Intel® Gen 13/14 K-SKU Desktop Processors Critical Q&A
Link to Summary Article for Gen 13/14 K-SKU Desktop Processors
If you do not see your Intel® Gen 13/14 desktop processor question and response below, you can escalate to Intel Customer Support.
Critical Q&As
Click or the question for details:
What is happening with Intel® Core™ 13th and 14th Gen desktop processors right now to cause these failure reports?
Intel is seeing increases to the minimum operating voltage (Vmin shift) in some 13th and 14th gen desktop processors. The increase in required operating voltage can lead to issues such as repeated crashes and/or freezes in applications. Based on extensive analysis of Intel Core 13th and 14th Gen desktop processors returned to Intel due to Vmin Shift Instability issues, Intel has determined that elevated operating voltage is a contributor to Vmin Shift Instability issues in some 13th and 14th Gen desktop processors. Analysis of returned processors confirms that the elevated operating voltage stems from a microcode algorithm resulting in incorrect voltage requests to the processor. Intel has delivered a microcode patch (0x129) as a partial mitigation addressing exposure to elevated voltages. Customers experiencing instability symptoms on 13th and 14th Generation desktop processors should contact their system manufacturer, or in the case of a boxed processor, contact Intel Customer Support.Is Intel confirming that elevated voltages are the root cause of the instability issues reported on 13th and 14th generation desktop processors?
Based on extensive analysis of Intel Core 13th and 14th Gen desktop processors returned to Intel due to Vmin Shift Instability issues, Intel has determined that elevated operating voltage is a contributor to Vmin Shift Instability issues in some 13th and 14th Gen desktop processors. Analysis of returned processors confirms that the elevated operating voltage stems from a microcode algorithm resulting in incorrect voltage requests to the processor. Intel has delivered a microcode patch (0x129) as a partial mitigation addressing exposure to elevated voltages.The press is reporting a manufacturing issue related to Intel 13th Generation desktop processors. What is the relation of that report to this issue?
The Via Oxidation manufacturing issue and the Vmin Shift Instability issue are separate issues, each with different causes. Regarding recent press reports, Intel confirms the Via Oxidation manufacturing issue can affect both Intel Core 13th and 14th Gen desktop processors. This issue was root caused and addressed with manufacturing improvements and screens in early 2023 on 13th Gen desktop processors, these improvements and screens were applied to 14th Generation desktop parts before product launch. Intel analysis has determined that only a small number of reports related to the Intel Core 13th and 14th Gen desktop processor Vmin Shift Instability issue can be connected to the manufacturing issue. For the Vmin Shift Instability issue, Intel has delivered a microcode patch (0x129) as a partial mitigation addressing exposure to elevated voltages, which is a key element of the Vmin Shift Instability issue. To be effective, the microcode patch (0x129) MUST be loaded via BIOS update. Contact your system or motherboard manufacturer for BIOS updates containing this microcode update (0x129). Customers experiencing instability symptoms on 13th and 14th Generation desktop processors should contact their system manufacturer, or in the case of a boxed processor, contact Intel Customer Support.How can I tell the difference between processors affected by Via Oxidation as opposed to elevated voltages?
There is no practical way to evaluate this on production systems in the field. Intel Core 13th and 14th generation desktop processors affected by the Via Oxidation issue display symptoms similar to processors affected by the elevated voltage related Vmin Shift Instability issue, including OS and application hangs and errors. For the Vmin Shift Instability issue, Intel has delivered a microcode patch (0x129) as a partial mitigation addressing exposure to elevated voltages, which is a key element of the Vmin Shift Instability issue. To be effective, the microcode patch (0x129) MUST be loaded via BIOS update. Contact your system or motherboard manufacturer for BIOS updates containing this microcode update (0x129). Customers experiencing instability symptoms on 13th and 14th Generation desktop processors should contact their system manufacturer, or in the case of an Intel Boxed Processor, contact Intel Customer Support.Even if I haven’t experienced instability issues so far, is there a way to tell if my processor has been impacted or is at risk of failing?
Not all processors are affected by the Vmin Shift Instability issues. Intel is investigating options to identify affected processors on end-user systems. Customers experiencing instability symptoms on 13th and 14th Generation desktop processors should contact their system manufacturer, or in the case of an Intel Boxed Processor, contact Intel Customer Support. Customers should ensure they are using the latest BIOS from their system or board manufacturer.Why aren’t we seeing this issue on prior-generation unlocked desktop processors?
Based on Intel’s analysis, Intel Core 12th Gen desktop processors are not at risk due to lower voltages and turbo frequencies than 13th and 14th Gen desktop processors.What is a microcode update?
Intel Core processors are accompanied by microcode, which is low-level software that ensures the processor architecture and circuits can carry out instructions. Intel works with its partners to implement microcode changes in system BIOS updates, including the microcode software updates addressing the current elevated voltage issue.Will the new microcode patch (0x129) for the elevated voltage issue fix my processor if it’s already experiencing issues?
This latest microcode update will primarily improve operating conditions for K/KF/KS processors. However, if users are experiencing consistent instability symptoms, they should contact their system manufacturer (OEM/System Integrator purchase), Intel Customer Support (boxed processor), or place of purchase (tray processor) for further assistance.Does the microcode patch (0x129) to limit voltage mean I can safely change my power delivery settings to those outside Intel Default Settings?
As a general best practice, Intel recommends users adhere to Intel Default Settings on their desktop processors. Intel is not changing the tuning capabilities of existing K SKU processors. Users who desire to overclock or utilize higher power delivery settings than recommended can still do so at their own risk, as overclocking may void the warranty or affect system health (learn more at www.intel.com/overclocking).When will the microcode patch (0x129) be available for users?
This patch is being distributed via BIOS update and will not be available through operating system updates. Intel is working with its partners to ensure timely validation and rollout of the BIOS update for systems currently in service.Even if my system has never experienced any instability symptoms, should I upgrade the BIOS to one with microcode patch 0x129?
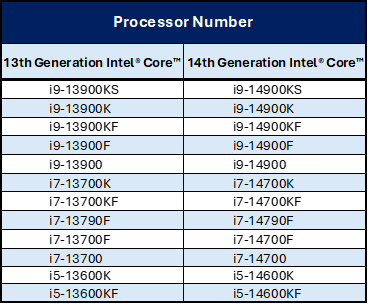
Yes, Intel recommends that customers update the BIOS with Microcode 0x129 for systems configured with 13th and 14th Generation Processors with CPUID 0xB0671.What is the list of affected products for the instability issue?
Intel has determined that the following Intel Core 13th and 14th Gen desktop processors could be impacted by the reported instability issue. See the Intel Gen 13/14 K-SKU Desktop Processors Warranty Statement for warranty information.