Channel bonding creates more room for data by bonding or combining two or more 20 MHz channels into a single 40, 80, or 160 MHz channel. Channel bonding increases the data rate because data rate is directly proportional to channel bandwidth. 802.11a/b/g networks use a single 20 MHz channel. 802.11n networks can use a 40 MHz channel. 802.11ac Wave 1 allows for 80 MHz channels, while 802.11ac Wave 2 introduces 160 MHz channels.
Channel bonding is configured under the Advanced Intel® Wireless Adapter Settings. Device Manager > Network Adapters > [your Intel® Wireless Adapter] > Properties > Advanced tab. Choose Channel Width.
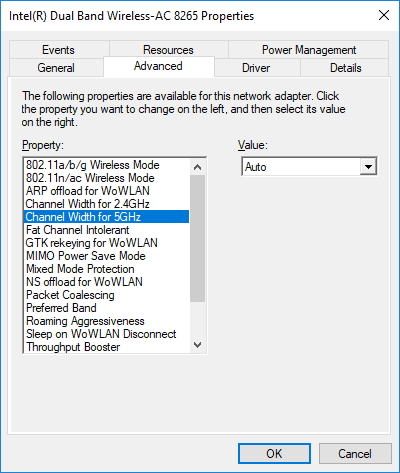
A separate configuration parameter exists for each frequency band that the wireless device supports. Not all legacy Intel® Wireless Adapters support 5 GHz. Two configuration values are available for Channel Width: 20 MHz Only and Auto (default setting).
Choosing a 20 MHz channel width effectively disables channel bonding. Choosing Auto allows the Access Point (AP) to determine the channel width. If the AP supports channel bonding, then the channel width will be 40, 80, or 160 MHz. If the AP does not, the channel width will be 20 MHz by default.
| Notes |
|