Visible to Intel only — GUID: syi1468877626861
Ixiasoft
Visible to Intel only — GUID: syi1468877626861
Ixiasoft
5.1. Example: Overriding a Coalesced Memory Architecture
Using memory attributes in various combinations in your code allows you to override the memory architecture that the Intel® HLS Compiler Standard Edition infers for your component.
The following code examples demonstrate how you can use the following memory attributes to override coalesced memory to conserve memory blocks on your FPGA:
- hls_bankwidth(n)
- hls_numbanks(n)
- hls_singlepump
- hls_numports_readonly_writeonly(m,n)
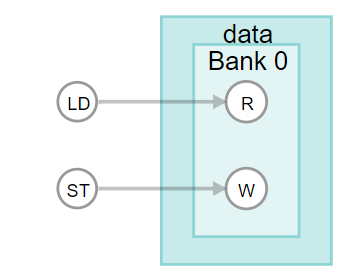
The original code coalesces two memory accesses, resulting in a memory memory system that is to 256 bits wide by 64 bits wide (two on-chip memory blocks):
component unsigned int mem_coalesce_default(unsigned int raddr,
unsigned int waddr,
unsigned int wdata){
unsigned int data[512];
data[2*waddr] = wdata;
data[2*waddr + 1] = wdata + 1;
unsigned int rdata = data[2*raddr] + data[2*raddr + 1];
return rdata;
}The following images show how the 256x64 bit memory for this code sample is structured, as well how the component memory structure is shown in the high-level design report (report.html)
 |
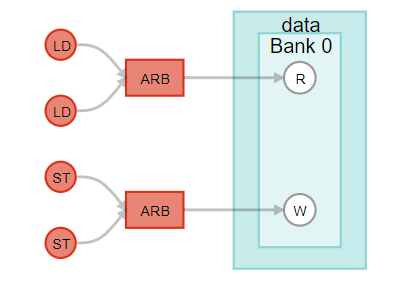
The modified code implements a simple dual-port on-chip memory block that is 512 words deep by 32 bits wide with stallable arbitration:
component unsigned int mem_coalesce_override(unsigned int raddr,
unsigned int waddr,
unsigned int wdata){
//Attributes that stop memory coalescing
hls_bankwidth(4) hls_numbanks(1)
//Attributes that specify a simple dual port
hls_singlepump hls_numports_readonly_writeonly(1,1)
unsigned int data[512];
data[2*waddr] = wdata;
data[2*waddr + 1] = wdata + 1;
unsigned int rdata = data[2*raddr] + data[2*raddr + 1];
return rdata;
} The following images show how the 512x32 bit memory with stallable arbitration for this code sample is structured, as well how the component memory structure is shown in the high-level design report (report.html).
 |
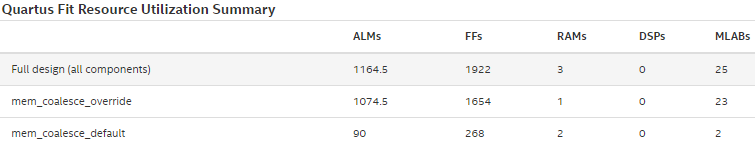
While it might appear that you save hardware area by reducing the number of RAM blocks needed for the component, the introduction of stallable arbitration increases the amount of hardware needed to implement the component. In the following table, you can compare the number ALMs and FFs required by the components.