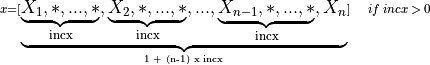Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-6DB7BC27-706B-4C9E-B17E-30EBFC9ED848
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-6DB7BC27-706B-4C9E-B17E-30EBFC9ED848
Matrix Storage
The oneMKL BLAS and LAPACK routines for DPC++ use several matrix and vector storage formats. These are the same formats used in traditional Fortran BLAS/LAPACK.
General Matrix
A general matrix A of m rows and n columns with leading dimension lda is represented as a one dimensional array a of size of at least lda * n if column major layout is used and at least lda*m if row major layout is used. Before entry in any BLAS function using a general matrix, the leading m by n part of the array a must contain the matrix A. For column (respectively, row) major layout, the elements of each column (respectively, row) are contiguous in memory while the elements of each row (respectively, column) are at distance lda from the same elements in the previous row (respectively, column).
Visually, the matrix

is stored in memory as an array
For column major layout

For row major layout
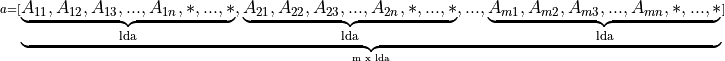
Triangular Matrix
A triangular matrix A of n rows and n columns with leading dimension lda is represented as a one dimensional array a, of a size of at least lda * n. When column (respectively, row) major layout is used, the elements of each column (respectively, row) are contiguous in memory while the elements of each row (respectively, column) are at distance lda from the same elements in the previous row (respectively, column).
Before entry in any BLAS function using a triangular matrix,
If upper_lower = uplo::upper, the leading n by n upper triangular part of the array a must contain the upper triangular part of the matrix A. The strictly lower triangular part of the array a is not referenced. In other words, the matrix

is stored in memory as the array
For column major layout
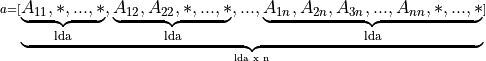
For row major layout
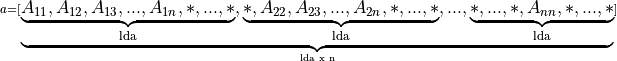
If upper_lower = uplo::lower, the leading n by n lower triangular part of the array a must contain the lower triangular part of the matrix A. The strictly upper triangular part of the array a is not referenced. That is, the matrix

is stored in memory as the array
For column major layout

For row major layout
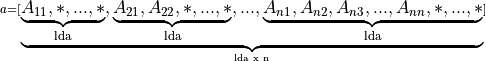
Band Matrix
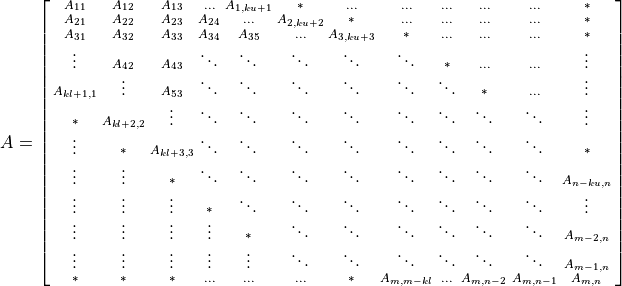
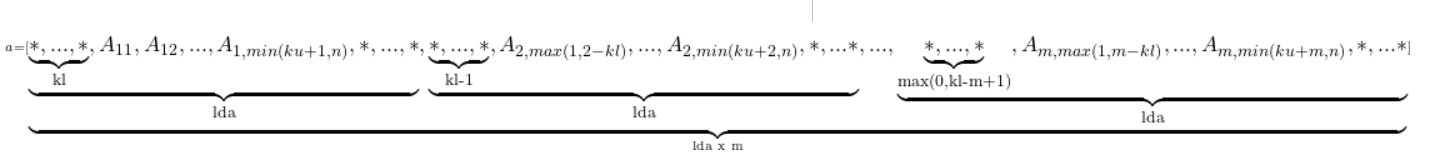
A general band matrix A of m rows and n columns with kl sub-diagonals, ku super-diagonals and leading dimension lda is represented as a one dimensional array a of size at least lda * n (respectively, lda * m) if column (respectively, row) major layout is used.
Before entry in any BLAS function using a general band matrix, the leading (kl + ku + 1) by n (respectively, m) part of the array a must contain the matrix A. This matrix must be supplied column-by-column (respectively, row-by-row), with the main diagonal of the matrix in row ku (respectively, column kl) of the array (0-based indexing), the first super-diagonal starting at position 1 (respectively, 0) in row (ku – 1) (respectively, column (kl + 1)), the first sub-diagonal starting at position 0 (respectively, 1) in row (ku + 1) (respectively, column (kl – 1)), and so on. Elements in the array a that do not correspond to elements in the band matrix (such as the top left ku-by-ku triangle) are not referenced.
Visually, the matrix A
is stored in memory as an array
For column major layout
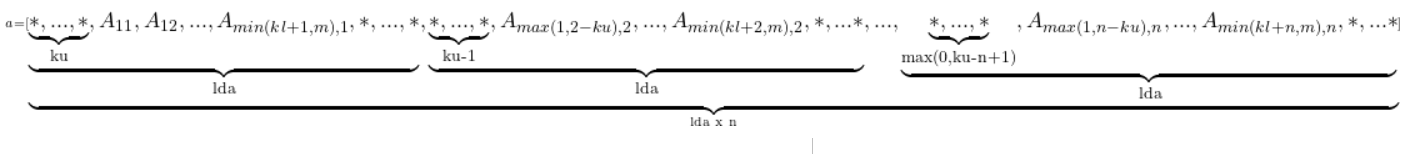
For row major layout
The following program segment transfers a band matrix from conventional full matrix storage (variable matrix, with leading dimension ldm) to band storage (variable a, with leading dimension lda):
Using column major layout
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { k = ku – j; for (i = max(0, j – ku); i < min(m, j + kl + 1); i++) { a[(k + i) + j * lda] = matrix[i + j * ldm]; } }Using row major layout
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) { k = kl – i; for (j = max(0, i – kl); j < min(n, i + ku + 1); j++) { a[(k + j) + i * lda] = matrix[j + i * ldm]; } }
Triangular Band Matrix
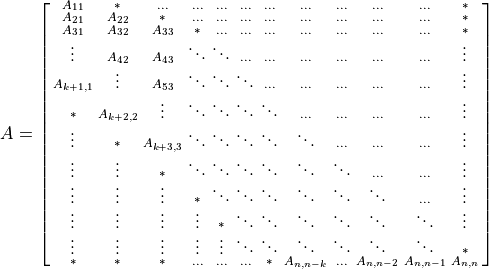
A triangular band matrix A of n rows and n columns with k sub/super-diagonals and leading dimension lda is represented as a one dimensional array a of size at least lda * n.
Before entry in any BLAS function using a triangular band matrix,
If upper_lower = uplo::upper, the leading (k + 1) by n part of the array a must contain the upper triangular band part of the matrix A. When using column major layout, this matrix must be supplied column-by-column (respectively, row-by-row) with the main diagonal of the matrix in row (k) (respectively, column 0) of the array, the first super-diagonal starting at position 1 (respectively, 0) in row (k - 1) (respectively, column 1), and so on. Elements in the array a that do not correspond to elements in the triangular band matrix (such as the bottom left k by k triangle) are not referenced.
Visually, the matrix

is stored as an array
For column major layout
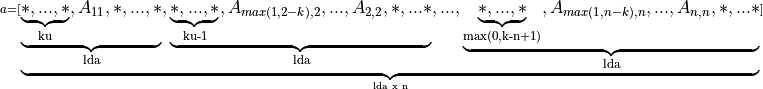
For row major layout
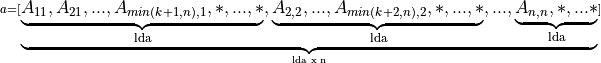
The following program segment transfers a band matrix from conventional full matrix storage (variable matrix, with leading dimension ldm) to band storage (variable a, with leading dimension lda):
Using column major layout
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { m = k – j; for (i = max(0, j – k); i <= j; i++) { a[(m + i) + j * lda] = matrix[i + j * ldm]; } }Using row major layout
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { m = –i; for (j = i; j < min(n, i + k + 1); j++) { a[(m + j) + i * lda] = matrix[j + i * ldm]; } }If upper_lower = uplo::lower, the leading (k + 1) by n part of the array a must contain the upper triangular band part of the matrix A. This matrix must be supplied column-by-column with the main diagonal of the matrix in row 0 of the array, the first sub-diagonal starting at position 0 in row 1, and so on. Elements in the array a that do not correspond to elements in the triangular band matrix (such as the bottom right k by k triangle) are not referenced.
That is, the matrix
is stored as the array
For column major layout
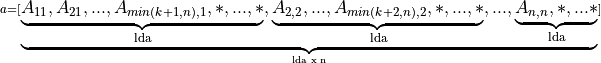
For row major layout
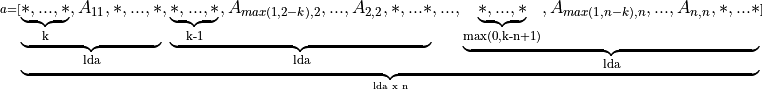
The following program segment transfers a band matrix from conventional full matrix storage (variable matrix, with leading dimension ldm) to band storage (variable a, with leading dimension lda):
Using column major layout
for (j = 0; j < n; j++) { m = –j; for (i = j; i < min(n, j + k + 1); i++) { a[(m + i) + j * lda] = matrix[i + j * ldm]; } }Using row major layout
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { m = k – i; for (j = max(0, i – k); j <= i; j++) { a[(m + j) + i * lda] = matrix[j + i * ldm]; } }
Packed Triangular Matrix
A triangular matrix A of n rows and n columns is represented in packed format as a one dimensional array a of size at least (n*(n + 1))/2. All elements in the upper or lower part of the matrix A are stored contiguously in the array a.
Before entry in any BLAS function using a triangular packed matrix,
If upper_lower = uplo::upper, the first (n*(n + 1))/2 elements in the array a must contain the upper triangular part of the matrix A packed sequentially, column by column so that a[0] contains A11, a[1] and a[2] contain A12 and A22 respectively, and so on. Hence, the matrix

is stored as the array
For column major layout

For row major layout
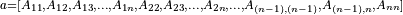
If upper_lower = uplo::lower, if column (respectively, row) major layout is used, the first (n*(n + 1))/2 elements in the array a must contain the lower triangular part of the matrix A packed sequentially, column by column (respectively, row by row) so that a[0] contains A11, a[1] and a[2] contain A21 and A31 respectively, and so on. The matrix

is stored as the array
For column major layout
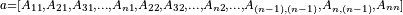
For row major layout
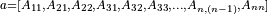
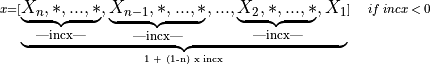
Vector
A vector X of n elements with increment incx is represented as a one dimensional array x of size at least (1 + (n - 1) * abs(incx)).
Visually, the vector
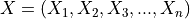
is stored in memory as an array