Intel® Integrated Performance Primitives (Intel® IPP) Developer Guide and Reference
A newer version of this document is available. Customers should click here to go to the newest version.
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-EBEB11A9-BEE0-43E9-9DAE-B943CF69791A
Visible to Intel only — GUID: GUID-EBEB11A9-BEE0-43E9-9DAE-B943CF69791A
Flood Fill Functions
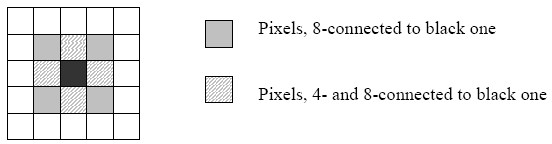
This section describes functions performing flood filling of connected areas. Flood filling means that a group of connected pixels with close values is filled with, or is set to, a certain value. The flood filling process starts with a specified point (“seed”) and continues until it reaches the image ROIboundary or cannot find any new pixels to fill due to a large difference in pixel values. For every pixel filled, the functions analyze neighbor pixels:
- 4 neighbors (except diagonal neighbors); this kind of connectivity is called 4-connectivity and the corresponding function name includes 4Con, or
- 8 neighbors (diagonal neighbors included); this kind of connectivity is called 8-connectivity and the corresponding function name includes 8Con.
These functions can be used for:
- segmenting a grayscale image into a set of uni-color areas,
- marking each connected component with individual color for bi-level images.
- FloodFillGetSize
Calculates size of temporary buffer for flood filling operation. - FloodFillGetSize_Grad
Calculates size of temporary buffer for the gradient flood filling. - FloodFill
Performs flood filling of connected area. - FloodFill_Grad
Performs gradient flood filling of connected area on an image. - FloodFill_Range
Performs flood filling of pixels with values in the specified range in the connected area on an image.