Guidance to ensure that cross signing certificates are set up correctly
There are a couple of error codes that may be possibly related to an invalid root certificate. One of the errors is as follows:
Exit with code 75: Details: Failed to complete remote configuration of this Intel® AMT device. Initial connection to the Intel(R) AMT device failed. A TCP error occurred. Make sure that the destination settings are correct and that a network connection exists to the target.
Another error that can be encountered:
Failed to complete remote configuration of this Intel(R) AMT device. Failed while calling WS-Management call GetAmtVersion (CIM_SoftwareIdentity.Get). Intel(R) AMT connection error 0xc000521f: An SSL error occurred. Verify the username and password, and the PSK or certificate settings, where applicable. Valid certificate for PKI configuration not found.
These are examples of errors related to various certificate issues. For this particular case, the remote configuration certificate is chaining to a root certificate that does not have the right hash for the Intel® AMT firmware.
One of the errors that come up potentially associated to a certificate issue (in this case, Cross-Signing) is an error 75 Invalid PKI certificate.
Frequently, the remote configuration certificate is chaining up to a root certificate that is not in the Intel AMT firmware (sometimes because a Certificate Authority (CA) has been purchased or merged with another public CA). In order to validate the remote configuration certificate, we need to inject an intermediate certificate in the chain to branch the certificate to a root certificate in the Intel AMT firmware.
The most efficient and effective way to get the correct intermediate root certificate is for the customer to go back to the issuing CA and ask for an intermediate cross-signing certificate that will chain up to a valid root certificate.
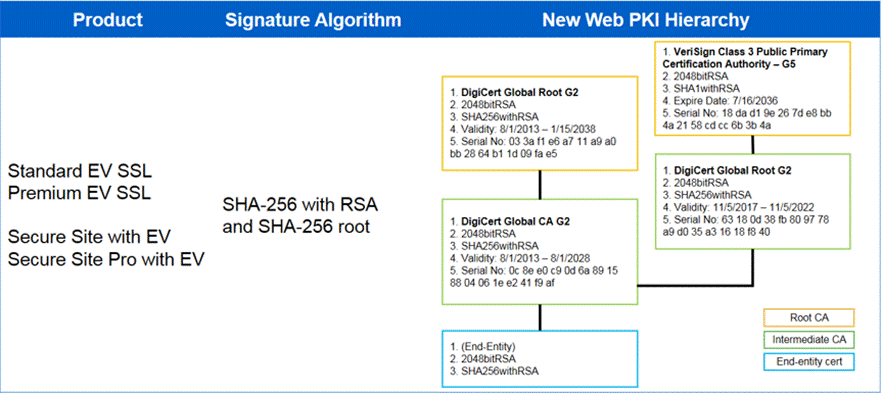
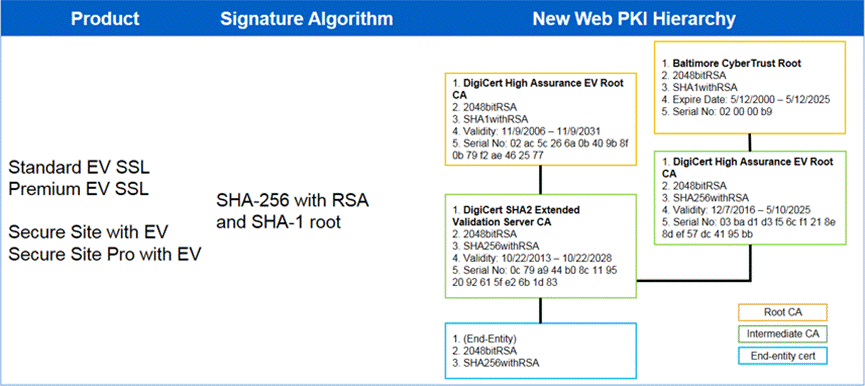
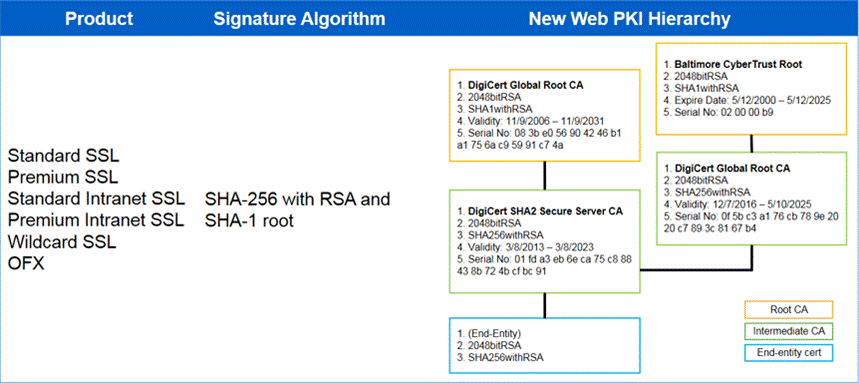
Some examples of a cross-signing certificate are as follows: