Visible to Intel only — GUID: nik1410905331095
Ixiasoft
1. Datasheet
2. Getting Started with the Arria® V GZ Hard IP for PCI Express
3. Getting Started with the Configuration Space Bypass Mode Qsys Example Design
4. Parameter Settings
5. Interfaces and Signal Descriptions
6. Registers
7. Interrupts
8. Error Handling
9. PCI Express Protocol Stack
10. Transaction Layer Protocol (TLP) Details
11. Throughput Optimization
12. Design Implementation
13. Additional Features
14. Hard IP Reconfiguration
15. Transceiver PHY IP Reconfiguration
16. Testbench and Design Example
17. Debugging
A. Lane Initialization and Reversal
B. Document Revision History
1.1. Arria® V GZ Avalon-ST Interface for PCIe Datasheet
1.2. Release Information
1.3. Device Family Support
1.4. Configurations
1.5. Avalon-ST Example Designs
1.6. Debug Features
1.7. IP Core Verification
1.8. Resource Utilization
1.9. Recommended Speed Grades
1.10. Creating a Design for PCI Express
2.1.1. Generating the Testbench
2.1.2. Simulating the Example Design
2.1.3. Generating Synthesis Files
2.1.4. Understanding the Files Generated
2.1.5. Understanding Simulation Log File Generation
2.1.6. Understanding Physical Placement of the PCIe IP Core
2.1.7. Compiling the Design in the Qsys Design Flow
2.1.8. Modifying the Example Design
2.1.9. Using the IP Catalog To Generate Your Arria® V GZ Hard IP for PCI Express as a Separate Component
3.3.1. Timing for Configuration Read to Function 0 for the 256-Bit Avalon-ST Interface
3.3.2. Timing for Configuration Write to Function 0 for the 256-Bit Avalon-ST Interface
3.3.3. Timing for Memory Write and Read of Function 1 256-Bit Avalon-ST Interface
3.3.4. Partial Transcript for Configuration Space Bypass Simulation
5.1. Clock Signals
5.2. Reset, Status, and Link Training Signals
5.3. ECRC Forwarding
5.4. Error Signals
5.5. Interrupts for Endpoints
5.6. Interrupts for Root Ports
5.7. Completion Side Band Signals
5.8. Configuration Space Bypass Mode Interface Signals
5.9. Parity Signals
5.10. LMI Signals
5.11. Transaction Layer Configuration Space Signals
5.12. Hard IP Reconfiguration Interface
5.13. Power Management Signals
5.14. Physical Layer Interface Signals
6.1. Correspondence between Configuration Space Registers and the PCIe Specification
6.2. Type 0 Configuration Space Registers
6.3. Type 1 Configuration Space Registers
6.4. PCI Express Capability Structures
6.5. Intel-Defined VSEC Registers
6.6. CvP Registers
6.7. Uncorrectable Internal Error Mask Register
6.8. Uncorrectable Internal Error Status Register
6.9. Correctable Internal Error Mask Register
6.10. Correctable Internal Error Status Register
16.6.1. ebfm_barwr Procedure
16.6.2. ebfm_barwr_imm Procedure
16.6.3. ebfm_barrd_wait Procedure
16.6.4. ebfm_barrd_nowt Procedure
16.6.5. ebfm_cfgwr_imm_wait Procedure
16.6.6. ebfm_cfgwr_imm_nowt Procedure
16.6.7. ebfm_cfgrd_wait Procedure
16.6.8. ebfm_cfgrd_nowt Procedure
16.6.9. BFM Configuration Procedures
16.6.10. BFM Shared Memory Access Procedures
16.6.11. BFM Log and Message Procedures
16.6.12. Verilog HDL Formatting Functions
16.7.1. Changing Between Serial and PIPE Simulation
16.7.2. Using the PIPE Interface for Gen1 and Gen2 Variants
16.7.3. Viewing the Important PIPE Interface Signals
16.7.4. Disabling the Scrambler for Gen1 and Gen2 Simulations
16.7.5. Disabling 8B/10B Encoding and Decoding for Gen1 and Gen2 Simulations
16.7.6. Changing between the Hard and Soft Reset Controller
Visible to Intel only — GUID: nik1410905331095
Ixiasoft
2.1. Qsys Design Flow
Copy the pcie_de_gen1_x8_ast128.qsys design example from the <install_dir>/ip/altera/altera_pcie/altera_pcie/altera_pcie_hip_ast_ed/example_designs/<dev> to your working directory.
The following figure illustrates this Qsys system.
Figure 6. Complete Gen1 ×8 Endpoint (DUT) Connected to Example Design (APPS)
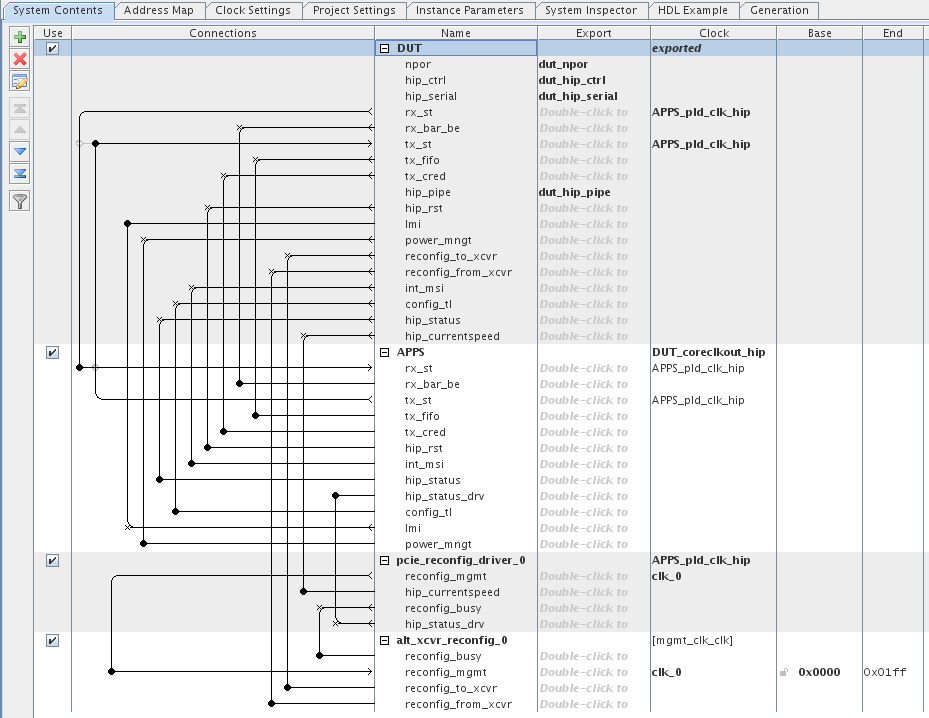

The example design includes the following components:
- DUT—This is Gen1 ×8 Endpoint. For your own design, you can select the data rate, number of lanes, and either Endpoint or Root Port mode.
- APPS—This Root Port BFM configures the DUT and drives read and write TLPs to test DUT functionality. An Endpoint BFM is available if your PCI Express design implements a Root Port.
- pcie_reconfig_driver_0—This Avalon‑MM master drives the Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller. The pcie_reconfig_driver_0 is implemented in clear text that you can modify if your design requires different reconfiguration functions. After you generate your Qsys system, the Verilog HDL for this component is available as: <working_dir>/<variant_name>/testbench/<variant_name>_tb/simulation/submodules/altpcie_reconfig_driver.sv.
- Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller—The Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller dynamically reconfigures analog settings to improve signal quality. For Gen1 and Gen2 data rates, the Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller must perform offset cancellation and PLL calibration. For the Gen3 data rate, the pcie_reconfig_driver_0 performs AEQ through the Transceiver Reconfiguration Controller.
Section Content
Generating the Testbench
Simulating the Example Design
Generating Synthesis Files
Understanding the Files Generated
Understanding Simulation Log File Generation
Understanding Physical Placement of the PCIe IP Core
Compiling the Design in the Qsys Design Flow
Modifying the Example Design
Using the IP Catalog To Generate Your Arria V GZ Hard IP for PCI Express as a Separate Component