This is a general troubleshooting guide for processor high temperature and blue screen issues especially in i-cafe (Internet café) environment.
Computer overheating, processor high temperature, or frequent blue screen errors are common problems that many players and Internet cafe owners are encountering. In particular, performance-seeking players and high-end Internet cafes pay special attention to the emergence of such issues. This article provides an analysis.
- Common causes of the blue screen of death and overheating of the processor or system.
- How to perform troubleshooting and the corresponding solutions!
The following factors contribute to the high temperature of the processor and the blue screen errors:
- Wrong choice of the the thermal solutions.
- Improper BIOS setting of the motherboard.
- Some low-cost power supplies cause weak power supply of the motherboard.
- Abnormal heat dissipation of the computer case.
- CPU overclocking.
- Too high ambient temperature.
Most processor and system overheating and the related blue screen problem can be resolved, and everyone's computers can maintain stable operation using the troubleshooting tips listed below.
Types of thermal solutions
Regardless of the type of thermal solutions used, the thermal design power (TDP) wattage marked with the heat dissipation specifications must first be checked to ensure that the specifications are higher than or equal to the TDP wattage of the CPU used.
Air cooling - tower type (single tower, double tower), and lower pressure type

Advantages:
- It can optimize heat dissipation by sufficiently utilizing the air duct of the case, and at the same time strengthening the air duct of the whole case and promoting the expulsion of hot air.
- The lower pressure type can simultaneously take into account the heat dissipation of the motherboard components.
- Long service life.
Disadvantages:
- The higher the specifications, the more space will be taken up.
- Due to the common ATX case, the CPU is located directly above the graphics card, so it is easily affected by the graphics card temperature.
- The temperature control is not as cold as water. It quickly reaches the highest temperature
Tips for installing air cooling thermal solution
- Do not screw the fastener too tight or too loose. This is to prevent damage to the hardware or insufficient pressure on the contact surface.
- Tighten the screw of the fastener to just a moderate tightness. Do not exert excessive force or just casually tighten.
- Gently press the radiator after installation to check whether it is installed well.
- The radiator base needs to be installed horizontally so that the thermal paste can spread evenly. Separately tighten the screws from the opposite corners halfway and then tighten them completely.
Water cooling thermal solution


Types of cold exhaust specifications: 120mm, 240mm, 280mm, 360mm, 480mm.
Advantages:
- Water has a higher specific heat capacity and can absorb more heat, making it difficult to reach the highest temperature.
- Except for the cold exhaust, not much of the space in the case will be occupied.
- It is less affected by the air duct of the case and graphics card temperature than by air cooling.
Disadvantages:
- Risk of liquid leakage.
- Its service life is not as cold as air cooling.
Tips for water cooling thermal solution
- Due to manufacturing limitations, the integrated water cooling currently in the market will contain 10%~20% air. Based on the principles of physics, the water level in the same container will always be the same height and the bubbles will always move toward the highest point. Therefore, if the cold head is higher than the position of the cold exhaust, the bubble will rise to the highest point so in the cold head, the heat of the cold head cannot be completely transferred to the water, leading to a temperature rise, and long-term operations may even cause the cold head to be damaged.
- When installing integrated water cooling, the best way is to install the cold exhaust at the top, filling the cold head with liquid, thus achieving the best cooling effect.
- If the cold exhaust is installed on the side, it should be noted that the connection between the cold exhaust and the water pipe should be placed at a low place. If placed at a high place, the air in the waterway will be in this position, which will produce bubble noise. This method also allows users to separate the integrated water cooling.

Tips for thermal paste coating (thermal interface material)
- Thermal paste (also known as thermal interface material (TIM) is used to fill the gaps between the planes of different materials so that heat can be transferred better. The thermal efficiency of thermal paste depends on its thermal conductivity and the application method.
- Avoid applying too much or too little, re-using the thermal paste, and avoid presence of foreign substances, which can lead to lower thermal conductivity and incomplete filling of contact surface.
- A common simple application method can be smearing in the middle of the CPU the amount of a green bean size, either a long strip or an X shape, and then apply by the radiator down pressure to make it spread evenly. (Adjust the specific amount according to CPU surface area.)
BIOS setting of motherboards
Most modern BIOS major manufacturers, especially for some high-end models, will unlock the power consumption limit of the processor (PL1 and PL2) by default and set higher voltages to fully release its performance.
Here is an example of two BIOS settings that can be different between motherboards.
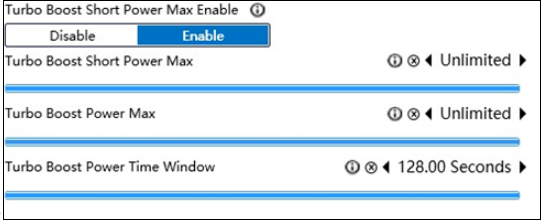
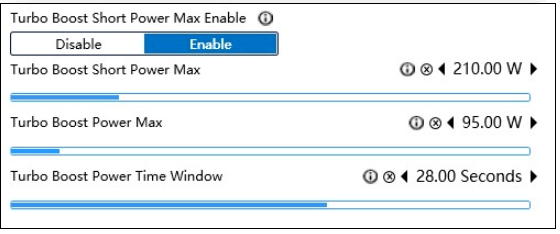
Tips for BIOS settings
- Most of the BIOS manufactures and vendors, especially the high-end ones, will unlock the power consumption limit of the processor (PL1, PL2) by default and set higher voltages to fully release its performance. This will keep the processor running outside the preset thermal design power (TDP).
- Better heat dissipation is needed to support this. If ultimate performance is not required and there is no strong heat dissipation, it can be set to the processor's default value.
- The PL2 of the processor is the short-term maximum power consumption limit. After maintaining operation and achieving the set time (Tau), it will be reduced to the long-term power consumption limit of the PL1 in order to achieve optimum power consumption and performance balance.
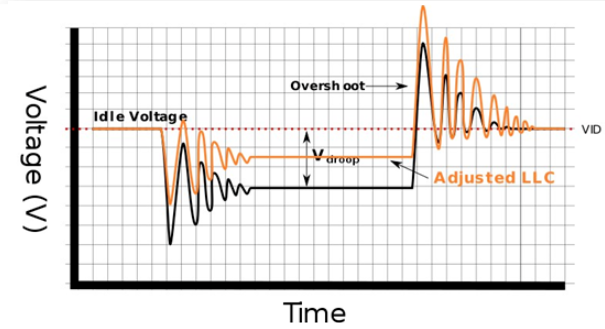
- As the voltage changes, it produces variation. The excess voltage is called "overshoot", which may go beyond the safe voltage range, causing the system to be hot and unstable. To avoid this situation, the load line can be installed, which can appropriately reduce the voltage (Vdroop) at the same time as the load. The purpose is to keep the voltage within a safe range.
Here is an example on BIOS setting.
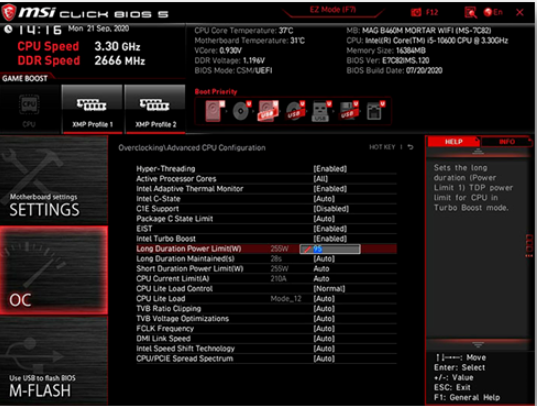
For better overclocking, this behavior can be "corrected" in the motherboard (LLC: Load Line Calibration), but it will also bring about a high CPU temperature and even damage.
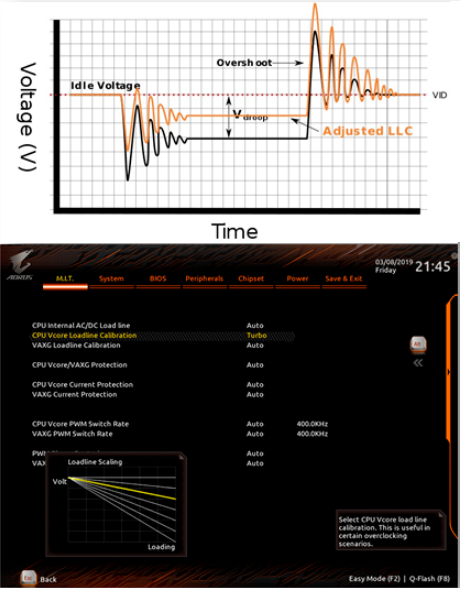
Voltage settings
Similarly, the CPU temperature will also be affected by the LLC (Load Line Calibration) and SVID Profile (different manufacturers have different names). Turning on the former will result in a higher temperature under CPU loads, while the latter will affect the temperature under all CPU conditions.
Motherboard power supply
The power supply of the motherboard and the power source will play a decisive role in the overall stability of the computer. This can be seen on some high-end motherboards: for example the power supply part of the CPU will adopt the 8+4 pin or even the 8+8 pin power supply design, aiming at stability under high load operations of the high-end processor.
Whether a power source is good or bad, it cannot be determined by the nominal wattage only. It also depends on the material of the components, workmanship, and the output stability. If the power source cannot meet the operating conditions, it may cause a blue or black screen, or even a hardware burnout.
Tips for power supplies
Consider the following:
- Heat dissipation of the CPU power supply part
- Materials used in the CPU power supply part
Attention should be paid to the power supply parts: voltage stability, ripple, noise, surge, boot time sequence, power down retention time. Generally choose a good brand when buying power supply and always follow the formula of at least one RMB=one watt.
Heat dissipation of the case
When the computer is operating, other hardware such as the CPU, graphics card, and the motherboard power supply, will generate heat. If a fan is not installed in the case, the internal heat cannot escape from the case, resulting in heat accumulation. This will affect the heat dissipation of all hardware, and the temperature will get higher and higher, creating a vicious cycle. Some Internet cafes may put the cases into cabinets for beauty, creating an enclosed space that makes heat dissipation more difficult.

Tips for heat dissipation of the case
- Keep the air ducts in the right direction. The common air ducts for ATX cases are: front-in and rear-out, bottom-in and top-out.
- Place the case in a ventilated environment.
- Heat dissipation effect cannot be achieved without cold-and-heat exchange, such as all-out or all-in.
Ambient temperature
During summer and winter, the temperature of computer hardware can vary by more than ten degrees because of the difference in the room temperature.
Delta T
ΔT = T2 - T1
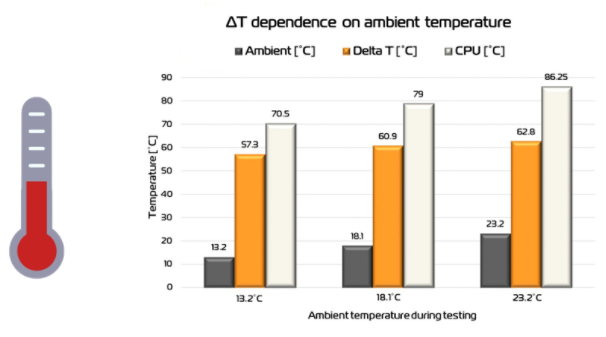
Tips for maintaining the ambient temperature
The temperature of the computer is also affected by room temperature. In summer and winter, the temperature of every computer hardware can vary by more than ten degrees because of the difference in the room temperature. To maintain ventilation of the case, it is recommended to use the system it in an air-conditioned room in hot weather.
Overclocking
When a system is operating beyond the preset specification, it is called overclocking. If overclocking is required, better hardware is needed to support it such as heat dissipation, motherboard, and power supply.
Overclocking the CPU
- By default, Intel® processors can sustain a maximum frequency (PL2) of 28 to 56 seconds(varies according to different processors), and will then fall to a long-term frequency (PL1).
- Modern BIOS has a CPU multi-core enhancement function (name varies according to different motherboards) that unlocks the limit, maintains the maximum CPU frequency for a long time, and even increases the all-core frequency to the single-core frequency, thus maximizing CPU performance.
- Overclocking the processor's voltage will reach a higher value and this generates more heat. High temperature is the biggest enemy of electronic components, and will cause blue screens, computer crashes, and even damage.
Overclocking the memory
The memory controller is located inside the CPU, and the DDR4 has a default frequency of 2133 MHz/2400MHz/2666 MHz. The exceeded frequency belongs to the overclocking range and is affected by both the CPU and motherboard.
When purchasing memory DRAM, consider these factors
- When selecting high-frequency memory, refer to the XMP profile documentation.
- Check the list of memory compatibility for the purchased motherboard.
