Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-C3844A30-9286-4AAB-87A8-F4BBF5A4CE6D
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-C3844A30-9286-4AAB-87A8-F4BBF5A4CE6D
Lazy Initialization
Problem
Delay the creation of an object, potentially expensive, until it is accessed. In parallel programming, initialization must also be guarded against race conditions.
Context
The cost of operations that take place during the initialization of the object may be considerably high. In that case, the object should be initialized only when needed. Lazy initialization is the common tactic that allows implementing such an approach.
Solution
Using oneapi::tbb::collaborative_call_once with oneapi::tbb::collaborative_once_flag helps to implement thread-safe lazy initialization for a user object.
In addition, collaborative_call_once allows other thread blocked on the same collaborative_once_flag to join other oneTBB parallel constructions called within the initializing function.
Example
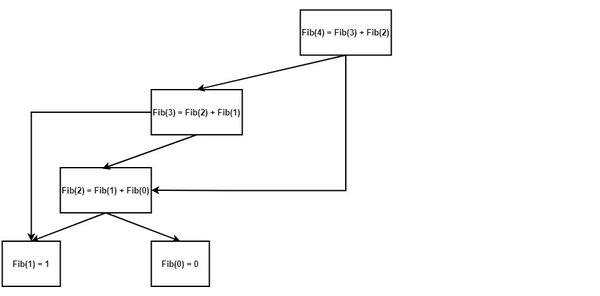
This example illustrates the implementation of lazy initialization for the calculation of the Fibonacci numbers. Here is a graphical representation of the Fibonacci recursion tree for N=4.

As seen in the diagram, some elements are recalculated more than once. These operations are redundant, so the “lazy initialized” Fibonacci numbers are relevant here.
An implementation without the use of lazy initialization would have O(2^N) time complexity due to the full recursion tree traversal and recalculation of values. Since all the nodes are traversed once, the tree becomes a list, making the time complexity O(N).
Here you can see the code for the implementation. Already calculated values are stored in a buffer paired with collaborative_once_flag and will not be recalculated when collaborative_call_once is invoked when initialization has already been done.
using FibBuffer = std::vector<std::pair<oneapi::tbb::collaborative_once_flag, std::uint64_t>>;
std::uint64_t LazyFibHelper(int n, FibBuffer& buffer) {
// Base case
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
// Calculate nth value only once and store it in the buffer.
// Other threads won't be blocked on already taken collaborative_once_flag
// but join parallelism inside functor
oneapi::tbb::collaborative_call_once(buffer[n].first, [&]() {
std::uint64_t a, b;
oneapi::tbb::parallel_invoke([&] { a = LazyFibHelper(n - 2, buffer); },
[&] { b = LazyFibHelper(n - 1, buffer); });
buffer[n].second = a + b;
});
return buffer[n].second;
}
std::uint64_t Fib(int n) {
FibBuffer buffer(n+1);
return LazyFibHelper(n, buffer);
}