Environment
In case of system crashing/screen of death/SSD IO timeouts and many other situations, obtaining system logs is imperative for further debug. Follow the instructions below on how to extract system logs from Windows* and Linux* systems.
Windows*
- In the system root folder, the "screen of death" info is present in a file similar to mem.dmp. It could also be in a folder with a name similar to memorydump. Obtain this file.
AND / OR
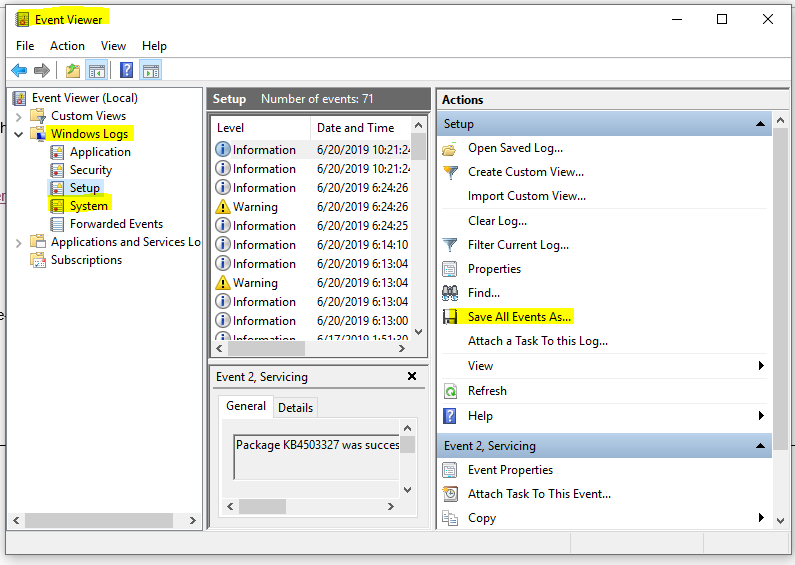
- Go to the Windows start menu and type Event Viewer to get the window shown below. Save all the events and obtain the .zip file.
Linux*
Kernel logs (such as VMkernel.log) is very helpful for debug in case of a crash, as well as a detailed log of steps that led to the crash — the more information, the better!
- For system logs: $ Dmesg > dmesg.log
- OS version: $ cat /etc/*-release
- Kernel version: $ uname –a
However, dmesg is the kernel ring buffer and only shows messages from the current boot process.
If there has been a system crash or reboot, the logs are dumped in /var/log/messages.
There are several other logs in /var/logs that may be useful, depending on the Linux distribution.
These are a few useful ones:
/var/log/Xorg.0.log /var/log/Xorg.0.log.old~/.xsession-errors /var/log/messages
/var/log/Xorg.0.log /var/log/Xorg.0.log.old
~/.xsession-errors
/var/log/messages
Identify and provide the file with relevant information to the system crash or issue.
For just the last x number of lines in any Linux system, one can use the parameter in the end of less or more commands in Linux: | tail -x (or) | last -x . This depends on the kernel version.