A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-09A4C51A-4BDD-4E00-94D5-3CC325E75A00
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-09A4C51A-4BDD-4E00-94D5-3CC325E75A00
IMF Device Library Special Functions
The IMF Device Library supports the following special functions and their inverses:
cdfnorm
Description: The cdfnorm(x) function returns the cumulative normal distribution function value of x.
This function is a useful one for Monte Carlo applications in computational finance.
![]()
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result cdfnorm(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | +0 |
| x < UDFL | +0 |
| +∞ | +1 |
Useful Identities:
cdfnorm(x) = 1/2 · ( 1 + erf( x/sqrt(2) ) ) cdfnorm(x) = 1 - 1/2 · erfc( x/sqrt(2) )
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::cdfnorm ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::cdfnorm ( double x ); // CUDA-specific naming for the same functions float sycl::ext::intel::math::cdfnorm ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::cdfnorm ( double x );
cdfnorminv
Description: The cdfnorminv(x) function returns the inverse cumulative normal distribution function value of x.
This function is a useful one for Monte Carlo applications in computational finance.
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result cdfnorminv(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | QNAN |
| x < -0 | QNAN |
| +/-0 | -∞ |
| +0.5 | +0 |
| +1 | +∞ |
| x > +1 | QNAN |
| +∞ | QNAN |
Useful Identities:
cdfnorminv(x) = sqrt(2) · erfinv( 2·x - 1 ) cdfnorminv(x) = sqrt(2) · erfcinv( 2 - 2·x )
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::cdfnorminv ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::cdfnorminv ( double x ); // CUDA-specific naming for the same functions float sycl::ext::intel::math::normcdfinv ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::normcdfinv ( double x );
cyl_bessel_i0
Description: The cyl_bessel_i0(x) function returns the value of the regular modified cylindrical Bessel function of an order of 0 for the input argument x.
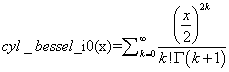
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result cyl_bessel_i0(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | +∞ |
| +/-0 | +1 |
| +∞ | +∞ |
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::cyl_bessel_i0 ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::cyl_bessel_i0 ( double x );
cyl_bessel_i1
Description: The cyl_bessel_i1(x) function returns the value of the regular modified cylindrical Bessel function of an order of 1 for the input argument x.
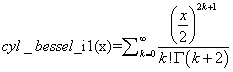
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result cyl_bessel_i1(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | -∞ |
| +/-0 | +/-0 |
| +∞ | +∞ |
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::cyl_bessel_i1 ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::cyl_bessel_i1 ( double x );
erf
Description: The erf(x) function returns the error function value of x.
![]()
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result erf(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | -1 |
| +∞ | +1 |
Useful Identities:
erf(x) = 1 - erfc(x)
Calling Interfaces:
- Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::erf ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::erf ( double x );
- High accuracy (HA):
float sycl::ext::intel::math::ha::erf ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::ha::erf ( double x );
- Low accuracy (LA):
float sycl::ext::intel::math::la::erf ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::la::erf ( double x );
- Enhanced performance:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::ep::erf ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::ep::erf ( double x );
erfc
Description: The erfc(x) function returns the complementary error function value of x: 1 - erf(x)
This function is useful when erf(x) is close to 1 to obtain greater accuracy.
![]()
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result erfc(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | +2 |
| x > UDFL | +0 |
| +∞ | +0 |
Useful Identities:
erfc(x) = 1 - erf(x)
Calling Interfaces:
- Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::erfc ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::erfc ( double x );
- High accuracy (HA):
float sycl::ext::intel::math::ha::erfc ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::ha::erfc ( double x );
- Low accuracy (LA):
float sycl::ext::intel::math::la::erfc ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::la::erfc ( double x );
erfcinv
Description: The erfcinv(x) function returns the inverse complementary error function value of x: erfinv(1-x).
The inverse complementary error function is useful for Monte Carlo applications in computational finance as it is closely related to the normal cumulative distribution. Use the erfcinv(x) function to replace expressions containing erfinv(1-x) for greater accuracy when x is close to 1.
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result erfcinv(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | QNAN |
| x < -0 | QNAN |
| +/-0 | +∞ |
| +1 | +0 |
| +2 | -∞ |
| x > +0 | QNAN |
| +∞ | QNAN |
Useful Identities:
erfcinv(x) = erfinv(1-x)
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::erfcinv ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::erfcinv ( double x );
erfcx
Description: The erfcx(x) function returns the scaled complementary error function value of x: exp(x^2)·erfc(x).
This computation sequence occurs in diffusion problems of physics and chemistry and may be useful to avoid underflow and overflow errors computing exp(x^2) and erfc(x) separately.
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result erfcx(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | +∞ |
| +∞ | +0 |
Useful Identities:
erfcx(x) ~ (1/sqrt(π))/x, for large x
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::erfcx ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::erfcx ( double x );
erfinv
Description: The erfinv(x) function returns the inverse error function value of x.
The inverse error function is useful for Monte Carlo applications in computational finance as it is closely related to the normal cumulative distribution.
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result erfinv(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | QNAN |
| +/-0 | +/-0 |
| +/-1 | +/-∞ |
| |x| > 1 | QNAN |
| +∞ | QNAN |
Useful Identities:
erfinv(x) = erfcinv(1-x)
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::erfinv ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::erfinv ( double x );
j0
Description: The j0(x) function returns the value of the Bessel function of the first kind of order 0 for the input argument x.
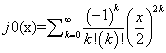
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result j0(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | +0 |
| +/-0 | +1 |
| +∞ | +0 |
Calling Interfaces:Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::j0 ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::j0 ( double x );
j1
Description: The j1(x) function returns the value of the Bessel function of the first kind of order 1 for the input argument x.
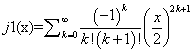
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result j1(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | +0 |
| +/-0 | +/-0 |
| +∞ | +0 |
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::j1 ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::j1 ( double x );
jn
Description: The jn(n,x) function returns the value of the Bessel function of the first kind of given order n for the input argument x.
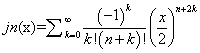
Special Values:
| Argument n | Argument x | Result jn(n,x) |
|---|---|---|
| any | -∞ | +0 |
| 0 | +/-0 | +1 |
| n >= 1 | +/-0 | +/-0 |
| any | +∞ | +0 |
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::jn ( int n, float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::jn ( int n, double x );
lgamma
Description: The lgamma(x) function returns the value of the natural logarithm of the absolute value of gamma: log( |tgamma(x)| ).
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result lgamma(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | +∞ |
| neg, int | +∞ |
| +/-0 | +∞ |
| +1 | +0 |
| +2 | +0 |
| +∞ | +∞ |
Useful Identities:
lgamma(x) = log(|tgamma(x)|), less accurate and impacted by overflows in tgamma
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::lgamma ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::lgamma ( double x );
tgamma
Description: The tgamma(x) function returns the gamma function value of x.
![]()
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result tgamma(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | QNAN |
| neg, int | QNAN |
| +/-0 | +/-∞ |
| x > OVFL | +∞ |
| +∞ | +∞ |
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::tgamma ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::tgamma ( double x );
y0
Description: The y0(x) function returns the value of the Bessel function of the second kind of order 0 for the input argument x.
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result y0(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | QNAN |
| x < +0 | QNAN |
| +/-0 | -∞ |
| +∞ | +0 |
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::y0 ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::y0 ( double x );
y1
Description: The y1(x) function returns the value of the Bessel function of the second kind of order 1 for the input argument x.
Special Values:
| Argument x | Result y0(x) |
|---|---|
| -∞ | QNAN |
| x < +0 | QNAN |
| +/-0 | -∞ |
| +∞ | +0 |
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::y1 ( float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::y1 ( double x );
yn
Description: The yn(n,x) function returns the value of the Bessel function of the second kind of given order n for the input argument x.
![]()
Special Values:
| Argument n | Argument x | Result yn(n,x) |
|---|---|---|
| any | -∞ | QNAN |
| any | x < +0 | QNAN |
| any | +/-0 | -∞ |
| any | +∞ | +0 |
Calling Interfaces:
Default accuracy:
float sycl::ext::intel::math::yn ( int n, float x ); double sycl::ext::intel::math::yn ( int n, double x );