Click or the topic for details:
What is HDMI?
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is an interface for transferring uncompressed video and audio data to a digital display device, such as a digital television. The HDMI interface can be used to transmit audio or video, or both audio and video.
HDMI supports the transmission of Consumer Electronics (CE) video formats and timings, and multi-channel audio data, with content protection capability.
Which Intel® graphics support HDMI?
Intel began supporting HDMI in 2005/2006 with the release of Intel® 945G/GM Chipsets.
What is HDCP and why is it required
High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection (HDCP) is a form of Digital Rights Management. Intel created the original technology to make sure that digital content followed the guidelines set by the Digital Content Protection group. HDCP is a copy protection method where the A/V stream is encrypted between the transmitter and the receiver (A/V receiver, TV), protecting it against illegal copying. HDCP is required to allow playback of protected media content on authorized devices only.
Does the HDMI interface support HDCP?
HDCP is supported by the HDMI interface in all Intel® Core™ Processors with Intel® Iris® and Intel® HD Graphics. It is also supported for all Intel® Pentium® Processors and Celeron® Processors with Intel® HD Graphics.
Does HDMI support dual display or cable splitting?
Dual display is supported via HDMI and other onboard ports such as DVI or VGA. Cable splitting is not supported.
What HDMI splitters are recommended?
We don't support HDMI splitters because their functionality cannot be guaranteed.
How to get audio from HDMI?
- Install the latest Intel® Graphics Driver, which will install the latest audio codecs for HDMI.
- After driver installation, connect to the HDMI TV or digital display using HDMI cable.
- Select the HDMI audio as your default playback device from Windows* Sound properties.
- This article has tips on how to setup surround sound.
What are the differences between different HDMI versions?
| HDMI version | 1.0 | 1.1 | 1.2 1.2a | 1.3 1.3a 1.3b 1.3b1 1.3c | 1.4 1.4a 1.4b | ||
| sRGB | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||
| YCbCr | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||
| 8 channel LPCM, 192 kHz, 24-bit audio capability | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||
| Blu-ray Disc and HD DVD video and audio at full resolution | YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||
Consumer Electronic Control (CEC)
| YES | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||
| DVD-Audio support | NO | YES | YES | YES | YES | ||
| Super Audio CD (DSD) support | NO | NO | YES | YES | YES | ||
| Deep color | NO | NO | NO | YES | YES | ||
| xvYCC | NO | NO | NO | YES | YES | ||
| Auto lip-sync | NO | NO | NO | YES | YES | ||
| Dolby* TrueHD bitstream capable | NO | NO | NO | YES | YES | ||
| DTS-HD Master Audio* bitstream capable | NO | NO | NO | YES | YES | ||
Updated list of CEC commands
| NO | NO | NO | YES | YES | ||
| 3D over HDMI | NO | NO | NO | NO | YES | ||
Ethernet channel
| NO | NO | NO | NO | YES | ||
Audio return channel (ARC)
| NO | NO | NO | NO | YES | ||
4K × 2K resolution support
| NO | NO | NO | NO | YES |
Are all new HDMI versions backward compatible?
Yes. All HDMI versions are backward compatible with previous versions.
What is the difference between HDMI and DVI?
HDMI sends both audio and video data, and supports HDCP. DVI can send video only.
What kinds of HDMI cables are supported?
All HDMI connections support all HDMI cables. Only a High Speed HDMI cable support 1080p, 4K, 3D and Deep Color. High Speed HDMI cables are also called Category 2 HDMI cables.
How long are HDMI cables?
HDMI specifies the performance for the cable, not the maximum cable length. The effective distance for standard HDMI cables is typically 30 feet. Some studies suggest no more than 25 feet for High Speed HDMI cables. For best results, use the shortest cable length possible.
Is it OK to bend HDMI cables?
No. For best results, do not bend, curve, or curl HDMI cables.
How do I enable audio through my HDMI cable?
- Install the latest Intel® Graphics Driver, this also installs the latest audio codecs for HDMI.
- After driver installation, connect to the HDMI TV or digital display, using an HDMI cable.
- Select HDMI audio as your default playback device. Click Start > Control Panel > Hardware and Sound.
- Click Sound. The Playback tab lists the audio playback devices for your computer.
- Right-click on the device for HDMI audio, and select Set as Default Device.
How do I troubleshoot audio issues?
- Verify that your HDMI cable is properly connected to both your computer as well as your display device.
- Verify that your HDMI TV’s volume is not muted, or that the volume is not turned all the way down.
- Verify that your computer is not muted, or the volume is not turned all the way down.
- Verify that you have graphics or audio drivers correctly installed on your system.
- Open Device Manager. Click Sound, video and game controllers and see if the listing shows the HDMI device. If it shows a yellow bang, re-install the graphics driver.
If your HDMI TV supports speakers, select HDMI audio as your default playback device from the Windows* Sound control panel:
- Click Start > Control Panel > Hardware and Sound.
- Click Sound. The Playback tab lists the audio playback devices for your computer.
- Right-click on the device for HDMI audio, and select Set as Default Device.
- Right-click and select Test. If you hear a test tone, click OK.
My HDMI TV overscans where the sides of the desktop screen are not visible. How do I fix this?
Example of an HDMI TV screen overscanned.
All HDMI TVs can overscan the image. To correct this, try the following:
- Press the Ctrl+Alt+F12. If using Windows 8*, switch to the Desktop before pressing these keys.
- Under Display, General Settings, Refresh Rate, select 60 Hz.
- Click Custom Aspect Ratio, and move the sliders on the image to adjust.
Note The Custom Aspect Ratio sliders are not available with interlaced refresh rates like 1080i, which cannot be scaled. - If the overscanning is not corrected, check to see if the following underscan resolutions display:
- 1184 x 666: If your HDMI TV supports 720p
- 1776 x 1000: If your HDMI TV supports 1080p
Note Windows* 8 requires a minimum resolution of 1024x768. 720p mode does not display in Windows 8.
Neither resolution works with a TV that supports 1080i.
- Select 1184x666 or 1776x1000 and click Apply.
- If you do not see 1184x666 or 1776x1000, contact your computer manufacturer to request a System BIOS or Intel® Graphics Driver that supports these video formats.
How can I see that the HDMI TV is selected as the display?
- Press Ctrl+Alt+F12 to open the Intel HD Graphics Control Panel or Graphics Properties window.
- In the Display section, click Monitor/TV Settings. If connected, the HDMI TV manufacturer and model number is displayed.
Display section of newer Intel graphics drivers:
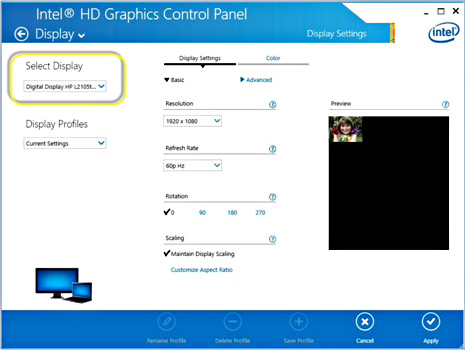
Display section of older Intel graphics drivers:

- Click Apply if changes are made.
- Click OK.
Nothing is showing on my HDMI TV. How do I troubleshoot?
Try the following suggestions until the problem is resolved:
- Verify that the HDMI display is powered on.
- Verify that the TV is set to the appropriate Input mode – specifically HDMI. Some TV’s have multiple HDMI connections, so make sure you are using the correct one that corresponds to the port the cable is connected to.
- Check all connections to make sure there are no loose cables.
- Unplug the HDMI cable and plug it in again.
- Press Ctrl + Alt + F12 to open the Intel® Graphics Control Panel. Verify that your TV shows up under Display > Multiple Displays, and that it is selected as an output device. If properly connected and recognized, you will see the make/model of the device listed under Active Displays.
- Try a different HDMI cable.
- If available, try connecting to a different display with both the same and a different cable. See if it functions properly.
- Download and install the latest graphics driver from Intel or the computer manufacturer.
- Update the System BIOS via the instructions and BIOS software provided by your computer manufacturer.
- Contact your computer manufacturer, and have them verify the proper working functionality of your system.
| Note | If you are attempting to connect to a TV that supports 1080p, 4K, 3D or Deep Color, you will need to use a High Speed HDMI Cable. To verify you have one of these, look along the cabling itself for the printed text which says “High Speed HDMI Cable.” If it is not there, you may not be using a cable that is required to work with your display device. |