver Tile Variants |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
L-Tile (17.4G) PCIe* Gen3x16 |
H-Tile (28.3G) PCIe* Gen3x16 |
E-Tile (30G/58G) 4x100GE |
P-Tile (16G) or |
|
| Intel® Stratix® 10 Device Variants | GX, SX | GX, SX, TX, MX | TX, MX | DX |
| Maximum Transceivers per Tile* | 24 | 24 | 24 | 20 |
| Maximum Chip-to-Chip Data Rates(NRZ/PAM4) | 17.4 Gbps/- | 28.3 Gbps/- | 28.9 Gbps/57.8 Gbps | 16 GT/s/- |
| Maximum Backplane Data Rates(NRZ/PAM4) | 12.5 Gbps/- | 28.3 Gbps/- | 28.9 Gbps/57.8 Gbps | 16 GT/s/- |
| Insertion Loss at Maximum Data Rate | Up to 18 dB | Up to 30 dB | Up to 35 dB | Refer to PCIe* Gen4 and UPI specs and conditions |
| Hard IP | PCIe* Gen1, 2, and 3 with x1, x4, x8, and x16 lane support 10G Fire Code FEC Hard IP |
PCIe* Gen1, 2, and 3 with x1, x4, x8, and x16 lanes SR-IOV with 4 Physical functions and 2K Virtual functions 10G Fire Code FEC Hard IP |
10/25/100 GbE MAC with RS-FEC and KP-FEC | Intel® Ultra Path Interconnect (Intel® UPI) PCIe* Gen1, 2, 3, and 4 with x1, x4, x8, and x16 lanes SR-IOV with 8 Physical functions 2048 Virtual functions Port bifurcation support for 2x8 Endpoint or 4x4 rootport Transaction Layer (TL) bypass features Configuration via Protocol (CvP) Initialization Autonomous mode VirtIO Scalable IOV Shared virtual memory |
| *Please refer to Intel® Stratix® 10 device Product Tables for exact number of transceivers available in a device & package combination. | ||||
Heterogeneous 3D SiP Advantages
Unprecedented Performance
- Intel® Stratix® 10 GX and SX devices support data rates up to 28.3 Gbps, enabling mainstream protocols.
- Intel® Stratix® 10 TX and MX devices support data rates up to 57.8 Gbps PAM4, enabling mainstream and future protocols including PAM4 support.
- Intel® Stratix® 10 DX devices support PCIe* data rates up to 16 GT/s per lane and UPI data rates up to 11.2 GT/s, enabling mainstream and coherent connection to future select Intel® Xeon® Scalable processor.
Highest Transceiver Count Family
- Up to 144 full duplex channels.
- Up to 6 Instances of PCI Express* (PCIe*) Gen3 with x16 hard IP.
- Up to 4 instances of PCI Express* (PCIe*) Gen4 with x16 hard IP (P-Tile).
- Up to 3 instances of Intel® Ultra Path Interconnect (Intel® UPI) hard IP.
- Hard IP support: 100GE MAC and PHY, RS-FEC.
Flexibility and Scalability
- Four different transceiver tiles capable of addressing the need of current and future protocol requirements.
- Dual-mode mode transceivers allow the switching between PAM4 and NRZ modulation schemes.
- Up to 16 GB of in package HBM2 DRAM memory at 512 Gbps.
Ease of Use
- Adaptive continuous time-linear equalization (CTLE) and adaptive decision feedback equalization (DFE) addresses the need of long reach applications.
- Precision Signal Integrity Calibration Engine (PreSICE).
- Both physical coding sublayer (PCS) and physical medium attachment (PMA) with dynamic reconfiguration capabilities.
Interconnect to CPUs, ASICs, and ASSPs
Targeting high-performance acceleration applications, increasingly used in Data Center, Networking, Cloud Computing, and Test & Measurement markets, Intel® Stratix® 10 DX FPGAs feature hard, and soft intellectual property blocks supporting both UPI and PCIe* Gen4 interfaces.
A low latency, high performance coherent interface is achieved when connecting the FPGA to selected Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors via Intel® Ultra Path Interconnect (Intel® UPI), while the non-coherent interface takes advantage of any PCI Express* (PCIe*) Gen4 capable device.
Detailed features of Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGAs and SoCs interconnect solution:
- Hard Intel UPI intellectual property blocks in Intel® Stratix® 10 devices, supporting Cache Agent, and Home Agent soft IP.
- Hard PCI Express Gen4 x16 intellectual property blocks, with features such as Endpoint and Root Port bifurcation modes, virtualization support for Single-Root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV), Virtual I/O device (VIRTIO), Intel® Scalable I/O Virtualization (Intel® Scalable IOV), and Transaction Layer bypass mode.
External Memory Interfaces
Intel® Stratix® 10 devices provide memory interface support, including serial and parallel interfaces.
Parallel Memory Interfaces
Intel® Stratix® 10 devices offer parallel memory support up to 2,666 Mbps for DDR4 SDRAM and supports a wide range of other protocols shown below.
- Hard memory controller delivers high-performance at low power including support for:
- DDR4.
- DDR3 / DDR3L.
- LPDDR3.
- Soft controller support delivers flexibility to support a wide range of memory interface standards including:
- RLDRAM 3.
- QDR II+ / QDR II + Xtreme / QDR IV.
- Select Intel® Optane™ DC persistent memory.
Secure Device Manager
The Intel® Stratix® 10 device family introduces a new Secure Device Manager (SDM) available in all densities and device family variants. Serving as the central command center for the entire FPGA, the Secure Device Manager controls key operations, such as configuration, device security, single event upset (SEU) responses, and power management. The Secure Device Manager creates a unified, secure management system for the entire device, including the FPGA fabric, hard processor system (HPS) in SoCs, embedded hard IP blocks, and I/O blocks.

Key Services Provided by the SDM
Configuration
- Manages device startup in user mode.
- Supports loading user configuration data.
- Configuration bitstream decompression.
Security
- Bitstream authentication and authorization.
- Bitstream decryption.
- Secure bitstream key provisioning and storage.
- Tamper monitoring.
Single-Event Upset (SEU)
- SEU detection and correction.
Power Management
- Manages Smart Voltage ID operations.
- Monitors critical power supplies.
Secure Device Manager Key Benefits
User-Configurable Boot Process
With a dedicated processor managing configuration, Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGA users can control the configuration order of the core logic in the FPGA or SoC. You can also select whether the FPGA design or the processor application boots up first, and whether the first system manages the configuration control of the second. The Secure Device Manager allows greater flexibility and user-selected configuration control compared to previous-generation FPGAs and SoCs.
User-Scripted Response to SEU and Tamper Detection
You can control the FPGA or SoC responses to SEU and tamper detection, using a dedicated processor in the Secure Device Manager. Intel® Stratix® 10 devices also support user-scripted device erasure, where reactive data zeroization serves a security response.
Physically Unclonable Function for Key Protection
Intel® Stratix® 10 devices implement a Physically Unclonable Function (PUF) that provides industry leading security for bitstream encryption key protection.
Anti-Tamper Protection
Intel® Stratix® 10 devices include on-chip temperature sensors and device voltage rail monitors to detect tamper attacks on the FPGA or SoC. Additionally, the secure processor in the Secure Device Manager lets you update the configuration process. You can deploy a different configuration order or updated encryption processes in the field if a particular configuration process is found to be ineffective against the threat profile.
Advanced Key Management Schemes
Intel® Stratix® 10 devices support a complex asymmetric key authentication and authorization scheme. You can use multiple keys to authenticate a bitstream section, and you may use different keys to authenticate different bitstreams or bitstream sections. You can control the permissions of an authorized signing key, as well as revoke and replace signing keys.
Intel® Stratix® 10 devices implement an advanced bitstream encryption scheme that minimizes the amount of data encrypted by any single key. You may choose to encrypt bitstream sections with different keys or enable a key update mode that automatically rolls encryption keys within each bitstream section.
Advanced Device Management
The user and command authentication capabilities of the Secure Device Manager also enable a whole class of new secure device maintenance functions for the Intel® Stratix® 10 device family. These functions include:
- Secure remote update (authenticated).
- Secure return material authorization (RMA) of devices without revealing user keys.
- Secure debug of designs and ARM* processor code.
- Secure key management.
Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
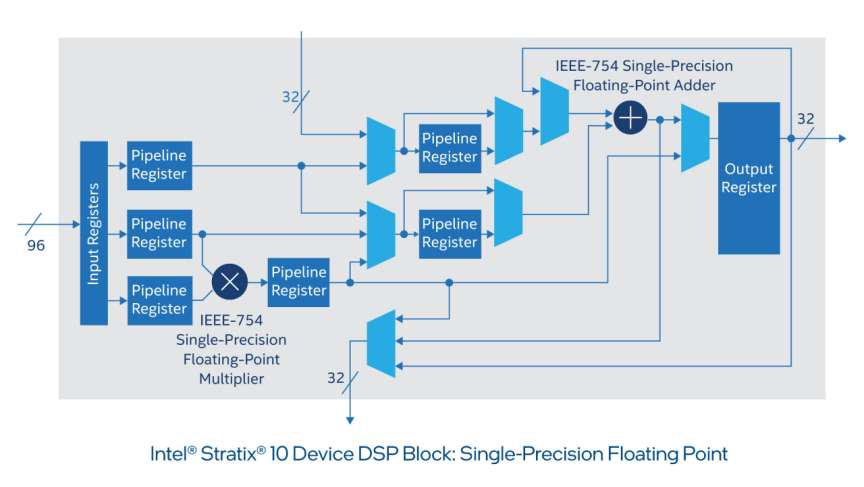
With Intel® Stratix® 10 devices, digital signal processing (DSP) designs can achieve up to 10 tera floating-point operations per second (TFLOPS) of IEEE 754 single-precision floating-point operations. This unprecedented degree of computational throughput is made possible by a hardened floating-point operator within each DSP block. It is initially introduced in the Intel® Arria® 10 device family and now extended to deliver an order of magnitude greater throughput in Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGAs and SoCs.
Intel® Stratix® 10 Device DSP Block
Unprecedented Performance
Intel® Stratix® 10 devices deliver up to 23 TMACs of fixed-point performance and up to 10 TFLOPS of IEEE-754 single-precision floating-point performance.
Breakthrough Performance per Watt Efficiency
In addition to high performance, Intel® Stratix® 10 devices can achieve power efficiency of up to 80 GFLOPS/Watt. This level of floating-point power efficiency is a significant innovation for the floating-point processing industry delivering performance at a fraction of the power of alternative computing elements.
Optimized and Integrated Design Entry
Designing with floating-point operations is achievable via a number of designs flows including:
- Intel® FPGA IP cores.
- DSP Builder for Intel® FPGAs model-based design flow.
- OpenCL* C-based design flow.
- HDL templates in Verilog HDL and VHDL.
AI Tensor Block
Using Intel® Stratix® 10 NX FPGA, AI acceleration designs can achieve up to 143 INT8/Block Floating Point 16 (Block FP16) TOPS/TFLOPS at ~1 TOPS/W or 286 INT4/Block Floating Point 12 (Block FP12) TOPS/TFLOPS at ~2 TOPS/W3. This computational throughput is made possible by a new type of AI-optimized computation block called the AI Tensor Block. The AI Tensor Block’s architecture contains three dot-product units, each of which has ten multipliers and ten accumulators, for a total of 30 multipliers and 30 accumulators within each block. The AI Tensor Block’s architecture is tuned for common matrix-matrix or vector-matrix multiplications used in a wide range of AI computations, with capabilities designed to work efficiently for both small and large matrix sizes.
Intel® Stratix® 10 NX FPGA AI Tensor Block
The AI Tensor Block multipliers have base precisions of INT8 and INT4 and support Block Floating Point 16 (Block FP16) and Block Floating Point 12 (Block FP12) numerical formats through shared-exponent support hardware. All additions or accumulations can be performed with INT32 or IEEE754 single-precision floating point (FP32) precision and multiple AI Tensor Blocks can be cascaded together to support larger matrices.
SEU Mitigation
Single-event upsets (SEUs) are rare, unintended changes in the state of internal memory elements caused by radiation effects. The change in state results in a soft error and there is no permanent damage to the device.
Intel® Stratix® 10 devices have intrinsically low upset rates as a result of the high SEU immunity provided by Intel's 14 nm tri-gate process. Additionally, Intel provides fine-grained capability for determining where an upset occurred in your design so you can design your system to have the appropriate response.
Intel® Stratix® 10 FPGAs and SoCs ensure high reliability and provides SEU mitigation capabilities.
- Advanced SEU Detection (ASD).
- Sensitivity processing.
- Hierarchy tagging.
- Fault injection.
- Use to characterize and improve your designs.
Hard Processor System
Building on Intel’s leadership in SoCs, Intel® Stratix® 10 SoCs include a next-generation hard processor system (HPS) to deliver the industry’s highest performance and most power-efficient SoCs. At the heart of the HPS is a highly efficient quad-core ARM* Cortex*-A53 processor cluster. This processor is optimized for ultra-high performance per watt, which reduces power consumption up to 50% over previous-generation SoC FPGAs. Additionally, the HPS includes a System Memory Management Unit, Cache Coherency Unit, a hard memory controller, and a rich feature set of embedded peripherals.
Intel® Stratix® 10 SoC Development Tools
The Intel® SoC FPGA Embedded Development Suite (SoC EDS) featuring ARM* Development Studio* 5 (DS- 5*) supports Intel® Stratix® 10 SoCs, providing heterogeneous debug, profiling, and whole-chip visualization. The SoC EDS unifies all software debugging information from the CPU and FPGA domains and presents them in an organized fashion within the standard DS-5 user interface. The toolkit gives users an unprecedented level of debugging visibility and control that delivers substantial productivity gains.
To learn more, visit the Intel® Stratix® 10 SoC page.
Additional Resources
Explore more content related to Altera® FPGA devices such as development boards, intellectual property, support and more.

Support Resources
Resource center for training, documentation, downloads, tools and support options.

Development Boards
Get started with our FPGA and accelerate your time-to-market with Altera-validated hardware and designs.

Intellectual Property
Shorten your design cycle with a broad portfolio of Altera-validated IP cores and reference designs.

FPGA Design Software
Explore Quartus Prime Software and our suite of productivity-enhancing tools to help you rapidly complete your hardware and software designs.

Contact Sales
Get in touch with sales for your Altera® FPGA product design and acceleration needs.

Where to Buy
Contact an Altera® Authorized Distributor today.
Product and Performance Information
Comparison based on Stratix® V vs. Intel® Stratix® 10 using Intel® Quartus® Prime Pro 16.1 Early Beta. Stratix® V Designs were optimized using 3 step optimization process of Hyper-Retiming, Hyper-Pipelining, and Hyper-Optimization in order to utilize Intel® Stratix® 10 architecture enhancements of distributed registers in core fabric. Designs were analyzed using Intel® Quartus® Prime Pro Fast Forward Compile performance exploration tool. For more details, refer to Intel® Hyperflex™ FPGA Architecture Overview White Paper: https://www.intel.com/content/dam/www/programmable/us/en/pdfs/literature/wp/wp-01220-hyperflex-architecture-fpga-socs.pdf. Actual performance users will achieve varies based on level of design optimization applied. Tests measure performance of components on a particular test, in specific systems. Differences in hardware, software, or configuration will affect actual performance. Consult other sources of information to evaluate performance as you consider your purchase. For more complete information about performance and benchmark results, visit www.intel.com/benchmarks.
Tests measure performance of components on a particular test, in specific systems. Differences in hardware, software, or configuration will affect actual performance. Consult other sources of information to evaluate performance as you consider your purchase. For more complete information about performance and benchmark results, visit www.intel.com/benchmarks.
Based on internal Intel estimates.
Tests measure performance of components on a particular test, in specific systems. Differences in hardware, software, or configuration will affect actual performance. Consult other sources of information to evaluate performance as you consider your purchase. For more complete information about performance and benchmark results, visit www.intel.com/benchmarks.
Intel® technologies may require enabled hardware, software or service activation.
No product or component can be absolutely secure.
Results have been estimated or simulated. Your costs and results may vary.
© Intel Corporation. Intel, the Intel logo, and other Intel marks are trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries. Other names and brands may be claimed as the property of others.