Visible to Intel only — GUID: pdo1638456111011
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: pdo1638456111011
Ixiasoft
4.5.1.1.2. Software Design Flow
Use the following steps to create the software project directory tree:
- In your design project folder, create a folder called software.
- In the software folder, create two folders called app and bsp.
Figure 22. Software Project Directory Tree
Creating the BSP Project Application
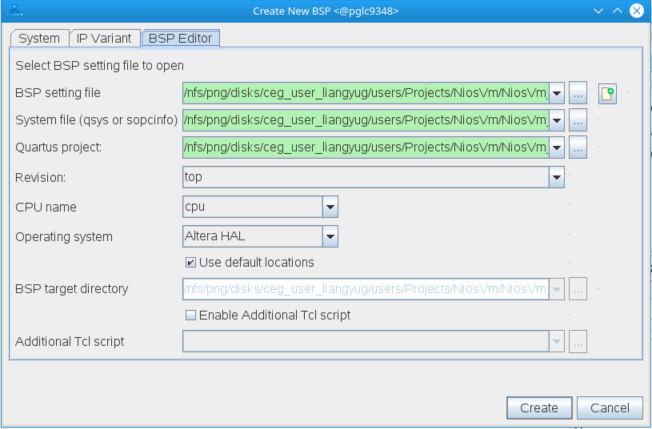
To launch the BSP Editor, perform the following steps:
- In the Platform Designer window, select File > New BSP. The Create New BSP windows appears.
- For BSP setting file, navigate to the software/bsp folder and name the BSP as settings.bsp.
BSP path: <project directory>/software/bsp/settings.bsp
- For System file (qsys or sopcinfo), select the Nios V/m processor Platform Designer system (*.qsys).
- For Quartus project, select the Quartus Project File.
- For Revision, select the correct revision.
- For CPU name, select the Nios V/m processor.
- Select the Operating system as Altera HAL.
- Click Create to create the BSP file.
Configuring BSP Editor and Generating the BSP Project
- In the BSP Editor, click BSP Linker Script.
- In the Linker Section Name perform the following settings:
- Set .text to the QSPI flash in the Linker Region Name.
- Set .exceptions to OCRAM/ External RAM or QSPI Flash according to your design preference.
- Set the rest of the items to the OCRAM or external RAM.
Figure 24. Linker Region Settings When Exceptions is set to OCRAM/ External RAMFigure 25. Linker Region Settings When Exceptions is set to QSPI Flash - Go to Main > Settings > Advanced > hal.linker.
- If exception is set to OCRAM or External RAM, enable the following:
- allow_code_at_reset
- enable_alt_load
- enable_alt_load_copy_rodata
- enable_alt_load_copy_rwdata
- enable_alt_load_copy_exceptions
Figure 26. hal.linker Settings for Exception Agent OCRAM or External RAM - If exception is set to QSPI flash, enable the following:
- allow_code_at_reset
- enable_alt_load
- enable_alt_load_copy_rodata
- enable_alt_load_copy_rwdata
Figure 27. hal.linker Settings for QSPI Flash - Click Generate BSP. Make sure the BSP generation is successful.
- Close the BSP Editor.
Generating the Application Project File
- Navigate to the software/app folder and create your Nios® V application source code.
- Launch the Nios V Command Shell.
- Execute the command below to generate the application CMakeLists.txt.
niosv-app --app-dir=software/app --bsp-dir=software/bsp \
--srcs=software/app/<Nios V application source code>Building the Application Project
You can choose to build the application project using the RiscFree* IDE for Intel FPGAs, Eclipse Embedded CDT or through the command line interface (CLI).
If you prefer using CLI, you can build the application using the following command:
cmake -G "Unix Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug -B \
software/app/debug -S software/app make -C software/app/debugThe application (.elf) file is created in software/app/debug folder.
Generating HEX File
You must generate a .hex file from your application .elf file, so you can create a .jic file suitable for programming flash devices.
- Launch the Nios V Command Shell.
- For Nios® V processor application execute-in-place (XIP) from configuration QSPI flash, use the following commands line to convert the ELF to HEX for your application. The commands create the application (.hex) file.
elf2flash --input software/app/debug/<Nios V application>.elf \
--output flash.srec --reset <reset offset + base address of GSFI AVL MEM> \
--base <base address of GSFI AVL MEM> \
--end <end address of GSFI AVL MEM>riscv32-unknown-elf-objcopy --input-target srec --output-target ihex \
flash.srec <Nios V application>.hex