Updating an Application-Over-The-Air
Application-Over-The-Air (AOTA) update enables cloud to edge manageability of application services running on the EII-enabled systems through the Device Manageability component. Device Manageability facilitates software updates and deployment from cloud to device which includes SOTA, FOTA, AOTA, and few system operations.
For EII use case, only AOTA features from Device Manageability are validated and will be supported through Azure*, ThingsBoard* and Telit* cloud-based management front-end services. Depending on your preference you can select either one of these options.
The following section will walk you through - setting up Azure*, ThingsBoard*, and Telit*. - creating and establishing connectivity with the target systems, as well as updating applications on those systems.
Refer to the user guide in docs for more detailed reference.
Device Manageability was previously named Turtle Creek. Remnants of the previous name still exist in some components. The name replacement is ongoing and will be completed in future releases.
Installation - Device Manageability
Prerequisites
Ubuntu 18.04
Install the latest docker cli/docker daemon. Refer to the Install using the repository section and the Install Docker Engine section at https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/ubuntu/#install-docker-ce.
Also, to run docker without sudo refer to the Manage Docker as a non-root user section at https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/linux-postinstall/
Complete the following steps only if the node or system on which the docker setup is tried out is running behind a HTTP proxy server. Skip this stp if that’s not the case.
Configure proxy settings for docker client to connect to internet and for containers to access internet. For more information, see: https://docs.docker.com/network/proxy/.
Configure proxy settings for docker daemon. For more information, see https://docs.docker.com/config/daemon/systemd/#httphttps-proxy.
Install the docker-compose tool. For more information, see https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/#install-compose
All Device Manageability devices can be controlled using a cloud service application. To install Device Manageability complete the following:
Install the Device Manageability agent on the machine.
Run the following commands to install from the manageability folder:
sudo chmod +755 install-tc.sh sudo ./install-tc.sh
NOTE:Before installing the newer version check if the system has an old version of Device Manageability. If an older version exists then uninstall it first using the same version of uninstall script.After reading all the licenses, press ‘q’ to finish.
Accept the License by entering ‘Y’.
Figure below shows the Terminal output you should expect to see after the installation is complete.
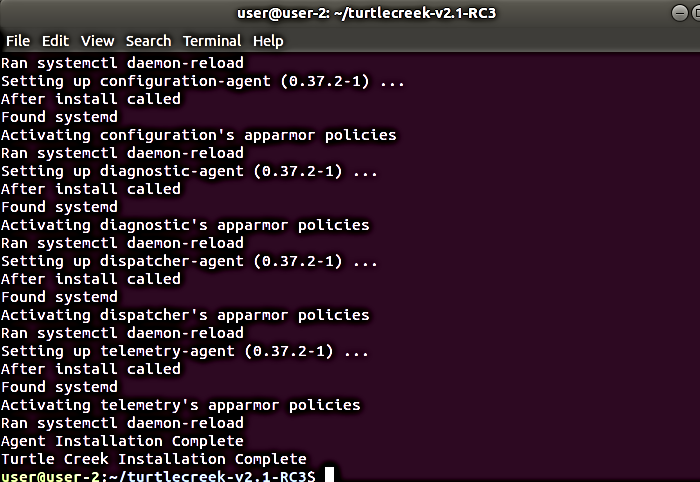
After the Device Manageability has been installed successfully, set the following values in the /etc/intel_manageability.conf file.
sudo vi /etc/intel_manageability.conf
Under <all> </all> section change dbs ON to OFF (refer to the following figures). DBS stands for Docker Bench Security, this feature of Device Manageability is not used for EII.
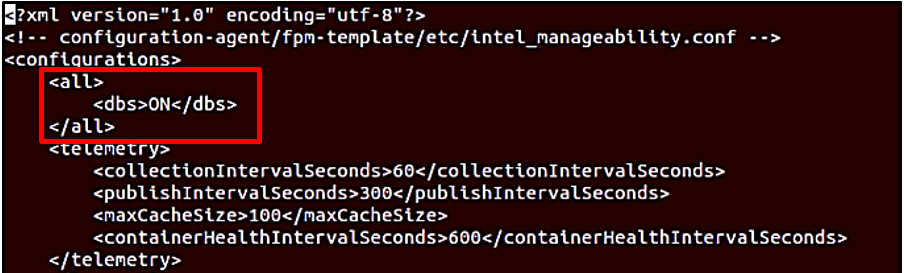
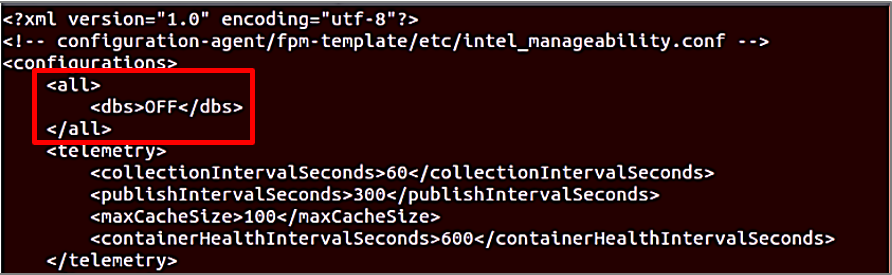
Add the URL endpoint for the developer files to the TrustedRepositories as shown in the followig figure.
<trustedRepositories> https://api-dev.devicewise.com </trustedRepositories>
Save and exit. You must restart the machine before these changes can take effect.
Multi-Node Deployment
EII deployment on multiple nodes requires the use of the Docker* registry. The following section outlines some of the commands to be run on the primary node and on any newly added secondary nodes.
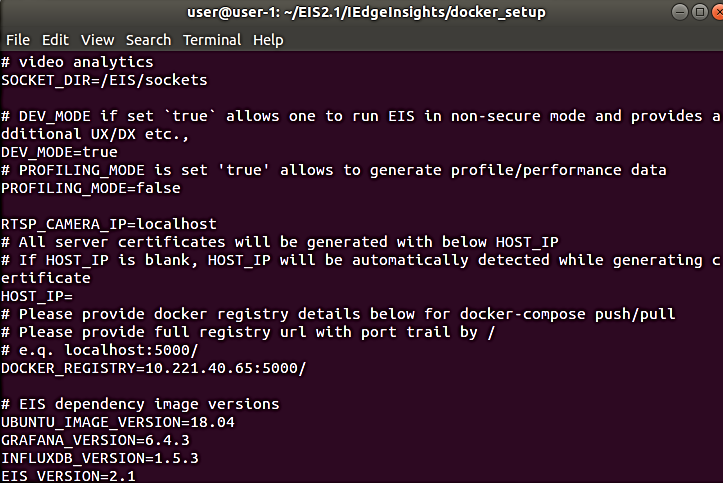
Set up the Docker registry URL, build, and push images. This is required to run on the primary node.
Update the docker registry URL in the DOCKER_REGISTRY variable <ip:port>. The example uses 10.221.40.65:5000/ as the Docker registry.
sudo vi [WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/build/.env
In the same build repository, build the image using the following command:
docker-compose build
On a successful build, you will see the following terminal output:
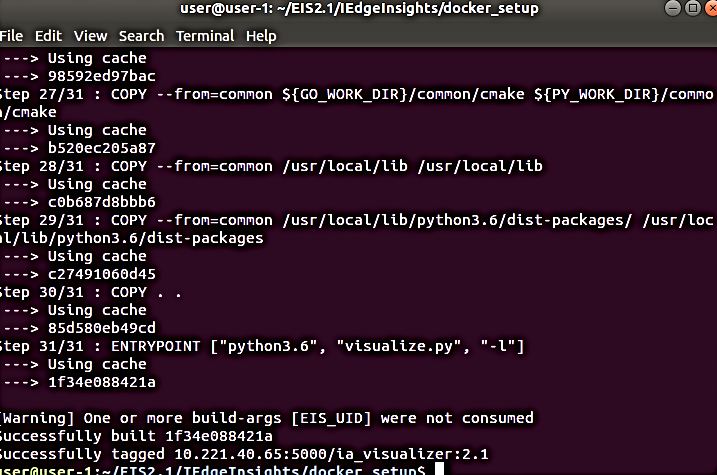
Push the image to the registry:
docker-compose push
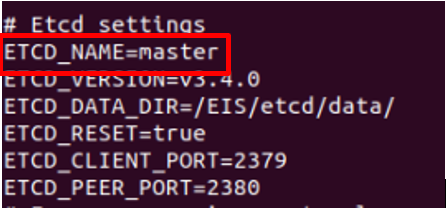
To run EII in multi-node, you must identify one primary node. To set the primary node, set ETCD_NAME in the [WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/build/.env file to master.
You can proceed to provision the primary node using the following command. This will create the ETCD server on the primary edge node.
cd [WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/build/provision sudo ./provision.sh <path_to_eii_docker_compose_file>
After provisioning on the primary node, you need to provision for each of the worker node that will be included in the multi node deployment. Below step need to be executed at the primary node. Users need to ensure the ETCD_NAME in [WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/build/.env have been set to other than “master” name.
cd [WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/build/deploy sudo python3.6 generate_eii_bundle.py -p
This step will generate the eii_provisioning.tar.gz at the same directory. Copy this to the worker node for provisioning.
After copying the generated file to the worker node, run the following commands on the worker node:
tar -xvzf eii_provisioning.tar.gz cd eii_provisioning/provision/ sudo ./provision.sh
Generating EII Bundle for deployment
On the EII primary node, on which EII is running, complete the following steps to generate the EII_bundle.
This software will only work on Python* 3 and onwards.
Update the config.json file to include the services that you need for the bundle. Ensure to exclude theservices that you do not want with the bundle.
$ sudo vi build/deploy/config.json { "docker_compose_file_version": "<docker_compose_file_version which is compose file version supported by deploying docker engine>", "exclude_services": [list of services which you want to exclude from your deployement] "include_services": [list of services needed in final deployment docker-compose.yml] }Note: Ensure that you have updated the DOCKER_REGISTRY in the build/.env file as mentioned in the Multi-Node deployment section.
Update the .env file at the [repo/build] directory for the worker node environment setting by changing below parameters
sudo gedit .env ETCD_NAME=<any name other than `master`> ETCD_HOST=<IP address of primary node> DOCKER_REGISTRY=<Docker registry details>
Run the following script in the terminal to generate the eii_bundle
cd [WORK_DIR]/IEdgeInsights/build/deploy/ sudo python3.6 generate_eii_bundle.py
The default value for bundle name is eii_bundle.tar.gz, while the tag name is eii_bundle.
Using -t options can give you a custom tag name which you can use for bundle generation.
The default value for the docker-compose yml path is ../docker-compose.yml.
The file eii_bundle.tar.gz will be created in the same folder. This bundle will be used to deploy EII on the other node via ThingsBoard.
Creating an HTTP Local Server
The generated EII bundle need to available via http server to perform AOTA fetching from the cloud services.
Prerequisites
Run sudo vi /etc/environment.
Under no_proxy variable, add the local http server (example, 10.221.40.65).
Perform sudo systemctl restart configuration
Run the following command on the ThingsBoard machine to create the HTTP server for sharing the eii_bundle:
python3 -m http.server [any port number]
Add the fileserver endpoint to the configuration file on the node that you will access via the local HTTP server.
In the example, the steps below must be done on the new node. The new node will access the local HTTP server to fetch the eii_bundle that is being created.
Open the configuration file
sudo vi /etc/intel_manageability.conf
Under “trustedRepositories”, add the bundle hosting server endpoint on a new line. http://xx.xxx.xxx.xx as used above.
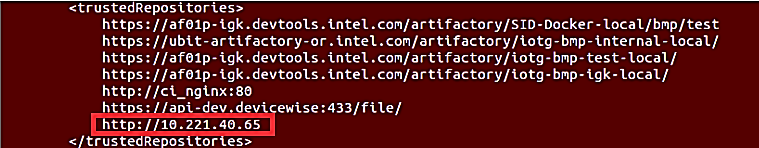 NOTE:The above example is running local HTTP server at 10.221.40.65:8000
NOTE:The above example is running local HTTP server at 10.221.40.65:8000Perform $ sudo systemctl restart configuration on the machine.
Cloud Service: Azure Server Set up
All Device Manageability devices can be connected and controlled via the Azure portal. An Azure account can be created through the following link:
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/free/, select start free, and create the account.
Setting up an Azure IoT Central Application
To generate a premade Device Manageability (Intel Manageability) IoT Central application get the link from /usr/share/cloudadapter-agent/azure_template_link.txt file on Device Manageability machine.
Copy and paste the link in your browser, you will be redirect to the Azure UI as shown below.
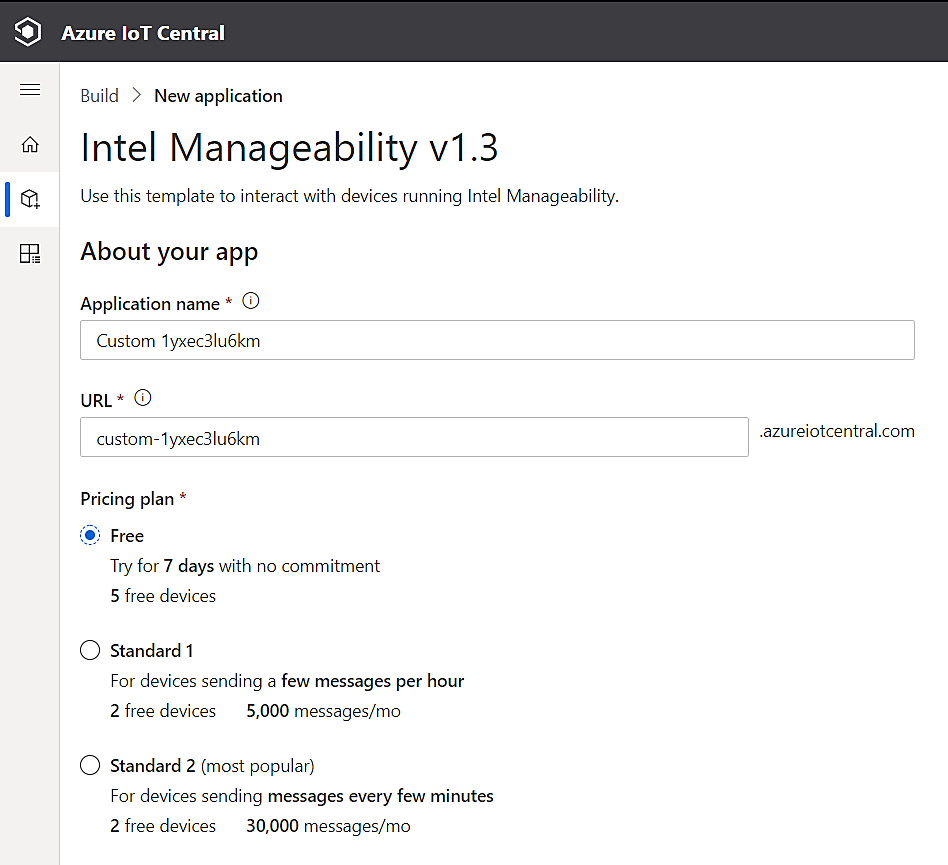
For the pricing plan, select free trial version. Fill up the necessary contact information and click on the create account button.
After provisioning, the IoT Central application with premade device templates and dashboards will appear. As noted before, this can be accessed at https://apps.azureiotcentral.com or through the Azure portal.
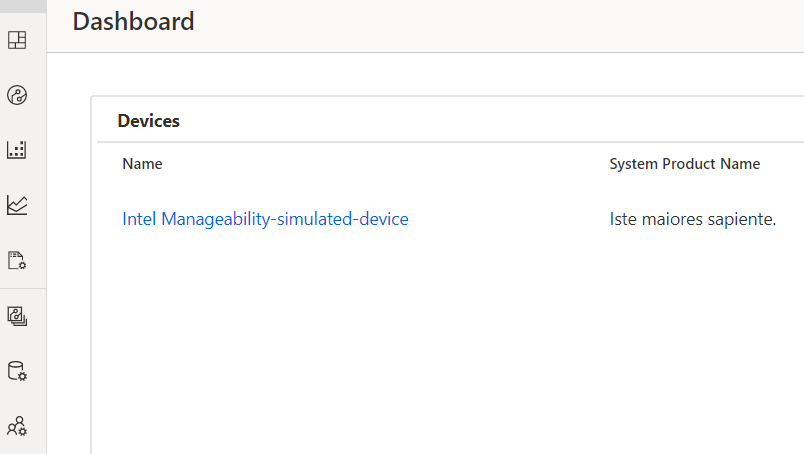
Obtaining device credentials
To add new device, click on the devices tab on the side bar, click on the add new device button.
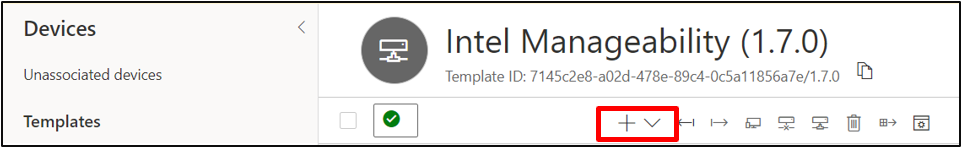
Select real on the drop-down list, create new device form will appear as below. Click on create button.
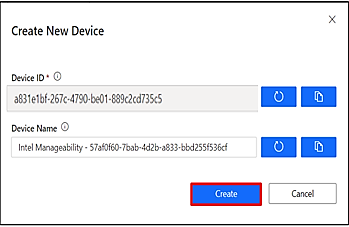
The new added device will appear on the list of the devices page. To connect the device, click on that specific device and click on the connect button at the top bar right side.
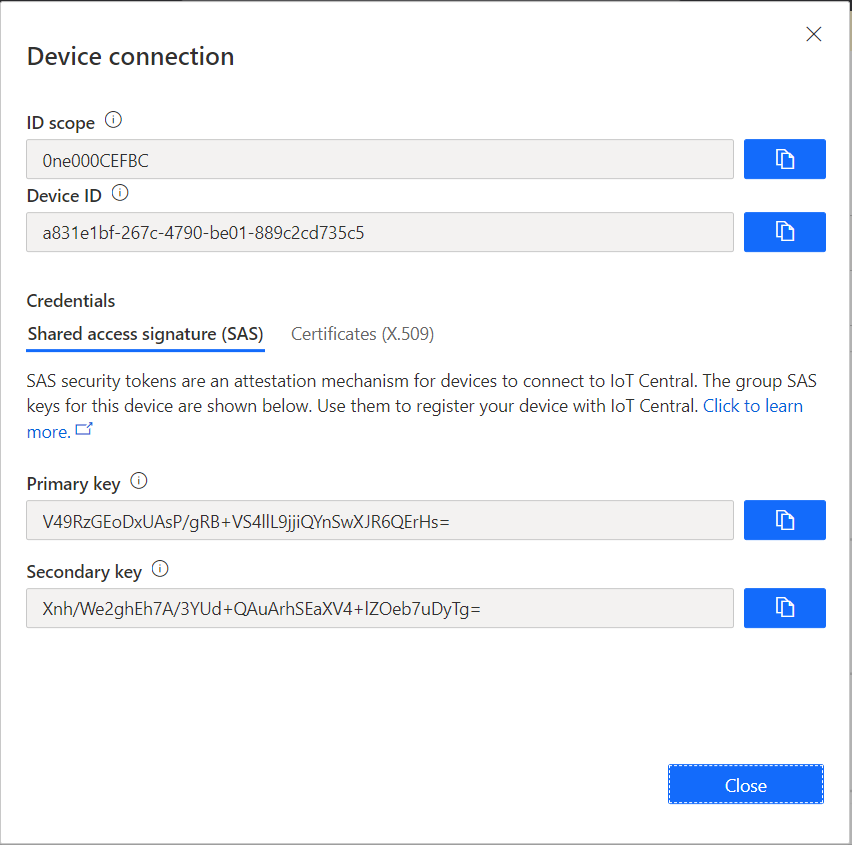
Device connection information form will appear as below.
Provisioning a device
Prerequisites : In order to perform this step, the Device Manageability device needs to be installed according to the instructions in the Installation Device Manageability section.
Provisioning can be done with or without the TPM security by setting ‘PROVISION_TPM’. Using the following commands you can set ‘PROVISION_TPM’ to the Device Manageability device:
auto: use TPM if present; disable if not present; do not prompt
disable: do not use TPM.
enable: use TPM; return error code if TPM not detected.
(unset): default behavior; use TPM if present, prompt if not
On the Device Manageability device, run the following command:
To run provisioning with detecting automatically TPM is present or not:
sudo PROVISION_TPM=auto provision-tc
To run without TPM security:
sudo PROVISION_TPM=disable provision-tc
If the device has been configured earlier, it will prompt as follows:
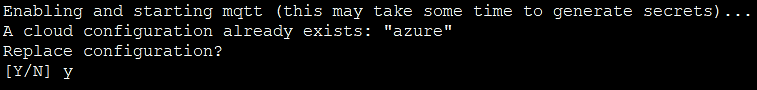
Press ‘Y’ to replace the existing configuration.
Select ‘2’ for cloud service option.
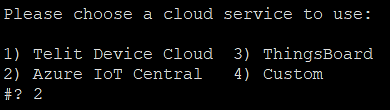
A prompt for Device provision type appears; select the type of device authentication preferred: Choose 1 for SAS key authentication. If you choose option2 - Refer secton [2.5 - Provisoning a Device ] at ./docs/In-Band_Manageability_UserGuide_Azure.pdf for further steps.
All the device credentials from obtaining device credentials will be used here. Enter the following information accordingly.
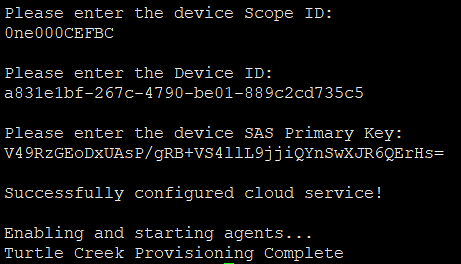
The script will then start the Intel Manageability services; when the script finishes, the device should be able to be interacted with on its associated IoT Central Application. To verify connectivity: a. Check to see if telemetry/events are appearing. If the info is not seen, use ‘’’systemctl restart cloudadapter telemetry’’’ command to restart the two agents give few seconds for the info to be populated and refresh the portal page. b. Alternatively, trigger a command like Reboot.
Run the provisioning script to change or update the cloud service configuration.
On the Azure portal, the device status should be changed from ‘Registered’ to ‘Provisioned’ as follows

The following example shows the telemetry data of the connected devices that is available on the measurement tab in the Azure portal.
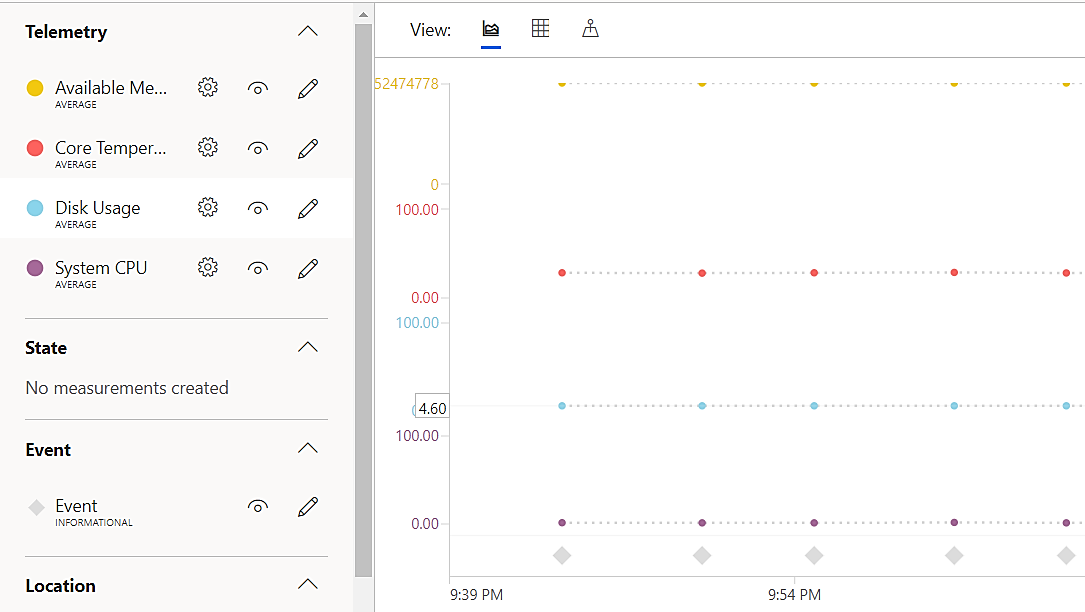
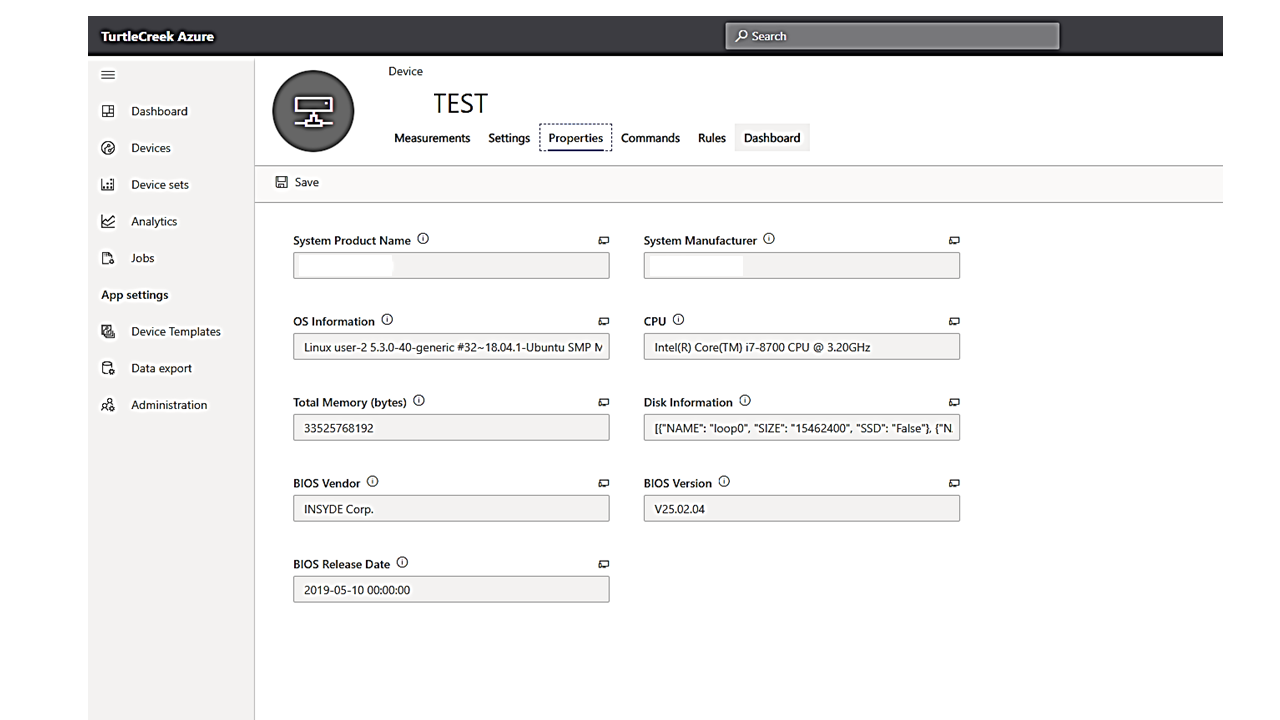
You can get the additional details information for the specific hardware and the event logs on the properties tab as follows:
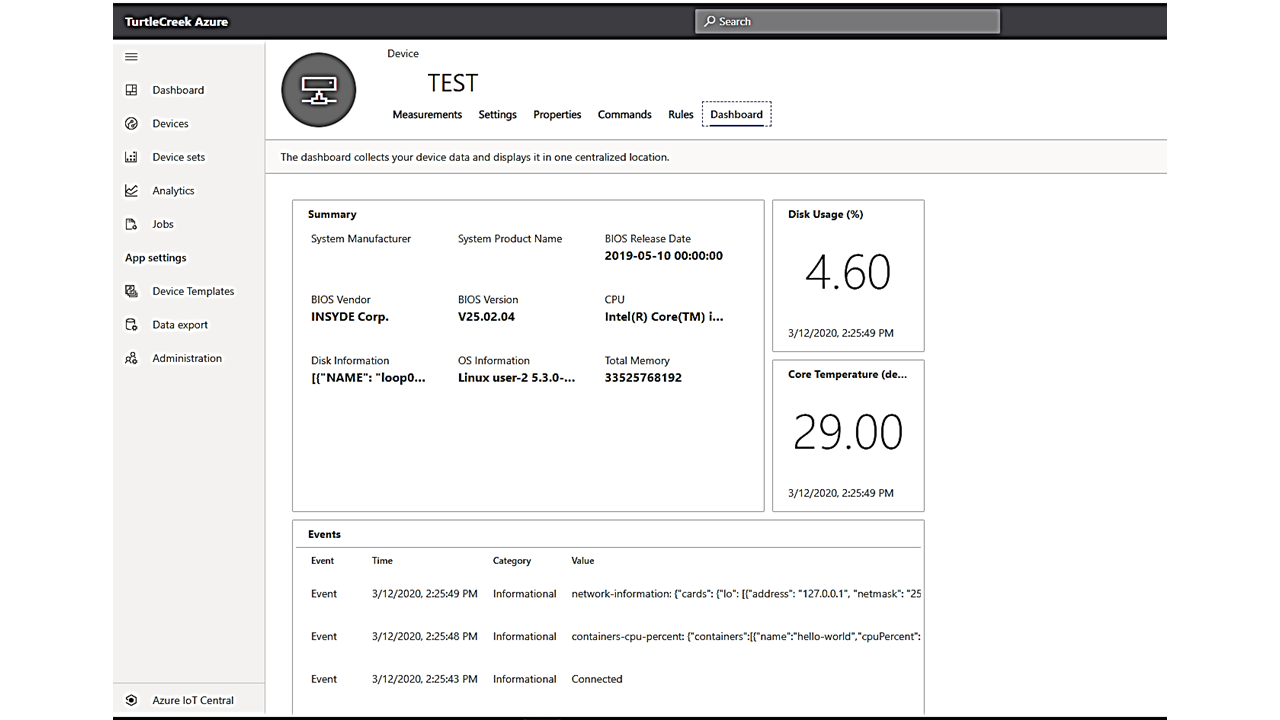
The following is the example of basic information that shown on the dashboard tab.
Performing AOTA Updates Through the Azure Portal
Prerequisites: To perform this step, generate the EII bundle as mentioned in the Generating EII Bundle for deployment section. For testing, run the local http server as mentioned in the Creating an HTTP Local Server [ONLY FOR DEVELOPMENT] section. For actual implementation, you are need to have your own http server or any cloud services that provides a valid URL to fetch the EII bundle.
Open the Azure portal, select for the specific device that user will trigger the AOTA.
On the top menu bar, select the Commands tab.
On the list command, fill up the trigger AOTA form as with detais as follows. To perform this step, the EII bundle needs to be generated as mentioned in the Generating EII Bundle for deployment section.
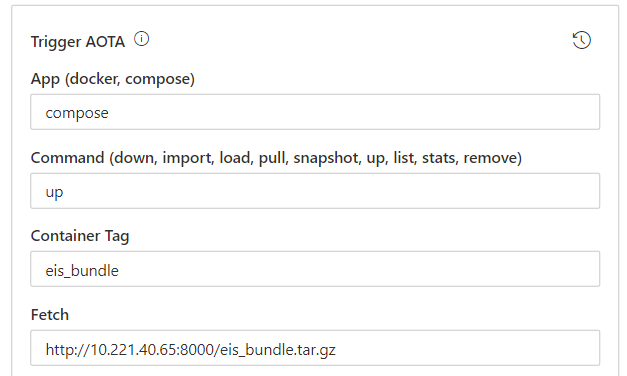
Above example assumes that the http server is being running at http://10.221.40.65:8000/eii_bundle.tar.gz and the EII bundle is generated using the default tag. You can leave all other sections empty and click Run.
The sample PCB demo example of the EII Visualizer application should appear on the new node. If the visualizer does not appear, run the following command on the new node terminal.
xhost +
You can check if EII has been successfully deployed on the new node. Run the following commands to view the list of running containers.
docker ps
The EII containers that are running are listed as output in the terminal.
You can also stop EII from running on the new node by repeating the AOTA method. Instead of passing command up parameter, you can pass command down parameter and the correct eii_bundle tag. You can check that EII has stopped by checking the list of running containers.
Verifying Triggered AOTA in Event
Once an AOTA event is triggered, you can verify the log of the triggered call. This can be one of the verification during development phase.
Go to the Device Manageability machine and run the following command to view the log of commands:
journalctl -fu dispatcher & journalctl -fu cloudadapter
Note the event logs on the Azure portal server showing which commands have been run.
NOTE:If the event log is not displayed then, follow the steps below.Change settings from ERROR to DEBUG everywhere in the following files. (Only for Development Purpose) /etc/intel-manageability/public/dispatcher-agent/logging.ini /etc/intel-manageability/public/cloudadapter-agent/logging.ini
Run the following commands
sudo systemctl restart dispatcher sudo systemctl restart cloudadapter sudo systemctl restart diagnostic
Cloud Service: ThingsBoard* Setup
All Device Manageability devices can be added into ThingsBoard to provision or enable AOTA updates.
Starting ThingsBoard* as Docker [macOS*/Linux*]
Choose an edge device to run as the ThingsBoard server. The edge devices for ThingsBoard machine can be either within the cluster setup or any other edge devices.
Run the following command to start ThingsBoard on the ThingsBoard machine.
docker run -it -p 9090:9090 -p 1884:2883 -p 5683:5683/udp -v ~/.mytb-data:/data -v ~/.mytb-logs:/var/log/thingsboard -e MQTT_BIND_PORT=2883 -name mytb -restart always thingsboard/tb-postgres:2.5.0
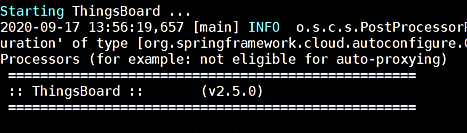
Assuming that ThingsBoard has started correctly, you should expect to see the terminal output as shown in figure below.
After executing the command, you can browse the ThingsBoard server:
<http://<host-ip>:9090>
Example: http://10.221.40.48:9090
The ThingsBoard login page is displayed as follows:
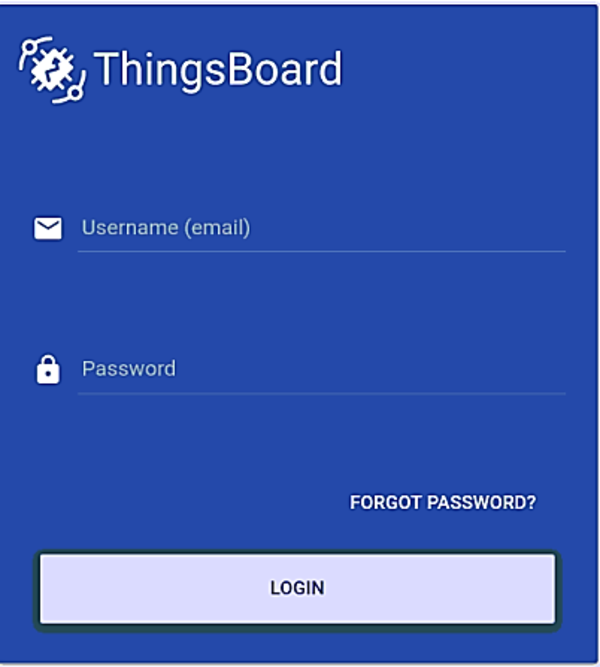
Enter the default username and password to access to the ThingsBoard home.
Username: sysadmin@thingsboard.org
Password: sysadmin
Creating a ThingsBoard* Account
On the homepage, click Tenant management.
Click the plus button in the bottom right to add a new tenant. Refer to the following:
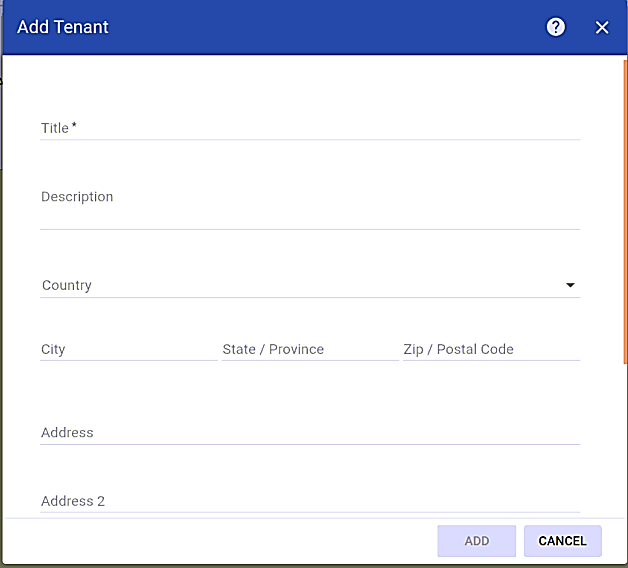
The Add Tenant form is displayed as follows. Complete the form, then click add.
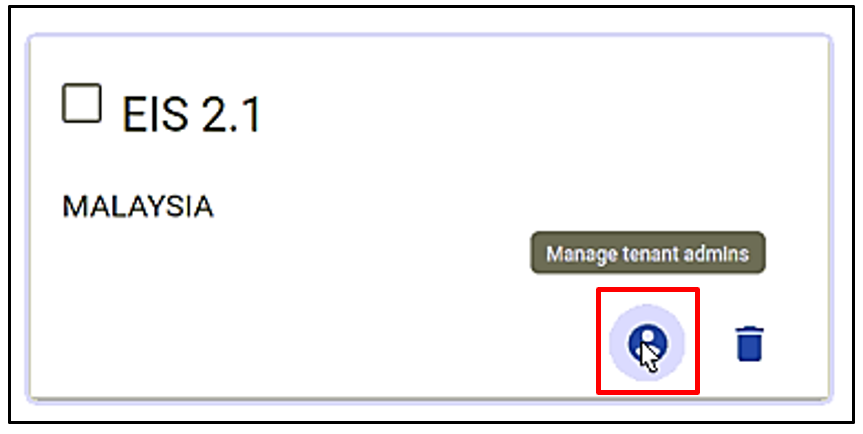
New tenant entry will appear in the tenant section as shown in figure below. Click Manage tenant admins to create a new user sign-in username and pssword.
Add User form will appear as shown in figure below. Complete the form accordingly. For the Activation method, click display activation link and then, click ADD.

User activation link box will appear as shown in figure below. Click the activation link.

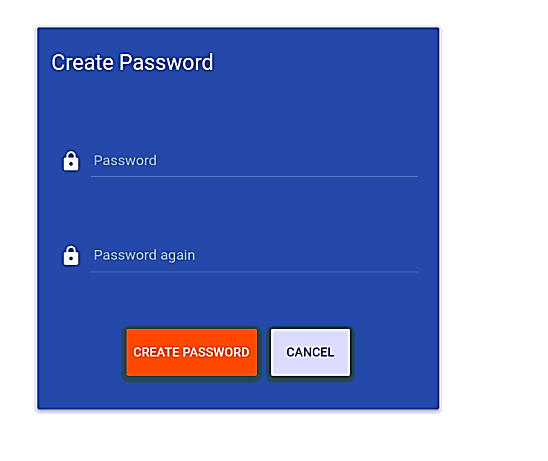
You will be redirected to create a new sign-in password. Click create password to create a new password as shown in the following figure:
You can now sign in using the tenant username and password, after which you will be redirected to the ThingsBoard dashboard page as shown in the following figure:
Adding Device Manageability Device to ThingsBoard*
Add the new Device Manageability device on ThingsBoard.
Log into the ThingsBoard page. On the left sidebar, click Devices as shown in the following figure:
Click the ‘plus’ button on the bottom right and select Add new device.
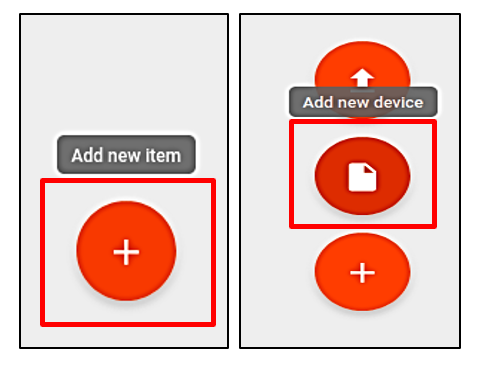
On the Add device window, complete the fields, then click ADD.
Newly added device will be shown on the devices page as shown in figure below.
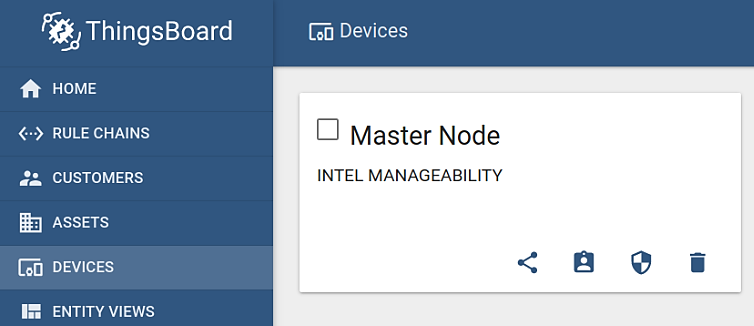
Obtaining device credentials.
Click the manage credentials icon as shown in figure below.
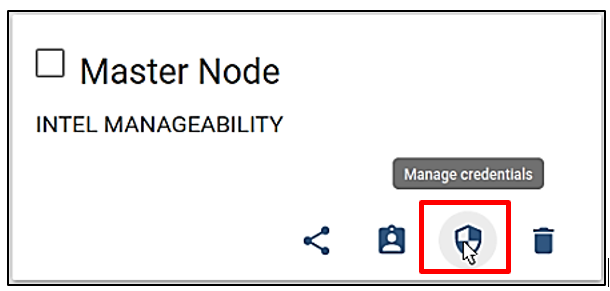
Device credentials window is displayed as follows. Access token is required for provisioning purposes.
Setting up the dashboard.
Some files need to be copied from the Device Manageability machine to ThingsBoard page in the next step. These files can be found in the following directory.
cd /usr/share/cloudadapter-agent/thingboard
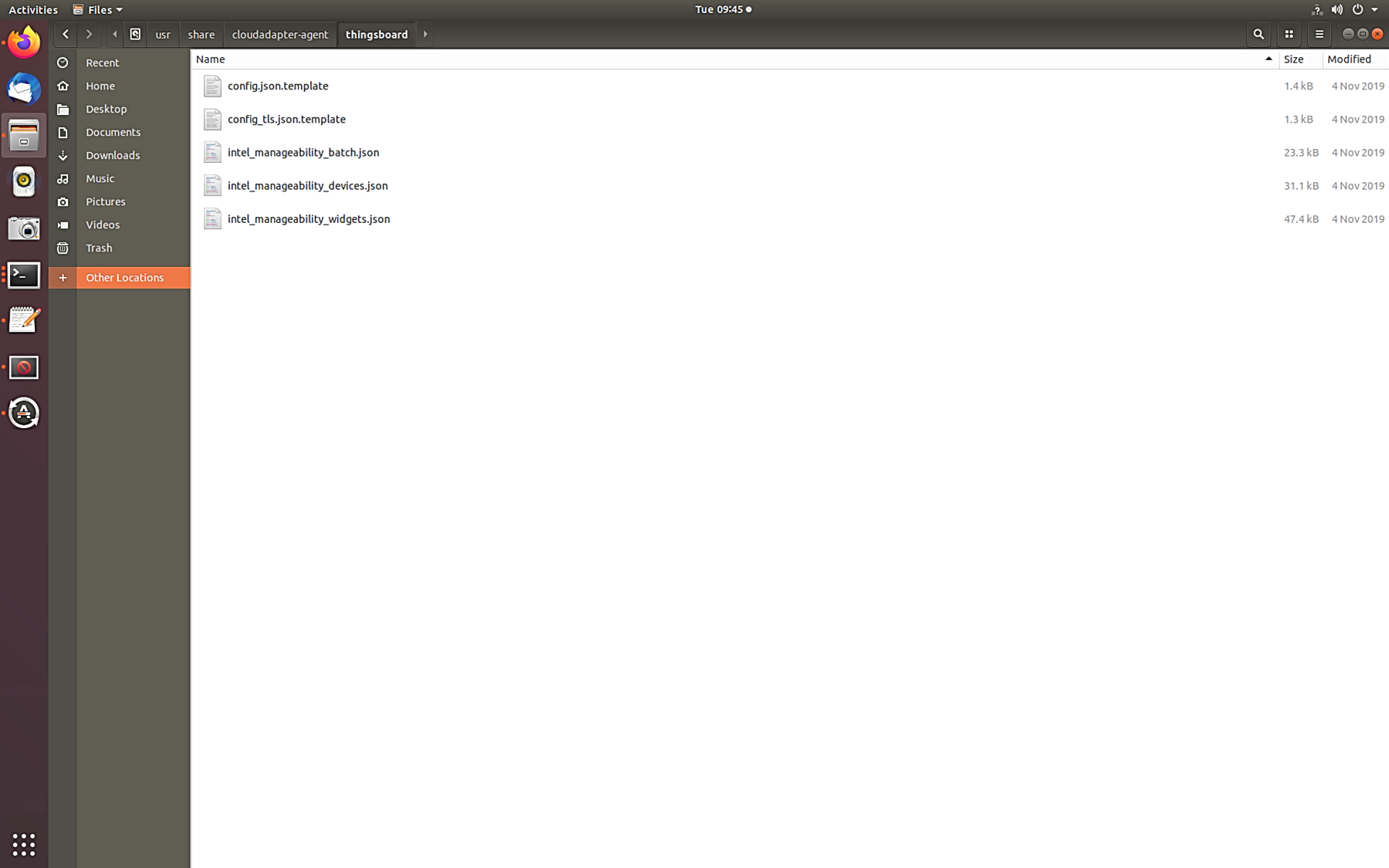
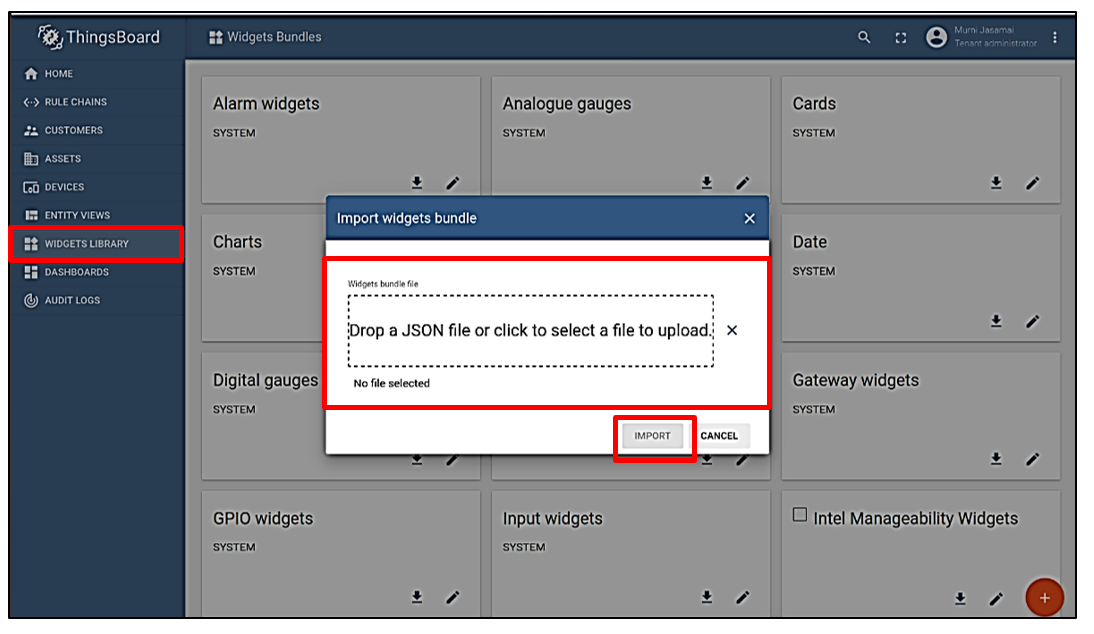
On the left side bar menu, click the Widget Library, then click Add new widget in the bottom right, and the Import widgets bundle. Drag the intel_manageability_widget.json file into the box provided and then click Import.
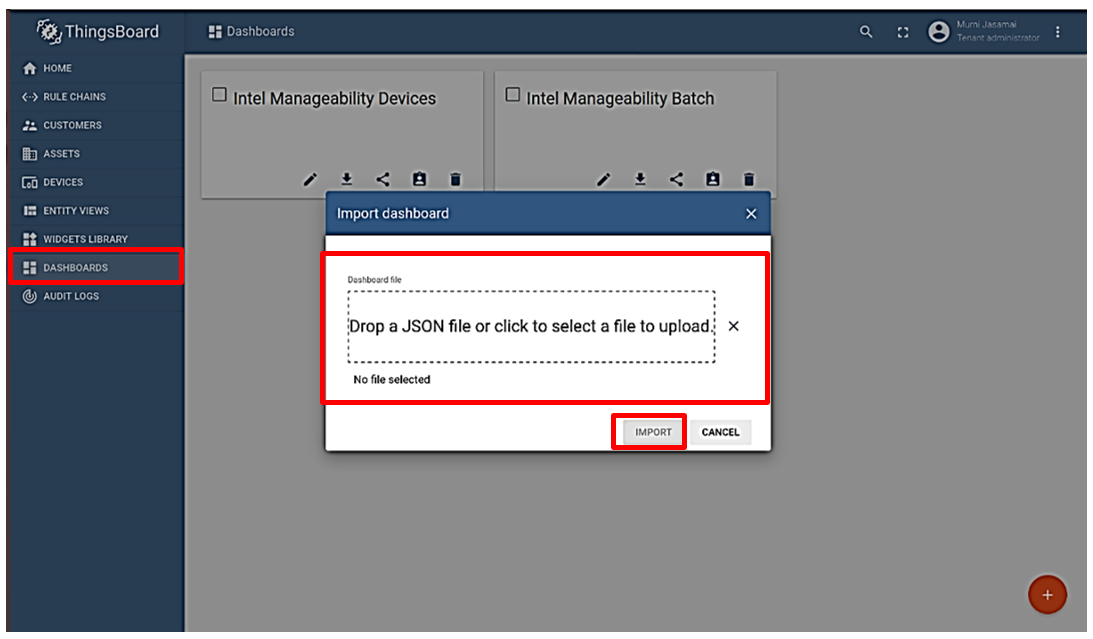
On the left sidebar menu, click on Dashboard, then click Add new dashboard** in the bottom right. Drag intel_manageability_devices.json into the box provided and the click Import. Repeat this step for intel_manageability_batch.json.
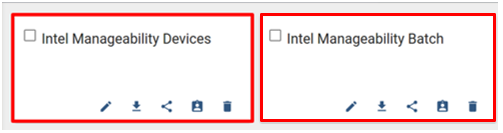
Both newly added dashboards will be displayed.
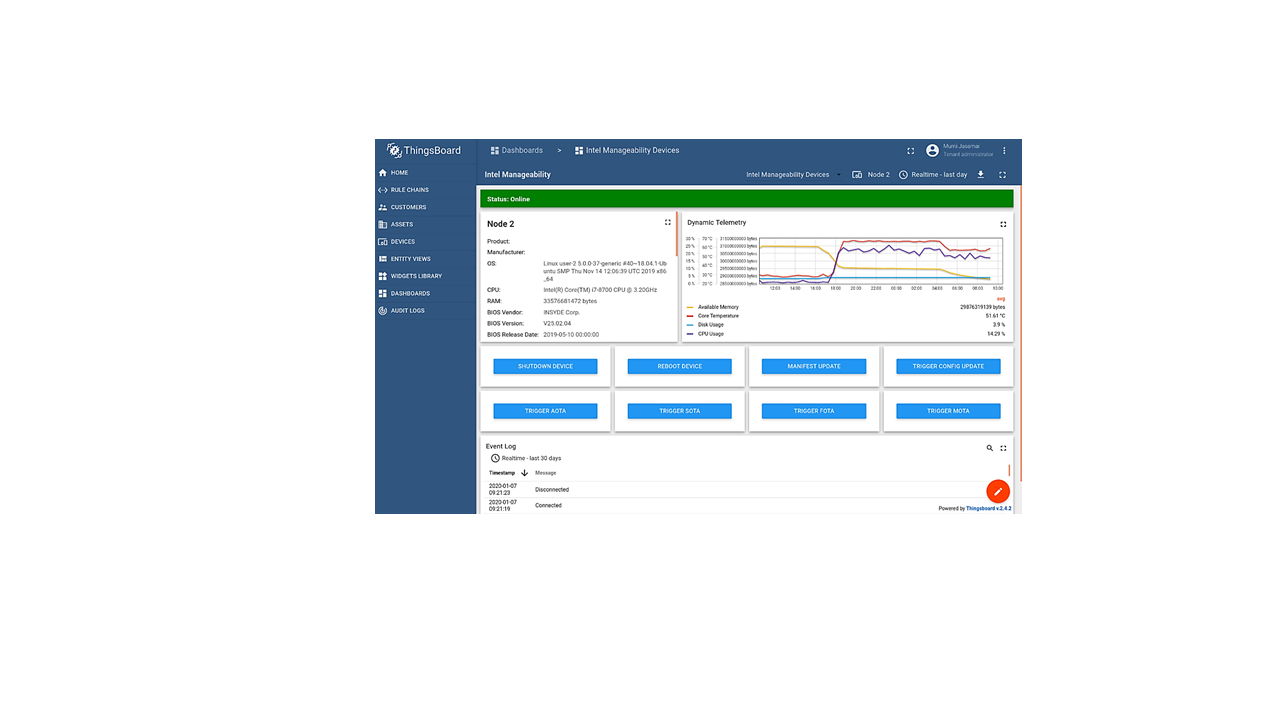
To access the dashboard, click Dashboard on the left sidebar, then click Intel Manageability Devices. Basic information about the added devices is available here.
If you have more than one device, then you can choose which device to view by clicking the highlighted button at the top right.
Buttons are also available in the lower part of the screen to view the entire event log, to search for specific event logs, or to expand the window to full screen.
Provisioning a Device
Prerequisites: To perform this step, Device Manageability needs to be installed following the instructions in the Installation - Device Manageability section.
You must provision the Device Manageability device for it to connect to ThingsBoard.
Provisioning can be done with or without TPM security by setting ‘PROVISION_TPM’. Run the following commands to set ‘PROVISION_TPM’ to the Device Manageability device:
auto: use TPM if present; disable if not present; do not prompt.
disable: do not use TPM.
enable: use TPM; return error code if TPM not detected.
(unset): default behavior; use TPM if present, prompt if not.
On the Device Manageability device, run the following command, change the bold parameter accordingly as mentioned above.
sudo PROVISION_TPM=auto provision
Read though the license and press Y to accept.
If the device was previously provisioned, the following message will appear. To override the previous cloud configuration, press Y.
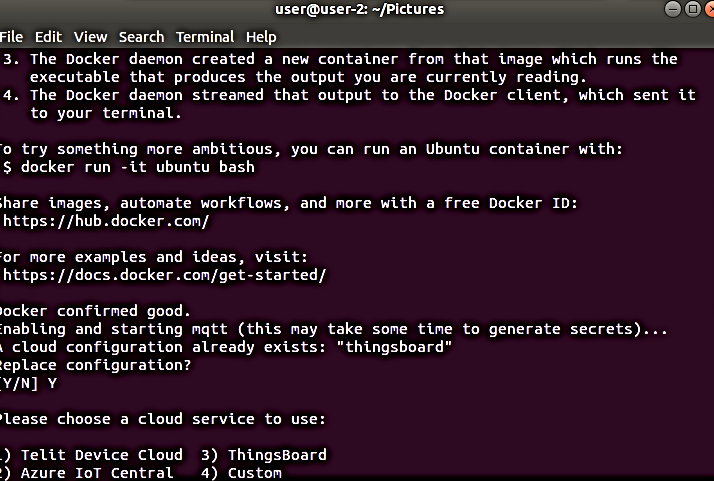
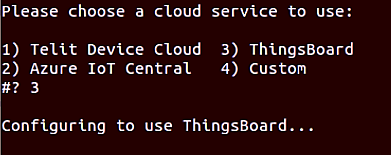
Select ThingsBoard as the cloud service by pressing 3 and [ENTER].
A prompt for Device provision type appears; select the type of device authentication preferred: Choose 1 for Token authentication. If you choose option2 - Refer secton [2.5 - Provisoning a Device ] at ./docs/In-Band_Manageability_UserGuide_ThingsBoard.pdf for further steps.
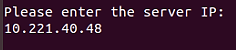
Provide the IP address of the server running ThingsBoard.
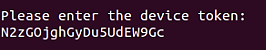
Provide the device token based on Step 3b.
Use 1884s for the port configuration.
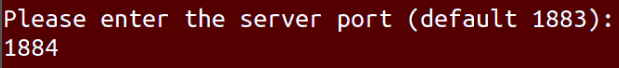
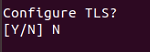
Prompts for ‘Configure TLS’ will appear and enter ‘N’ for this.
The following screen will appear if cloud provisioning has been completed successfully.
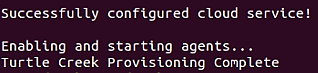
The script will then start the Intel® Manageability Services. When the script finishes, you should be able to interact with the device via the ThingsBoard dashboard.
If at any time the cloud service configuration needs to be changed or updated, run this provisioning script again.
To add more than one device, repeat each of the previous steps, except for Step 4 (Setting Up the Dashboard).
Performing AOTA Updates Through the ThingsBoard* Page
Prerequisites: In order to perform this step EII bundle need to be generated as mentioned in section Generating EII Bundle for deployment and local http server (for development) need to be run as mentioned in Creating an HTTP Local Server [ONLY FOR DEVELOPMENT].
Open the ThingsBoard page, then click on the Dashboard page. Select Intel Manageability Devices.
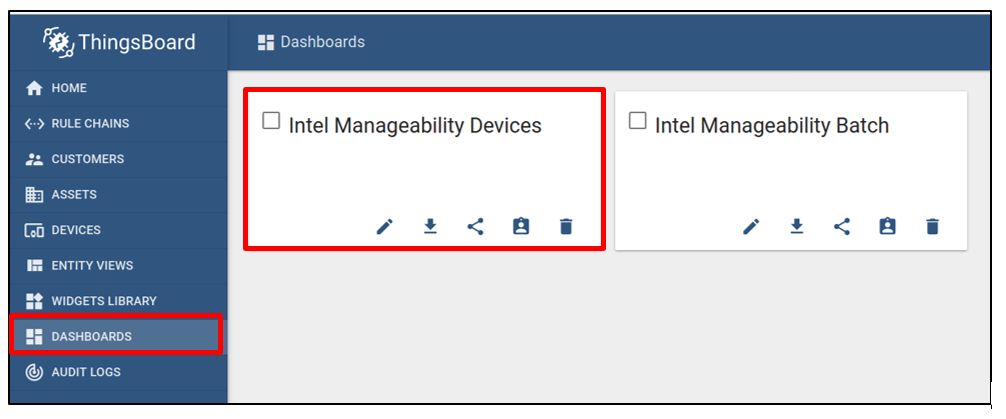
Select one of the previously added Device Manageability devices. In this case, the user can select the new node (node 2) in which they want to deploy the eii_bundle.
Click Trigger AOTA.
Once the Trigger AOTA window opens, complete each field per the information below:
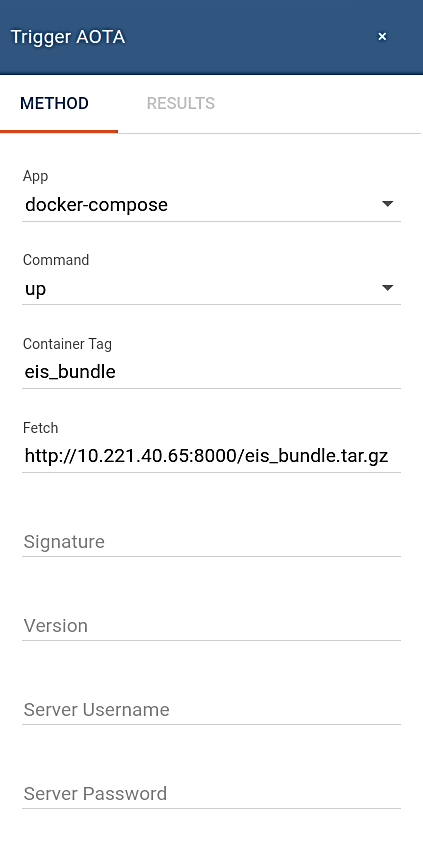
For the fetch information, provide the local HTTP server being set up in section Creating an HTTP Local Server [ONLY FOR DEVELOPMENT]. The example uses http://10.221.40.48:9000/eii_bundle.tar.gz in this case.
Leave the other section empty and click Send.
In the step above, the new node will access the primary node through the local HTTP server that being set up to fetch the eii_bundle.
In the ThingsBoard log, the user can see that the eii_bundle has been fetched from the local server and was deployed successfully:

The sample PCB demo example of the EII Visualizer application should appear on the new node. In case the visualizer does not appear, run the following command on the new node terminal.
xhost +
The user can also verify that EII has been successfully deployed on the new node by checking the list of running containers using the following command:
docker ps
This action should yield the following terminal output listing the running EII containers.
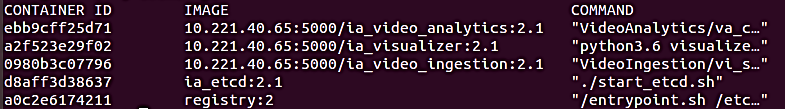
The user can also stop EII from running on the new node by repeating the AOTA method. Instead of passing command up parameter, the user can pass the command down parameter and the correct eii_bundle tag. The user can verify that EII has stopped by checking on the list of running containers.
Verifying Triggered AOTA in Event
Once an AOTA event is triggered, we can verify the log of the triggered call. This can be one of the verification done during development phase.
Go to the Device Manageability machine and run the following command to view the log of commands:
journalctl -fu dispatcher & journalctl -fu cloudadapter
Note the event logs on the ThingsBoard server showing which commands have been run.
NOTE:If the event log does not appear, follow the steps below.Change settings from ERROR to DEBUG everywhere in below files. (Only for Development Purpose) /etc/intel-manageability/public/dispatcher-agent/logging.ini /etc/intel-manageability/public/cloudadapter-agent/logging.ini
Run the following commands
sudo systemctl restart dispatcher sudo systemctl restart cloudadapter
Cloud Service: Telit* Cloud Setup
It is necessary to creating a Telit account and to receive an org token from Telit to provision/enable AOTA updates. You will also need to import the Thing Definition, which provides the buttons created to support AOTA functionality in EII.
A connection to Telit can only be made if the user has a group/organization on the service. Visit the deviceWise domain to create an account and get an “org” or “application”.
Create Your Telit* IoT Portal Account
Telit provides a Getting Started Guide for creating an account. This guide can be referenced here:
https://docs.devicewise.com/Content/GettingStarted/IoT-Portal-Part-1—Creating-your-account.htm
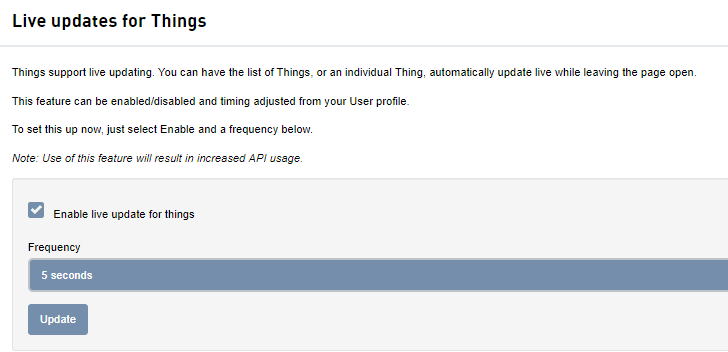
After setting up your password and accepting Telit’s terms, the first time you click on Things you will be asked to set up live updates. Although this is optional, Intel recommends setting the frequency of live updates to 5 seconds.
Import Thing Definition
Pre-Requisites: In order to perform this step Device Manageability need to be installed based on Installation Device Manageability section.
To work with EII’s AOTA capability, import INTEL-MGB as a Thing.
Login to Telit* at https://portal.telit.com/app/login
Ensure the correct org in the top right corner, left of the gear wheel.
Select the Developer tab along the top bar.
Select Thing Definitions at the bottom left sidebar menu.
From the Things sub-screen, find Import in the upper-right corner.
Click Attach File and then select **thingsdefinition.json* that is available inside the turtlecreek repository.
Click Import. You should see the new Things definition added to your account.

The new Thing definition should now be visible within the Telit list of things under Things definitions, in the Developer` tab.
Copy Application Token
Within the Telit portal, view the “Developer” tab and click Applications from the menu on the left. Copy and retain the token, which will be required during the provisioning script or step.
This token is used to link your Thing to the Telit cloud and is used during provisioning.
Log in to your Telit IoT Portal: https://portal.devicecloud.windriver.com
NOTE:The first time you log in, you will be asked to Enable Live Updates for Things. Click the box, set 5 seconds for the setting.Retrieve Token.
Click Developer.
Click Application.
Copy the encrypted token.
 NOTE:Alternately, you can paste the token into a text editor.
NOTE:Alternately, you can paste the token into a text editor.
Provision with the Token
Once you have copied your Application Token, you are ready to provision Device Manageability. You will need the provisioning script.
Provisioning can be done with or without TPM security by setting ‘PROVISION_TPM’. ‘PROVISION_TPM’ can be set to the turtlecreek device, users need to run be run below command.
auto: use TPM if present; disable if not present; do not prompt
disable: do not use TPM.
enable: use TPM; return error code if TPM not detected.
(unset): default behavior; use TPM if present, prompt if not
On the Device Manageability device, users need to run the command below, change the bold parameter accordingly as mentioned above.
sudo PROVISION_TPM=auto provision-tc
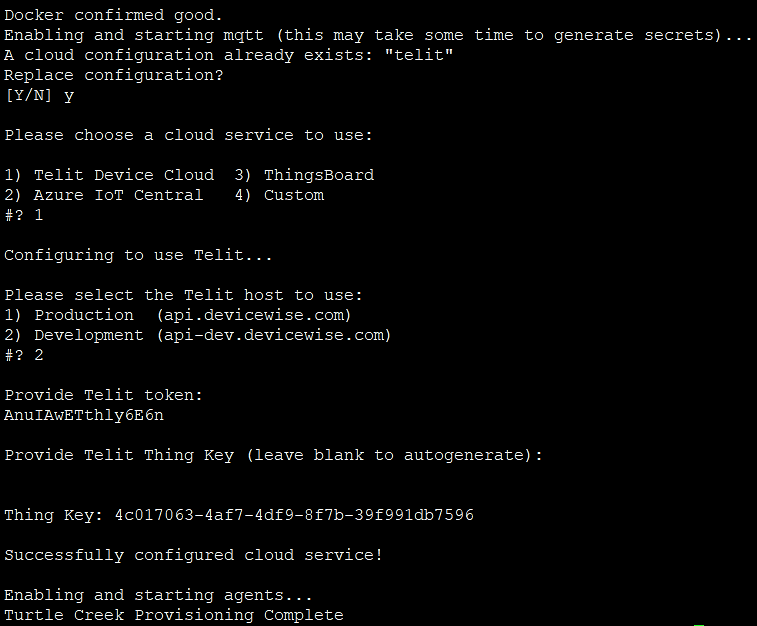
You will be asked to replace configuration, if there is any existing configured cloud service. Type ‘Y’.
Choose Telit Cloud service.
Select development for Telit host.
Insert application token that have been copied on previous step.
Leave the Telit thing key blank.
User will be prompted by ‘successfully configured cloud service’ and ‘Device Manageability provision complete’ message.
Verify your Connectivity.
Click Things.
Verify that your system is now visible on Telit.
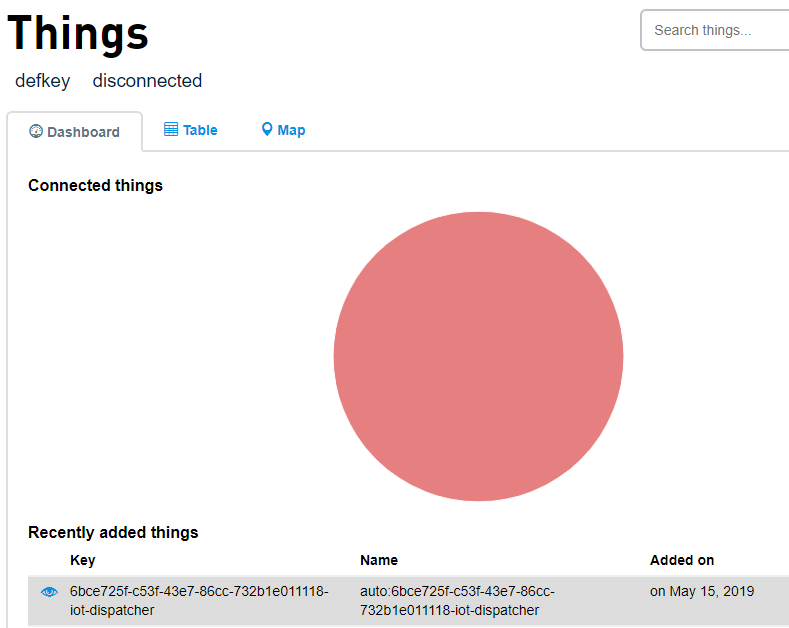
Once your device is identified as a Thing in Telit, your system can be updated through Telit.
Telit serves as the UI to support the following OTAs (Over-the-Air) without manual intervention:
AOTA (Application Over the Air update)
FOTA (Firmware Over the Air update)
SOTA (Software/OS Over the Air update)
Config Update (configuration parameter update)
Power Management (Remote Shutdown and Restart)
Link to Thing definition
Set Thing definition
Click Things.
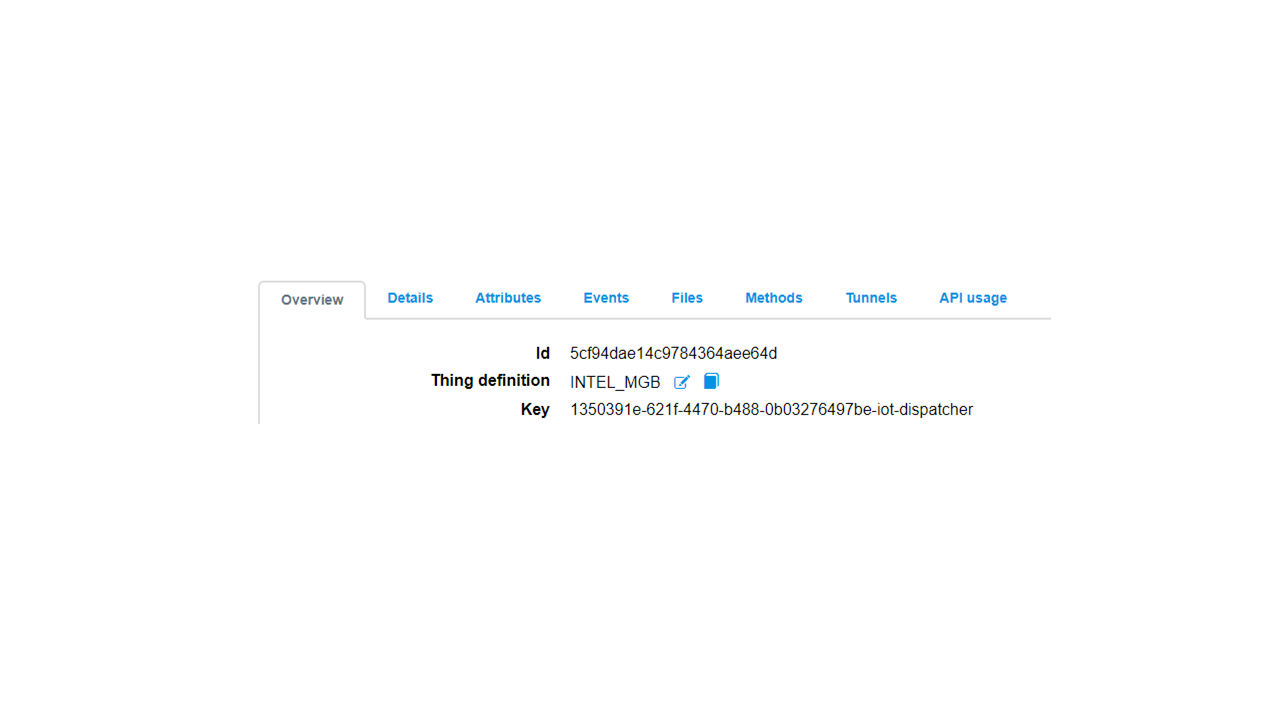
Click the (eye) icon for your Thing.
Set Thing Definition, then click (book).
Choose definition: INTEL_MGB.
Submit, Okay.
After the Things definition is installed, you will see the Methods tab is enabled, which will show you the widgets that EII supports.
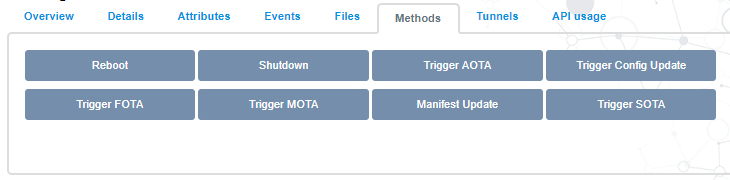 NOTE:Your ‘Methods’ might look different.
NOTE:Your ‘Methods’ might look different.
The Telit website provides instructions for navigating the user interface to complete the steps of importing a thing definition and performing required configuration tasks. The following steps are generalized, as the name and placement of specific buttons and menus within the Telit website can change without notice.
View and Name Your Thing
Name your Thing (optional)
Click Action.
Click Edit.
Under Name* <enter name>.
Update, Okay
 NOTE:This helps to identify your device.
NOTE:This helps to identify your device.
Identify thing on system (Thing Key)
Open terminal.
$ cat/usr/share/dispatcher-agent/device_id
Uploading the Telit deployment Bundle in the Telit Portal
Prerequisites: To perform this step EII bundle need to be generated as mentioned in the Generating EII Bundle for Deployment section. The EII bundle need to be in the same system as you access the Telit portal.
Go to the Developer Page and select Files general menu on the left side panel.
On the Files page, click New File.
In the Add File dialog, click Attach File and attach the generated TC-Telit Bundle eii_bundle.tar.gz.
Select the Public checkbox.
Click Upload.
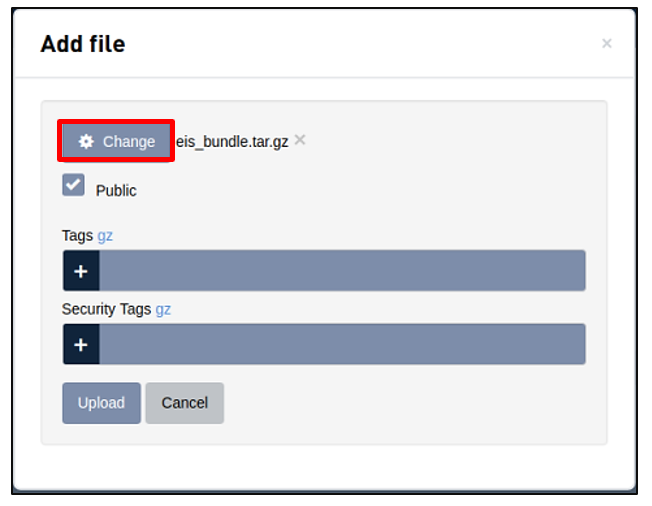
The new file will be listed in the Files section. Copy the Url of the uploaded file for the AOTA method.

Performing AOTA Updates Through Telit
Go to the Things page.
Click the eye icon to select the provisioned device.
Select Methods.
Select Trigger AOTA as follows:
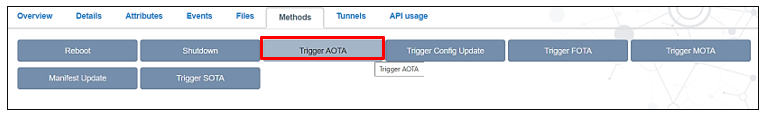
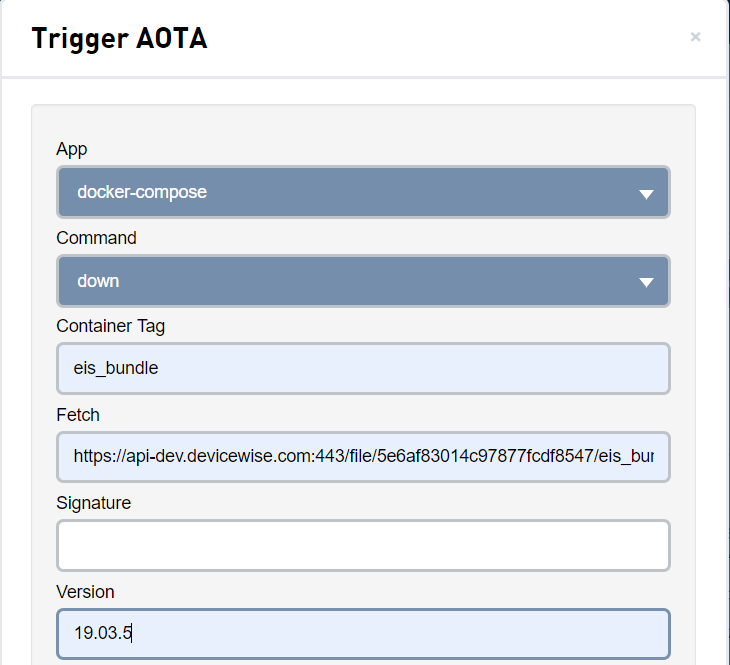
Fill up the trigger AOTA form accordingly.
Container tag should be eii_bundle if you generate the bundle using default value.
Fetch should be the copied URL from the upload bundle in the uploading the Telit deployment bundle in the Telit* portal.
The version should be the docker compose file version number used for the tc-telit bundle generation.
Skip other sections and then, click execute.
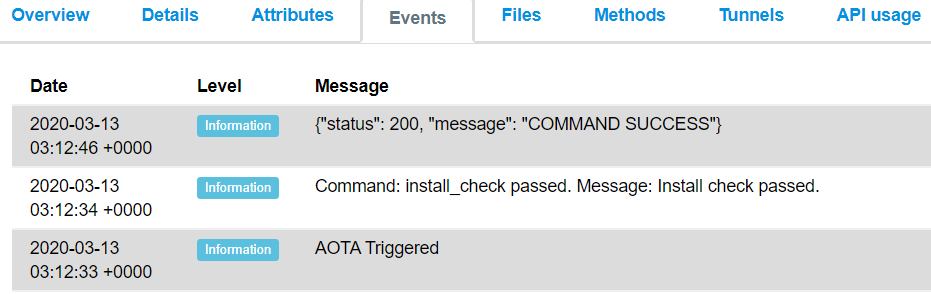
Click the event tab to check on the AOTA status. If the AOTA is executed successfully, a success message is shown as follows:
Multi-node Deployment Without Using Device Manageability
This step deploys EII on multi-node by using the native method without any installation of Device Manageability and Cloud service. To continue on this section, it is required to complete the steps mentioned in the Multi-node deployment section and Generating EII Bundle for Deployment section.
sudo tar -xvf <eii_bundle gz generated> cd build docker-compose up
After completing this step, you can see that the container generated on the EII bundle is running.