Intel® oneAPI Threading Building Blocks Developer Guide and API Reference
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-48A69CDD-D1A8-4F77-A679-EFF8E46D3105
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-48A69CDD-D1A8-4F77-A679-EFF8E46D3105
Wavefront
Problem
Perform computations on items in a data set, where the computation on an item uses results from computations on predecessor items.
Context
The dependences between computations form an acyclic graph.
Forces
Dependence constraints between items form an acyclic graph.
The number of immediate predecessors in the graph is known in advance, or can be determined some time before the last predecessor completes.
Solution
The solution is a parallel variant of topological sorting, using oneapi::tbb::parallel_for_each to process items. Associate an atomic counter with each item. Initialize each counter to the number of predecessors. Invoke oneapi::tbb::parallel_for_each to process the items that have no predessors (have counts of zero). After an item is processed, decrement the counters of its successors. If a successor’s counter reaches zero, add that successor to the oneapi::tbb::parallel_for_each via a “feeder”.
If the number of predecessors for an item cannot be determined in advance, treat the information “know number of predecessors” as an additional predecessor. When the number of predecessors becomes known, treat this conceptual predecessor as completed.
If the overhead of counting individual items is excessive, aggregate items into blocks, and do the wavefront over the blocks.
Example
Below is a serial kernel for the longest common subsequence algorithm. The parameters are strings x and y with respective lengths xlen and ylen.
int F[MAX_LEN+1][MAX_LEN+1];
void SerialLCS( const char* x, size_t xlen, const char* y, size_t ylen )
{
for( size_t i=1; i<=xlen; ++i )
for( size_t j=1; j<=ylen; ++j )
F[i][j] = x[i-1]==y[j-1] ? F[i-1][j-1]+1:
max(F[i][j-1],F[i-1][j]);
}
The kernel sets F[i][j] to the length of the longest common subsequence shared by x[0..i-1] and y[0..j-1]. It assumes that F[0][0..ylen] and F[0..xlen][0] have already been initialized to zero.
The following figure shows the data dependences for calculating F[i][j].
Data dependences for longest common substring calculation. 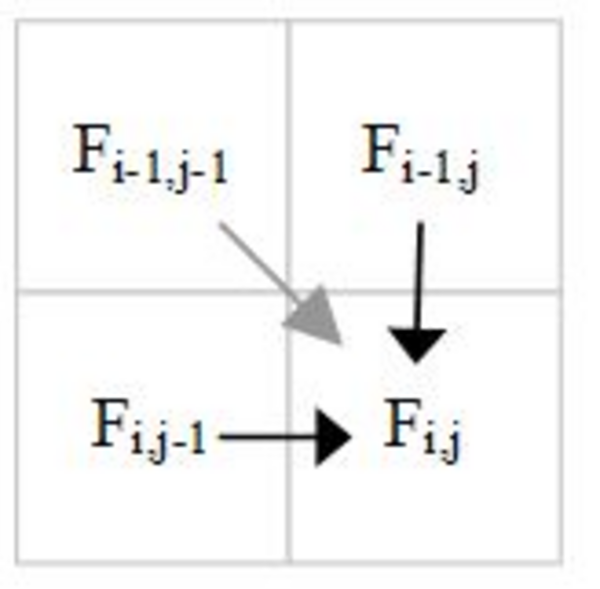
The following figure shows the gray diagonal dependence is the transitive closure of other dependencies. Thus for parallelization purposes it is a redundant dependence that can be ignored.
Diagonal dependence is redundant. 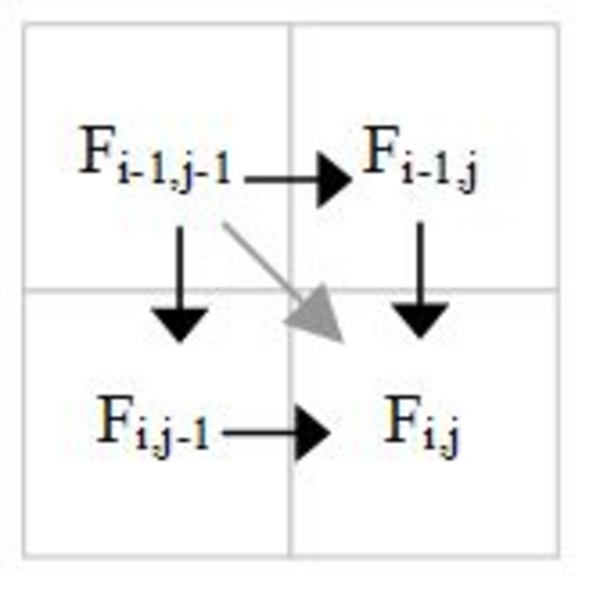
It is generally good to remove redundant dependences from consideration, because the atomic counting incurs a cost for each dependence considered.
Another consideration is grain size. Scheduling each F[i][j] element calculation separately is prohibitively expensive. A good solution is to aggregate the elements into contiguous blocks, and process the contents of a block serially. The blocks have the same dependence pattern, but at a block scale. Hence scheduling overheads can be amortized over blocks.
The parallel code follows. Each block consists of N×N elements. Each block has an associated atomic counter. Array Count organizes these counters for easy lookup. The code initializes the counters and then rolls a wavefront using parallel_for_each, starting with the block at the origin since it has no predecessors.
const int N = 64;
std::atomic<char> Count[MAX_LEN/N+1][MAX_LEN/N+1];
void ParallelLCS( const char* x, size_t xlen, const char* y, size_t ylen ) {
// Initialize predecessor counts for blocks.
size_t m = (xlen+N-1)/N;
size_t n = (ylen+N-1)/N;
for( int i=0; i<m; ++i )
for( int j=0; j<n; ++j )
Count[i][j] = (i>0)+(j>0);
// Roll the wavefront from the origin.
typedef pair<size_t,size_t> block;
block origin(0,0);
oneapi::tbb::parallel_for_each( &origin, &origin+1,
[=]( const block& b, oneapi::tbb::feeder<block>&feeder ) {
// Extract bounds on block
size_t bi = b.first;
size_t bj = b.second;
size_t xl = N*bi+1;
size_t xu = min(xl+N,xlen+1);
size_t yl = N*bj+1;
size_t yu = min(yl+N,ylen+1);
// Process the block
for( size_t i=xl; i<xu; ++i )
for( size_t j=yl; j<yu; ++j )
F[i][j] = x[i-1]==y[j-1] ? F[i-1][j-1]+1:
max(F[i][j-1],F[i-1][j]);
// Account for successors
if( bj+1<n && --Count[bi][bj+1]==0 )
feeder.add( block(bi,bj+1) );
if( bi+1<m && --Count[bi+1][bj]==0 )
feeder.add( block(bi+1,bj) ); }
);
}
References
Eun-Gyu Kim and Mark Snir, “Wavefront Pattern”, http://snir.cs.illinois.edu/patterns/wavefront.pdf